In the fast-evolving field of information technology (IT), professionals are constantly looking for ways to enhance their skill set, stay relevant, and gain a competitive edge in the workforce. One of the most effective ways for IT professionals to elevate their careers is by earning the Certified Network Associate (CNA) certification, particularly in the realm of cyber security. The increasing demand for security professionals has made cyber security one of the most sought-after fields within IT, and CNA certification can open many doors for career growth. In this blog, we’ll explore the top 5 benefits of CNA certification for IT professionals, and how it can transform your career trajectory.
Related Blog: How to Get CNA Certification in Cyber Security
Why IT Professionals Should Consider CNA Certification for Cyber Security Roles
Cyber security has become a critical concern for organizations globally, with an ever-growing number of cyber threats targeting sensitive data, systems, and networks. As the digital landscape continues to expand, the demand for skilled cyber security professionals rises sharply. IT professionals who already possess foundational knowledge of networks and systems can significantly enhance their expertise by obtaining a CNA certification.
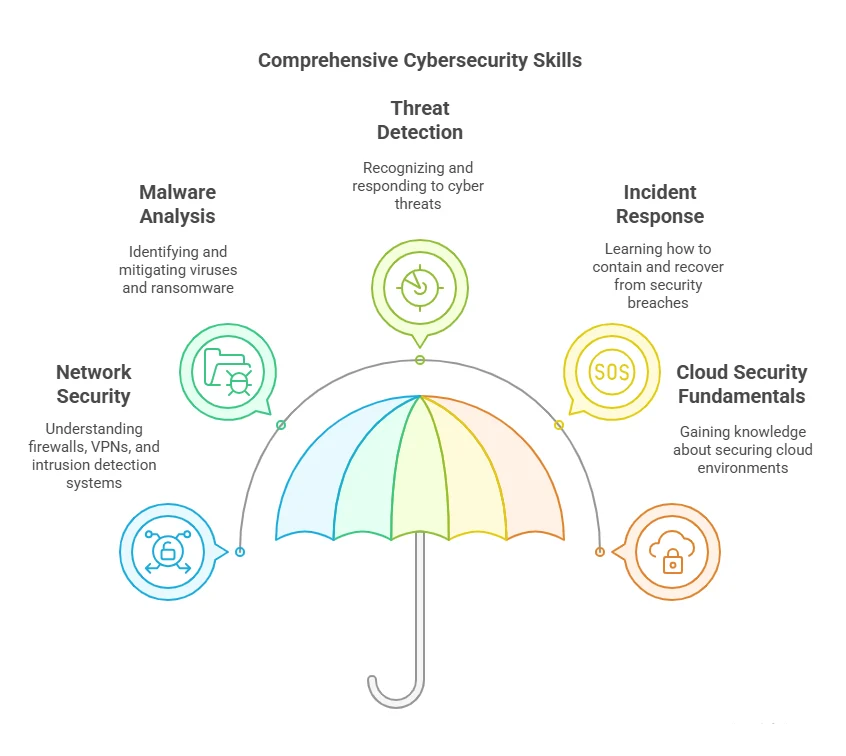
CNA certification equips individuals with the necessary tools to secure networks, protect sensitive data, and defend against cyber threats, making it an essential credential for those interested in cyber security roles. The good news is that CNA certification doesn’t require years of experience in cyber security – it is designed for IT professionals looking to pivot into this field, providing the perfect stepping stone.
