Implementing an effective security management system is one of the most crucial steps an organization can take to safeguard its assets, data, and employees. As cyber threats evolve and physical security concerns become more complex, organizations must adopt best practices to ensure their security systems are robust, comprehensive, and adaptable.
A well-implemented security management system not only helps prevent threats but also ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, enhances incident response times, and fosters a culture of security awareness across the organization.
In this blog, we will explore the best practices for implementing security management systems, including how to develop a tailored security plan, integrate advanced technologies, and ensure that your employees are engaged in securing your business environment.
To learn more about why security management is essential, check out our blog on what is security management.
1. Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Assessment
The first step in implementing an effective security management system is conducting a thorough risk assessment. Without a proper understanding of potential threats and vulnerabilities, organizations may overlook critical gaps in their security framework. Risk assessment allows organizations to proactively identify, analyze, and address risks before they can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, or operational disruption. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, a detailed risk assessment is essential to ensure your assets remain secure and your operations resilient.
Why Risk Assessment Matters
Risk assessment is not just a compliance activity—it is a foundational process that drives informed decision-making throughout an organization. It gives business leaders the insights they need to prioritize resources, develop policies, and implement safeguards tailored to their unique environment. By taking the time to understand the types of threats facing your organization, you can develop a customized, robust security management system that protects against both common and emerging risks.
A generic, one-size-fits-all security strategy is no longer sufficient in today's dynamic threat landscape. Organizations face a broad range of risks—from cyber threats and insider attacks to environmental hazards and supply chain vulnerabilities. Each of these risks requires specific countermeasures. Risk assessment helps ensure that your strategies are focused, efficient, and aligned with your organization’s goals.
Key Steps in Risk Assessment:
To effectively evaluate and manage risks, organizations must take a structured approach. Here are the essential steps in conducting a successful risk assessment:
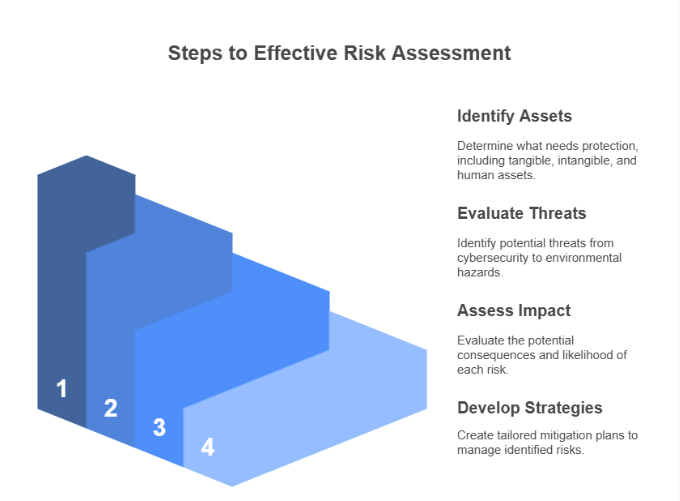
1. Identify Assets
The first step is to determine what assets need protection. These may include:
-
Tangible assets: Such as buildings, servers, laptops, and inventory.
-
Intangible assets: Like intellectual property, trade secrets, brand reputation, and digital data.
-
Human assets: Employees, contractors, and executives who contribute to operations and decision-making.
Understanding what is at stake helps to establish the scope of the assessment and focus efforts on the most critical areas.
2. Evaluate Threats and Vulnerabilities
Once you know what you need to protect, the next step is identifying the potential threats that could compromise those assets. These threats may come from various sources, including:
-
Cybersecurity threats: Malware, phishing, ransomware, and denial-of-service attacks.
-
Physical security threats: Theft, vandalism, or unauthorized access to facilities.
-
Internal threats: Employee negligence, insider fraud, or policy violations.
-
Environmental threats: Natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, fires, or pandemics.
Simultaneously, you need to assess the vulnerabilities that make your organization susceptible to these threats. These could include outdated systems, lack of employee training, insufficient access controls, or poor physical security measures.
3. Assess Impact and Likelihood
After identifying the threats and vulnerabilities, it’s important to evaluate the potential impact of each risk and the likelihood of it occurring. This step helps prioritize the risks and determine which ones require immediate attention.
Impact refers to the consequences a threat could have on the organization—such as financial loss, regulatory penalties, reputational damage, or operational downtime. Likelihood refers to the probability of the threat materializing. Risks that have both high impact and high likelihood should be prioritized over those with lower consequences or rare occurrences.
You can use risk matrices or scoring systems to categorize and rank risks, making it easier to visualize and communicate your findings to stakeholders.
