Table of Contents
Cybersecurity is no longer just a niche career; it’s become a critical profession that protects sensitive data, financial systems, and the infrastructure of our modern world. With the increasing reliance on digital platforms and the rapid adoption of technologies such as cloud computing, IoT, and AI, businesses and governments are facing a constant threat of sophisticated cyberattacks. To counteract these threats, organizations are in desperate need of skilled cybersecurity professionals who can safeguard their systems and sensitive information.
For individuals aiming to build or advance their careers in this rewarding field, navigating the overwhelming number of available cybersecurity certifications can be daunting. The Guide to Cybersecurity Certification Pathway acts as a crucial tool in making informed decisions about the best certifications to pursue. This comprehensive guide helps individuals identify where to start, how to specialize, and which credentials will elevate them to expert or leadership roles. Whether you’re just starting with entry-level certifications or striving for advanced certifications like the ACSMI certification with its extensive 400+ modules, the certification map offers a structured pathway through the complexity of the cybersecurity landscape.
Why Certifications Matter in Cybersecurity
The cybersecurity field is dynamic, with new technologies and threats emerging every day. To stay competitive, professionals must continuously build both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. This is where certifications play a pivotal role in validating expertise and making individuals more attractive to employers.
1. Validation of Skills and Knowledge
Certifications serve as trusted proof of a professional’s ability to handle real-world cybersecurity challenges. For employers, these credentials provide confidence that the certified individual is capable of addressing the complexities of modern cyber defense. Globally recognized certifications, such as CISSP and the ACSMI certification, are critical in ensuring that a cybersecurity professional is equipped to manage the rapidly evolving threat landscape.
2. Competitive Advantage
In today’s competitive job market, certifications can make all the difference in getting hired, promoted, or considered for specialized roles. Many employers prioritize candidates with validated skills and certifications over those with only a degree or experience. Certifications help differentiate professionals in an increasingly crowded job market and show that they have the knowledge required to succeed in high-pressure cybersecurity environments.
3. Higher Earning Potential
Cybersecurity certifications often correlate with higher salaries. On average, certified professionals earn significantly more than their uncertified counterparts. High-level certifications, such as CISSP or the ACSMI certification, open doors to lucrative positions, making it an investment that pays off in the long term. In addition, cybersecurity roles continue to be in high demand, further boosting the earning potential of those with advanced certifications.
4. Specialization Opportunities
As cybersecurity becomes more specialized, advanced certifications allow professionals to focus on niche areas, such as penetration testing, cloud security, and governance. These specializations allow individuals to become experts in specific domains, increasing their value to organizations and giving them the opportunity to work on complex and high-impact cybersecurity issues.
5. Career Mobility
Certifications like the ACSMI certification offer global recognition, allowing cybersecurity professionals to pursue job opportunities across various industries and geographies. Whether you’re looking to move into a leadership role, transition to a different industry, or relocate to a different part of the world, certifications can provide the credentials necessary for career mobility.
What Is a Cybersecurity Certification Map?
A Cybersecurity Certification Graph is a visual tool designed to help individuals understand the wide array of cybersecurity certifications available. This structured roadmap helps professionals align their current skills, career aspirations, and areas of interest with the right credentials. Think of it as a comprehensive guide that shows you which certifications to pursue at each stage of your career, helping you avoid confusion and making it easier to plan your cybersecurity career trajectory.
The cybersecurity certification map typically includes the following components:
-
Entry-Level Certifications – For beginners looking to learn the basics of cybersecurity and build a solid foundation.
-
Intermediate-Level Certifications – For professionals who want to specialize in specific areas such as ethical hacking, compliance, or vulnerability assessment.
-
Advanced-Level Certifications – For seasoned experts targeting leadership roles, such as Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or Security Architect.
-
Costs, Duration, and Prerequisites – Clear comparisons help you evaluate the ROI of each certification and understand the time commitment required.