Benefit 1: Career Transition to Cyber Security
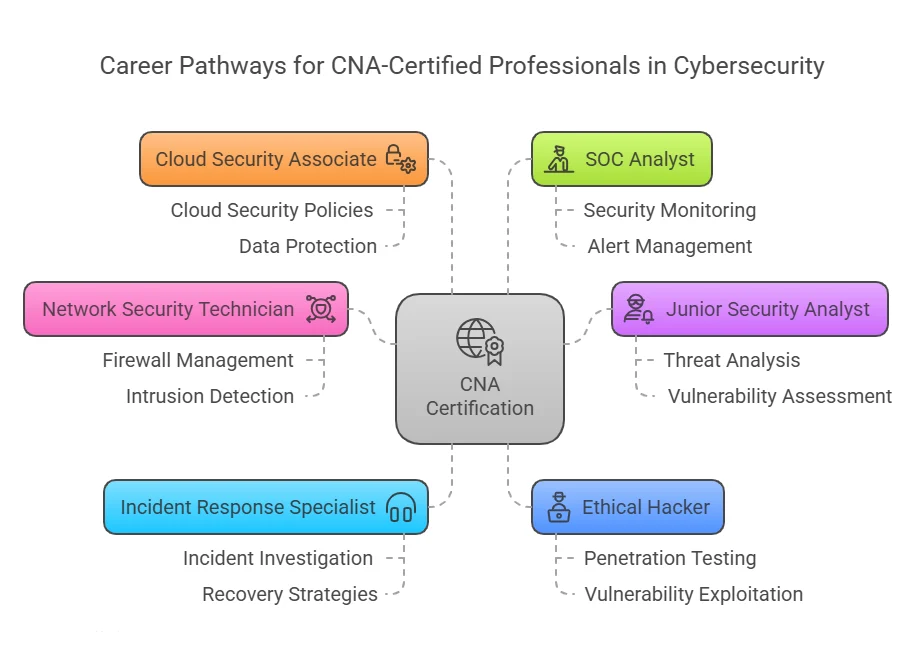
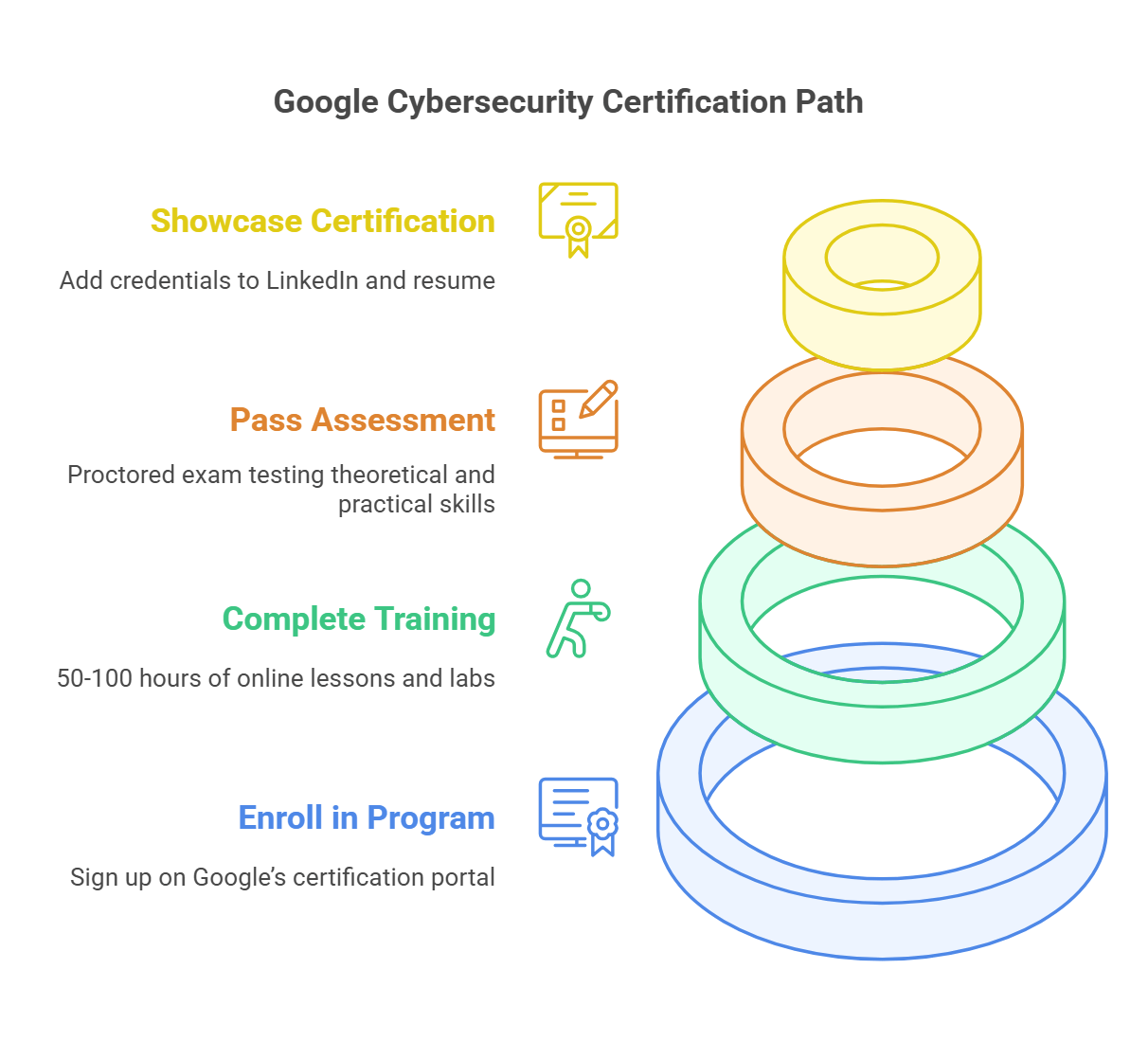
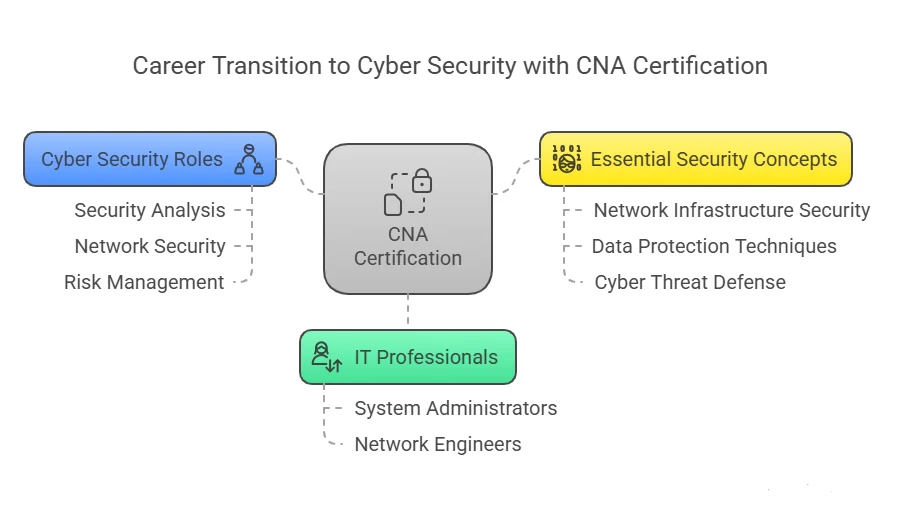
One of the primary benefits of obtaining a CNA certification is the ability to transition into a cyber security career. For many IT professionals, the switch from traditional IT roles, such as system administrators or network engineers, to specialized cyber security positions can be challenging. However, CNA certification provides a structured learning path that covers essential security concepts and practices.
This certification equips IT professionals with knowledge of securing network infrastructures, data protection techniques, and defending against cyber threats. With the rapid growth of cyber security job opportunities, certified professionals are highly sought after to fill roles in security analysis, network security, and risk management.
Related Blog: How CNA Certification Can Boost Your Cyber Security Career
Why is this important?
- For IT professionals, CNA certification acts as a bridge, facilitating a seamless transition into the rapidly expanding field of cyber security. By gaining the necessary skills and competencies, IT professionals can confidently step into specialized cyber security roles and further advance their careers.