4. Develop Mitigation Strategies
Once you've prioritized the risks, the next step is to define how to manage them. Common strategies include:
-
Avoidance: Eliminating the risk entirely by discontinuing risky operations or changing procedures.
-
Mitigation: Reducing the likelihood or impact through security controls, training programs, or infrastructure upgrades.
-
Transfer: Shifting the risk to a third party, such as through insurance or outsourcing.
-
Acceptance: Acknowledging the risk and choosing to live with it, typically when the cost of mitigation outweighs the benefit.
Each risk should have a corresponding mitigation plan tailored to your organization’s risk appetite, budget, and operational needs.
Benefits of Conducting a Risk Assessment
Conducting a thorough risk assessment offers numerous benefits:
-
Informed decision-making: Leaders can allocate resources more effectively.
-
Enhanced security posture: Targeted strategies lead to stronger protection.
-
Regulatory compliance: Risk assessments are often required under regulations like ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR.
-
Improved awareness: Employees become more conscious of risks and security protocols.
-
Business continuity: Risk mitigation helps ensure minimal disruption during incidents.
By going through this process, organizations build a security management plan that is tailored to their unique circumstances. Rather than applying generic security solutions, a risk-based approach ensures that defenses are both cost-effective and impactful.
To dive deeper into risk assessment, visit our blog on how to conduct a risk assessment.
2. Define Clear Security Policies and Procedures
A cornerstone of an effective security management system is the development and enforcement of clear security policies and procedures. These documents serve as a formal framework that defines how security is managed within an organization. By setting specific rules, responsibilities, and processes, organizations can ensure that every employee understands their role in maintaining a secure environment. Without these foundational policies, even the most advanced security technologies can be rendered ineffective due to inconsistent or improper use.
Clear security policies and procedures help align the entire organization on key security practices and expectations. They minimize ambiguity and ensure that everyone—from senior executives to new hires—follows consistent protocols when dealing with information systems, data handling, and security events. These policies should be written in clear, understandable language and made easily accessible to all staff members.
Key Elements of Security Policies:
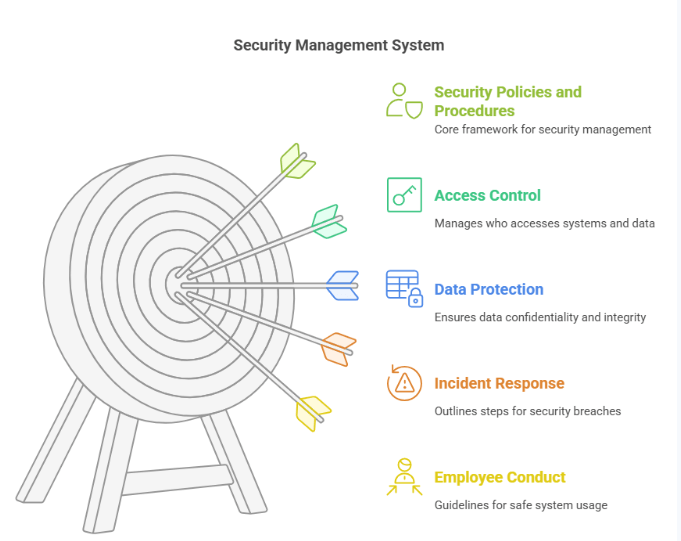
1. Access Control
Access control policies determine who is authorized to access specific systems, data, or physical areas within the organization. These policies should define user roles, access levels, and the methods of authentication, such as secure passwords, biometric scans, smart cards, or two-factor authentication. Limiting access based on job responsibilities reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
2. Data Protection
Data protection policies should specify how sensitive or confidential data—such as customer information, financial records, or intellectual property—is to be collected, processed, stored, and transmitted. This includes encryption protocols, secure storage methods, and restrictions on data sharing. Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data is essential for protecting both the organization and its clients.
3. Incident Response
A well-defined incident response policy outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach, cyberattack, or data loss. It should include procedures for detecting incidents, escalating them to the appropriate personnel, and communicating with internal and external stakeholders. Additionally, the policy should address containment, mitigation, recovery, and post-incident analysis to prevent future occurrences.
4. Employee Conduct
Security policies must include guidelines for expected employee behavior, particularly when it comes to using company systems and handling sensitive information. This can include rules for safe internet usage, recognizing and reporting phishing emails, using company-approved devices and software, and following best practices to prevent social engineering attacks. Training and awareness programs should support these guidelines to ensure ongoing compliance.