By following a well-structured certification map, individuals can make smarter decisions about which courses to take and which certifications to pursue at different stages of their career. It helps ensure that your educational investments are aligned with your long-term goals.
Popular Certifications Mapped Out
To give you a clearer understanding of where to start and how to progress, here’s a breakdown of the most common certifications based on your level of experience:
1. Entry-Level Certifications
If you’re new to cybersecurity, start with certifications that cover the basics. These certifications lay a solid foundation in essential concepts such as risk management, security protocols, and basic threat assessment.
Some popular entry-level certifications include:
-
CompTIA Security+: A globally recognized certification that covers basic cybersecurity concepts, including network security, cryptography, and threat management.
-
Cisco’s CCNA Cyber Ops: This certification focuses on the skills needed for working in security operations centers (SOCs) and managing security incidents.
2. Mid-Level Certifications
Once you’ve mastered the basics, it’s time to move on to more specialized certifications. These credentials provide hands-on training, penetration testing, and security audits.
Some examples of mid-level certifications include:
-
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): Focuses on ethical hacking and penetration testing, teaching individuals how to identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks.
-
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP): Offers more advanced penetration testing techniques and real-world hacking scenarios, requiring candidates to prove their skills in a hands-on lab environment.
-
Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA): Focuses on information system audits, risk management, and governance, making it ideal for professionals interested in compliance or audit-focused roles.
3. Advanced Certifications
For seasoned professionals aiming for leadership roles, these certifications offer in-depth knowledge in advanced cybersecurity topics, strategic leadership, and large-scale security governance.
Examples include:
-
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): One of the most respected certifications in the industry, CISSP covers eight domains of cybersecurity, including risk management, asset security, and security engineering. It is perfect for those seeking managerial or executive-level roles.
-
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): A certification tailored to those in charge of managing and overseeing an organization’s security strategy and operations.
-
ACSMI Certification: With its 400+ modules, the ACSMI program stands out as one of the most comprehensive certifications, covering both technical and strategic leadership skills necessary for high-level cybersecurity roles.
Benefits of Using a Cybersecurity Certification Map
The use of a cybersecurity certification map has numerous advantages, providing clarity and helping you maximize your professional growth. Here are the key benefits of using a certification map:
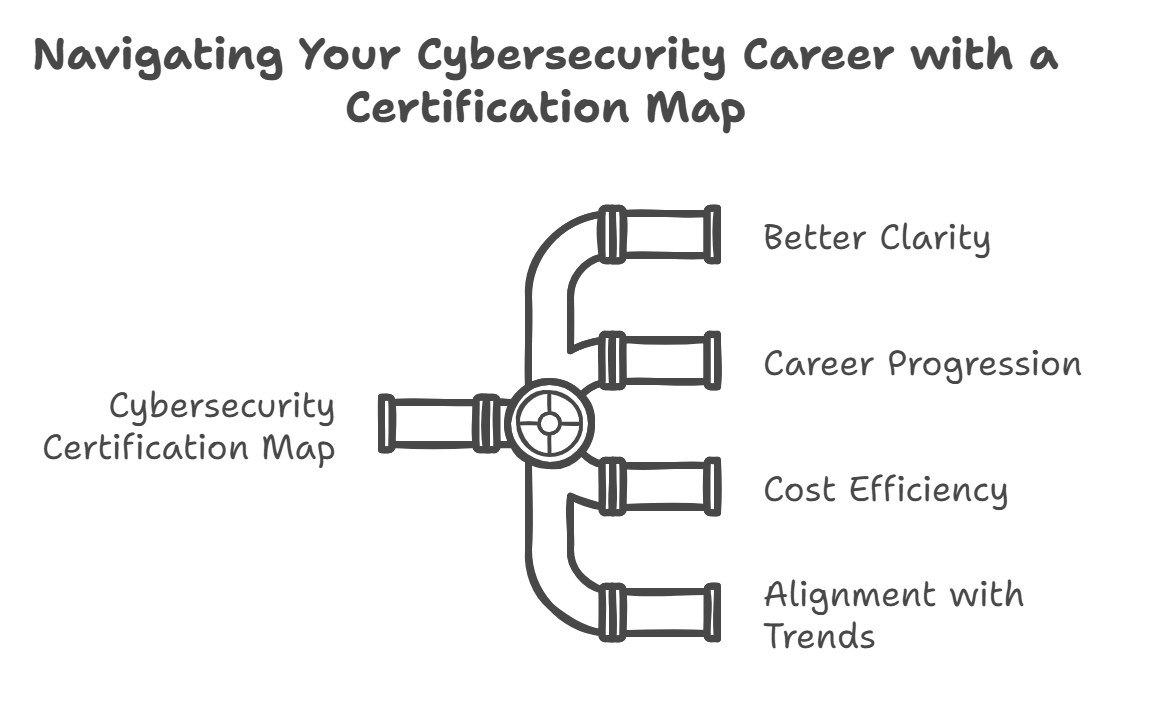
1. Better Clarity
The certification map simplifies the decision-making process by organizing certifications based on career relevance, prerequisites, and the required level of expertise. This structure allows professionals to choose the right certifications without feeling overwhelmed by the vast number of available options.