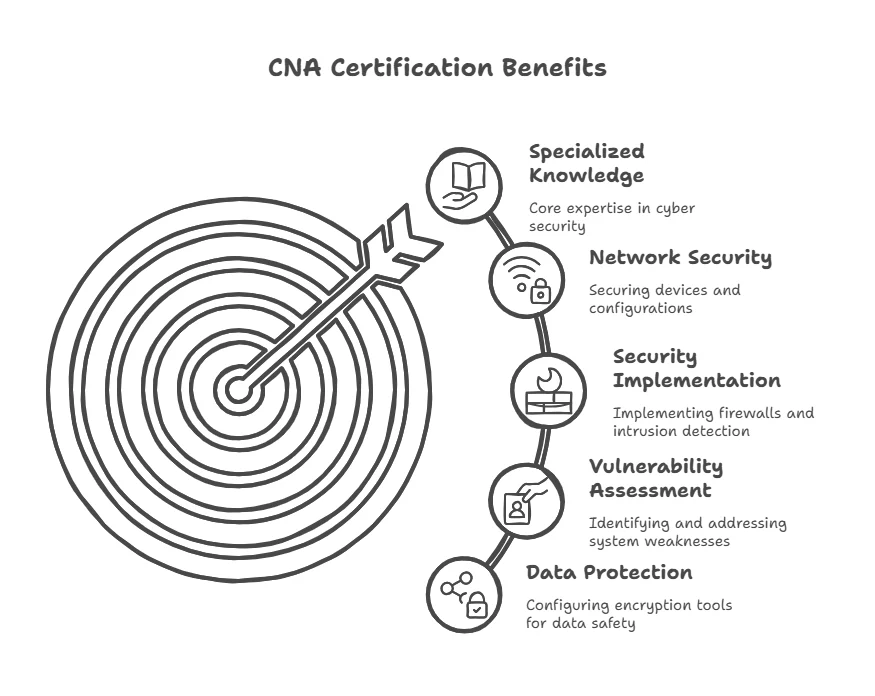
Benefit 2: Gaining Specialized Knowledge
Cyber security is a highly specialized field, and professionals working within it need to have comprehensive knowledge of various security mechanisms, protocols, and technologies. The CNA certification offers in-depth training on securing networks, systems, and data – a vital area of expertise for professionals aiming to secure critical infrastructure and safeguard sensitive information.
CNA-certified professionals are trained to handle tasks such as:
- Securing network devices and configurations
- Implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems
- Performing vulnerability assessments
- Configuring encryption tools to protect data
By gaining specialized knowledge, IT professionals can offer more than just basic IT support – they can provide advanced, security-focused solutions that are essential to modern enterprises.
Related Blog: Is CNA Certification Worth It for Cyber Security Careers?
Why is this important?
- Specialized knowledge is one of the cornerstones of cyber security. With CNA certification, IT professionals gain expertise that enables them to navigate complex security challenges and ensure the safety of critical business data and infrastructure.
Benefit 3: Competitive Advantage in the Job Market
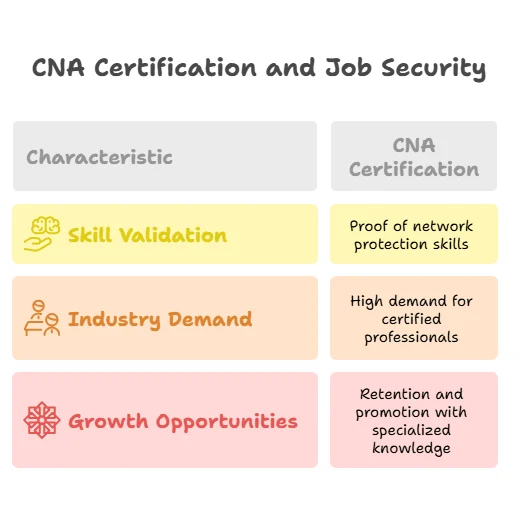
In today’s highly competitive job market, a certification like CNA can set IT professionals apart from their peers. While many IT professionals may have the necessary experience and technical skills, certification demonstrates a proactive approach to career development and a commitment to learning.
The CNA certification serves as proof that an individual has mastered essential security principles and is ready to take on the challenges of the cyber security landscape. Employers often prioritize certified candidates over those who are not certified, making the certification a valuable tool in increasing job prospects.
Why is this important?
- In a field flooded with job applicants, CNA certification acts as a differentiator. It showcases your commitment to the field, making you stand out to hiring managers and decision-makers, ultimately enhancing your job opportunities and career growth.