Ongoing Review and Updates
Security is not static—threats evolve constantly, as do technologies and regulatory requirements. For this reason, security policies and procedures should not be one-time documents. They must be reviewed and updated on a regular basis to stay relevant. Organizations should establish a formal review cycle, involve key stakeholders from IT, HR, and legal departments, and incorporate feedback from audits, risk assessments, and real-world incidents.
By defining, documenting, and maintaining clear security policies and procedures, organizations can create a culture of security awareness and preparedness. This proactive approach not only strengthens defense mechanisms but also supports compliance with industry standards and legal obligations.
3. Choose the Right Security Technologies and Tools
Implementing a comprehensive security management system is not just about creating policies—it’s also about using the right security technologies and tools to defend against evolving threats. In today’s digital landscape, organizations face a wide range of cyber risks that can result in data breaches, operational disruptions, and financial losses. That’s why choosing the right mix of security tools is critical for safeguarding information, maintaining compliance, and ensuring business continuity.
The right technologies help you identify vulnerabilities, prevent unauthorized access, detect suspicious activity, and respond to incidents efficiently. However, with countless security tools available on the market, it’s important to focus on those that provide real value to your organization. Below are some essential tools every security-conscious business should consider.
Essential Security Tools to Consider:
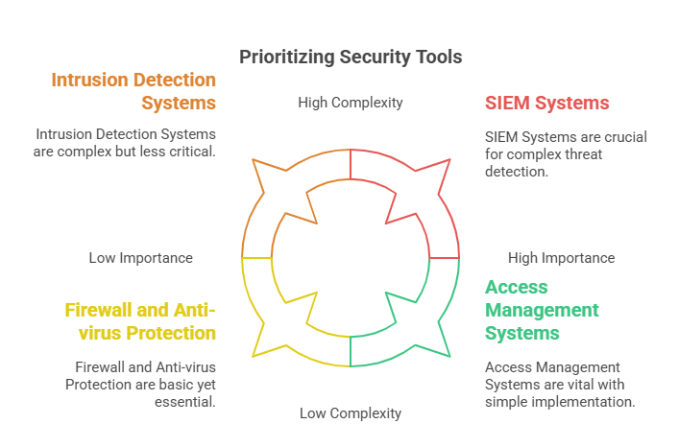
1. Firewall and Anti-virus Protection
One of the foundational layers of cybersecurity is the use of firewalls and anti-virus software. Firewalls act as a barrier between your internal network and external threats, filtering traffic to block unauthorized access. Anti-virus and anti-malware programs protect individual systems from malicious software, including viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware. These tools should be updated regularly to recognize and respond to the latest threats.
2. Encryption Tools
Data encryption is a must-have for organizations handling sensitive or confidential information. Encryption tools ensure that even if data is intercepted or accessed without permission, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. Data should be encrypted both at rest (stored data) and in transit (data being transmitted over a network) to maintain its confidentiality and integrity.
3. Access Management Systems
Controlling who has access to what information is a critical component of a secure system. Access management solutions like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) help enforce security at the user level. MFA adds an extra layer of authentication, requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods, while RBAC limits access based on an individual’s job role, ensuring users can only access information necessary for their responsibilities.
4. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM systems provide centralized visibility into your organization's IT infrastructure by collecting and analyzing log data in real time. These tools offer alerting capabilities that help security teams detect and respond to incidents quickly. They also support regulatory compliance by maintaining detailed logs for audits and investigations.
5. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
IDS tools monitor network traffic to detect and report suspicious behavior that could indicate a cyber attack. They work by comparing current activity against known threat patterns and alerting administrators if anomalies are found. Some advanced systems also offer intrusion prevention features to actively block threats as they’re detected.
Selecting the right mix of tools will depend on your organization's specific security needs, regulatory requirements, and the nature of your data and assets.
For more information on selecting security tools, visit our blog on how to choose the right security management tools.
4. Train Employees and Foster a Security Culture
No matter how sophisticated your security management system is, the human element often remains the most vulnerable point in any organization’s cybersecurity framework. Technology alone cannot protect your organization if employees are unaware of basic security protocols or fail to follow them. That’s why it’s essential to provide ongoing training and create a workplace environment that promotes a strong culture of security awareness.