2. Career Progression
The map offers a clear pathway from entry-level to senior leadership positions in cybersecurity. By following the recommended progression, professionals can gradually build their expertise and secure roles that align with their career ambitions.
3. Cost Efficiency
By guiding you toward the right certifications at the right time, a certification map helps you avoid spending money on unnecessary courses. You can focus your resources on credentials that provide the best career ROI, ensuring you don’t waste time or money on certifications that won’t further your career goals.
4. Alignment with Trends
The map often includes certifications that reflect the latest industry trends, such as cloud security, threat intelligence, and AI-driven cybersecurity. By following the map, you ensure that the certifications you pursue align with current and future cybersecurity needs, keeping you relevant in the job market.
Final Thoughts
A cybersecurity certification map is an invaluable tool for anyone looking to navigate the complex and ever-evolving cybersecurity field. Whether you’re just starting your journey with entry-level certifications, looking to specialize in a specific area, or aiming for leadership roles, a certification map helps you make informed decisions and plan your career path.
Using the map allows you to avoid wasting time and resources on certifications that don’t align with your goals. It ensures you’re always progressing toward the skills and credentials that will help you reach your desired career milestones. Whether you’re starting with CompTIA Security+ or aiming for advanced certifications like CISSP or ACSMI, a well-structured certification map is your roadmap to success in cybersecurity.
In a fast-paced and high-demand field like cybersecurity, continuous learning and the right certifications are essential for long-term success. Start charting your path today, and make smarter decisions that will elevate your career in this exciting and rewarding field.
FAQ Section
1. What is a cybersecurity certification map?
A cybersecurity certification map is a structured guide that outlines the certification pathways available in cybersecurity. It helps professionals choose the right certifications based on their skills, career goals, and expertise level.
2. Do certifications increase earning potential?
Yes, certifications significantly increase earning potential. Certified professionals tend to earn 15-20% more than their uncertified peers, with advanced certifications like CISSP or ACSMI often leading to lucrative career opportunities.
3. What is the most advanced certification?
The ACSMI certification, with its 400+ modules, is one of the most advanced and comprehensive certifications available, offering both technical and strategic leadership training.
4. Do certifications require renewal?
Most certifications, including CISSP and ACSMI, require renewal every 2-3 years. This can involve passing a re-examination or earning continuing education credits to ensure professionals stay updated with the latest cybersecurity trends.
5. What is a good starting certification?
CompTIA Security+ is an ideal starting point for beginners, covering fundamental concepts in cybersecurity and providing the essential knowledge needed to pursue more specialized certifications.

Leave a Reply