Benefit 4: Networking Opportunities
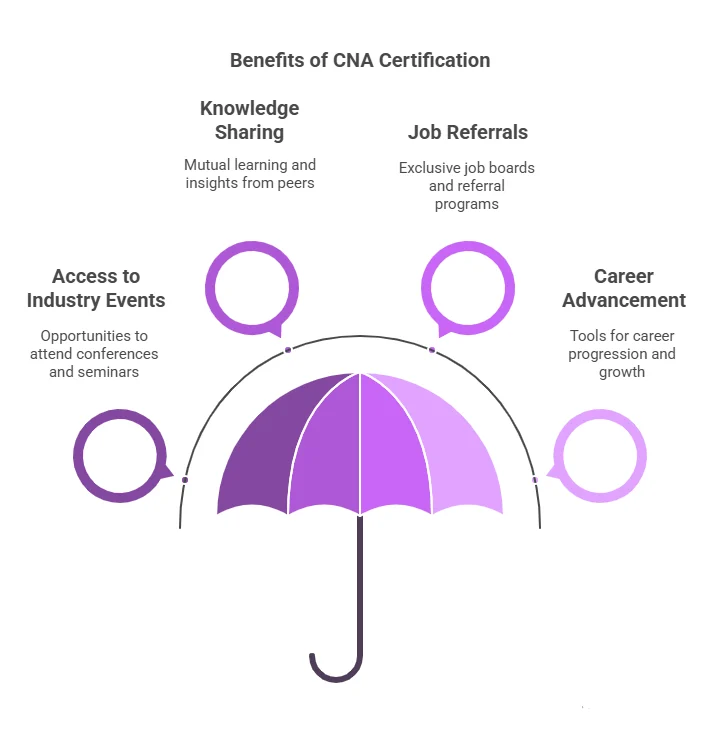
Another significant advantage of becoming a CNA-certified professional is the networking opportunities that come with it. When you earn this certification, you join a community of like-minded professionals who share similar career goals, challenges, and knowledge. Being part of a certification community offers numerous benefits, including:
- Access to industry events: You can attend cyber security conferences, workshops, and seminars that will keep you updated on the latest industry trends and best practices.
- Knowledge sharing: Being part of a network of certified professionals allows for mutual learning, providing valuable insights into real-world security challenges and solutions.
- Job referrals: Certification communities often have exclusive job boards or job referral programs, making it easier for you to find opportunities or get recommended for new roles.
Why is this important?
- Networking is a powerful tool for career advancement. By joining a community of certified professionals, IT experts can broaden their knowledge base, connect with industry leaders, and increase their chances of career progression.
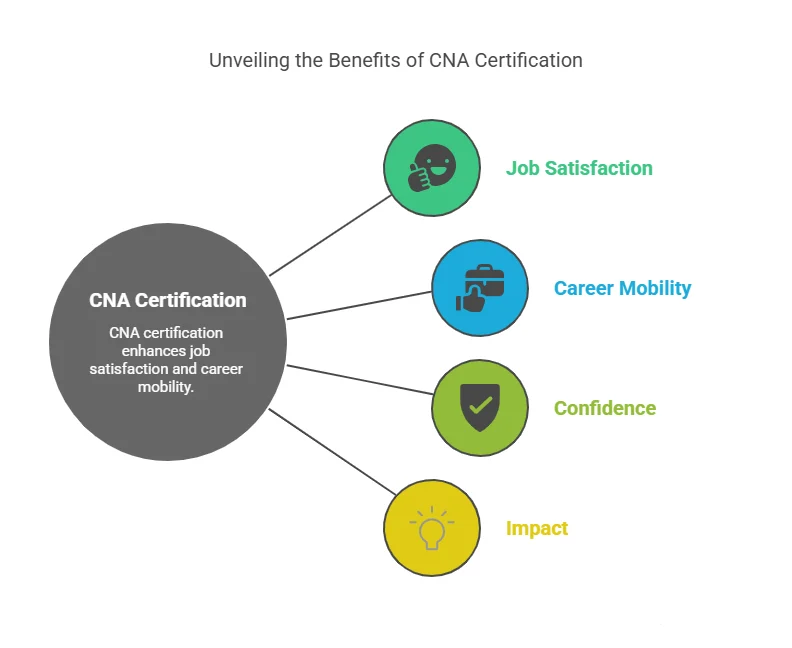
Benefit 5: Increased Job Satisfaction and Career Mobility
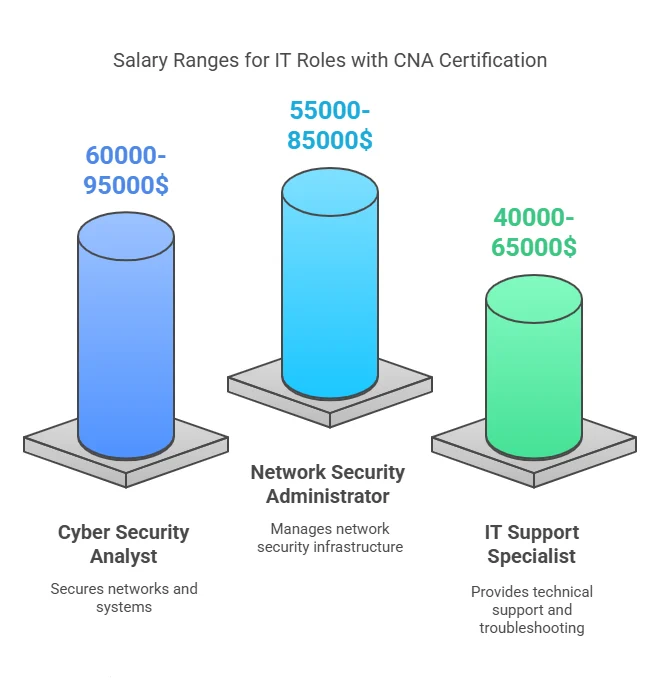
Achieving CNA certification can lead to greater job satisfaction by opening doors to more challenging and rewarding positions. Cyber security roles, such as network security analyst or information security manager, are often well-compensated and offer opportunities for career mobility. With cyber threats continuously evolving, professionals with advanced security certifications are in high demand, which provides ample room for career advancement.
Additionally, many CNA-certified professionals report feeling more confident and empowered in their roles, knowing they have the skills and expertise to address complex security issues. As a result, job satisfaction tends to increase when individuals feel that they can make a significant impact within their organization and the broader cyber security industry.
Why is this important?
- Job satisfaction is closely linked to career growth. By obtaining CNA certification, IT professionals can gain access to more fulfilling and high-level positions, ultimately improving both their career trajectory and job satisfaction.
Comparison to Other IT Certifications
While CNA certification is highly beneficial for those pursuing cyber security roles, it’s important to consider how it compares to other IT certifications, such as CompTIA A+ or Network+.
- CompTIA A+: This certification is generally more entry-level, focusing on foundational IT skills. It is an excellent starting point for beginners but does not delve deeply into cyber security.