Employees at all levels should be empowered with the knowledge and tools they need to recognize, respond to, and prevent security threats. Regular training not only equips staff with critical information but also reinforces the importance of cybersecurity in their daily roles. Here are some key focus areas to prioritize when designing an effective employee security training program:
Key Training Focus Areas:
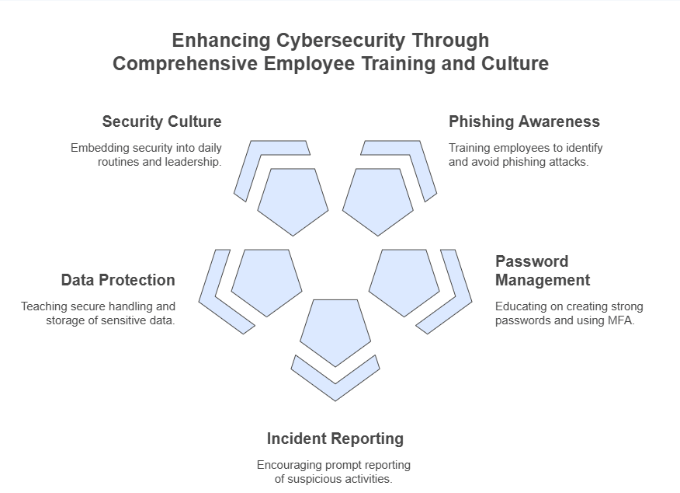
Phishing Awareness
One of the most common cyber threats today is phishing. These attacks are designed to trick individuals into clicking on malicious links or revealing confidential information. Training employees to identify suspicious emails, unknown attachments, and manipulative language is crucial. Role-playing scenarios and simulated phishing tests can be highly effective in helping staff recognize red flags in real-world situations. Encourage them to verify requests for sensitive information and always report anything that seems unusual.
Password Management
Weak or reused passwords are an open door for cybercriminals. Educate employees on the importance of creating strong, unique passwords for each system or application they access. Implementing password managers and enforcing password policies can help maintain security without burdening users. Additionally, promoting multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to verify their identity through a second method, such as a mobile app or text code.
Incident Reporting Procedures
Often, a security breach can be minimized or avoided altogether if employees report suspicious activity promptly. However, many people may hesitate to come forward due to fear of being wrong or facing blame. Make it clear that all employees are encouraged to report potential incidents, no matter how small. Provide clear, simple steps for reporting and reassure staff that their vigilance is both valued and expected. Quick reporting can make a significant difference in mitigating damage and containing threats.
Data Protection Best Practices
Employees should understand how to handle, store, and transmit sensitive data securely—whether they are in the office or working remotely. Training should cover topics such as encrypting files, avoiding public Wi-Fi for work-related tasks, locking screens when away from desks, and proper disposal of physical documents. Emphasize the shared responsibility in protecting customer information, intellectual property, and other critical data assets.
Creating a Culture of Security
Beyond formal training sessions, organizations must embed security into their everyday culture. This means making cybersecurity a routine topic of conversation, recognizing employees who demonstrate good security habits, and having leadership set a strong example. When employees view cybersecurity as a shared responsibility rather than an IT department concern, the entire organization becomes more resilient.
5. Establish a Regular Review and Audit Process
Security threats are constantly evolving, and your security management system should evolve with them. Establishing a regular review and audit process helps ensure that your system remains effective and compliant with any new regulations or emerging threats.
Key Review and Audit Activities:
-
Internal Audits: Regularly review your security policies, tools, and practices to identify weaknesses and opportunities for improvement.
-
Penetration Testing: Conduct simulated attacks to identify vulnerabilities before real attackers can exploit them.
-
Compliance Audits: Ensure your security practices comply with relevant laws and industry regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
Regular audits ensure that any security gaps are identified and addressed quickly, minimizing the impact of potential threats.
Conclusion
Implementing an effective security management system requires careful planning, the right tools, and continuous evaluation. By conducting risk assessments, defining security policies, choosing the appropriate security technologies, training employees, and regularly reviewing your security posture, you can create a robust system that protects your business from evolving threats.
At ACSMI, we understand the importance of securing your business environment. We offer medical coding and billing certifications, ensuring that professionals are equipped to safeguard sensitive data and comply with industry regulations. Additionally, we provide a variety of snacks online to fuel your team as they manage and maintain your security infrastructure.
FAQs
What is the first step in implementing a security management system?
The first step is conducting a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential threats and evaluate the level of risk they pose to your organization.
Why are security policies important in a security management system?
Security policies define clear guidelines and rules for securing organizational assets and data, ensuring that all employees understand their roles in maintaining security.
What are the most important tools in a security management system?
Key tools include firewalls, encryption software, access management systems, SIEM, and intrusion detection systems (IDS) for real-time threat detection.
How can employee training improve security management?
Regular employee training on phishing awareness, password management, and incident reporting reduces human error and strengthens your organization's defense against security breaches.
Why is regular auditing and review essential for security management systems?
Regular audits help identify security gaps, ensure compliance with regulations, and allow organizations to adapt to new threats and technologies.

Leave a Reply