- CompTIA Network+: This certification covers networking basics but does not provide specialized security training. It is helpful for those looking to build a solid understanding of networks but lacks the depth in security that CNA offers.
- CNA vs. others: Unlike these general certifications, CNA certification provides a specialized focus on cyber security, preparing professionals for the challenges of securing modern IT infrastructures.
Conclusion
For IT professionals looking to expand their careers into cyber security, CNA certification is an invaluable asset. It not only helps with career transitions but also equips professionals with specialized knowledge, gives them a competitive advantage, and opens doors to networking opportunities and increased job satisfaction. By obtaining CNA certification, IT professionals can significantly boost their career prospects, stay relevant in the fast-changing tech landscape, and contribute to building more secure digital environments.
ACSMI encourages IT professionals to explore the value of CNA certification as an essential step toward a rewarding career in cyber security. By investing in your professional development and gaining the credentials necessary to succeed in this growing field, you’ll be better equipped to tackle cyber security challenges and capitalize on the abundance of career opportunities available.
FAQs
- What is CNA certification, and how does it help IT professionals?
- CNA certification provides IT professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to specialize in cyber security, helping them transition into security-focused roles and enhancing their job prospects.
- Do I need previous cyber security experience to pursue CNA certification?
- No, CNA certification is designed for IT professionals who want to move into cyber security roles, even without prior specialized experience in the field.
- How does CNA certification compare to other certifications like CompTIA A+?
- CNA certification offers more in-depth training in cyber security, while CompTIA A+ focuses on basic IT skills. CNA is specialized for those pursuing careers in securing networks and systems.
- Can CNA certification help with career growth and salary increases?
- Yes, CNA-certified professionals are in high demand and can benefit from better job opportunities, higher salaries, and greater career mobility within IT and cyber security fields.
- What networking opportunities are available with CNA certification?
- CNA certification connects you with a community of certified professionals, offering access to industry events, job boards, and networking opportunities that can advance your career.