Table of Contents
- Why Choose Cybersecurity Certification CISSP?
- Who Should Pursue Cybersecurity Certification CISSP?
- The Eight CISSP Domains
- How Cybersecurity Certification CISSP Compares to Other Certifications
- Benefits of Obtaining Cybersecurity Certification CISSP
- Career Paths with Cybersecurity Certification CISSP
- FAQs About Cybersecurity Certification CISSP
- Highlighting ACSMI Certification
- Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity is an evolving field that plays a crucial role in safeguarding the digital infrastructure of businesses, governments, and organizations. As the threat landscape becomes more complex, certifications like the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) have emerged as vital credentials for security experts seeking to validate their expertise. If you’re exploring options to elevate your cybersecurity career, a cybersecurity certification CISSP stands out for its global recognition, comprehensive syllabus, and advanced skill-building focus. Recognized by industry leaders worldwide, CISSP is designed for professionals involved in designing, implementing, and managing cybersecurity programs.
Why Choose Cybersecurity Certification CISSP?
Earning a cybersecurity certification CISSP positions you as a trusted expert in information security. Below are a few reasons why CISSP is highly recommended for professionals aiming for advanced roles in the cybersecurity industry.
1. Global Recognition
The CISSP certification, offered by (ISC)², is renowned worldwide. It demonstrates your ability to design and manage security programs effectively and aligns with international standards of excellence.
2. Advanced Skill Validation
CISSP covers eight domains ranging from security risk management to software development security. It validates your expertise across these diverse topics, making it the gold standard for security professionals.
3. Career Opportunities and Salary Growth
Professionals with a CISSP certification are often recruited for high-level roles like Security Architects, Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs), and IT Directors. CISSP holders earn significantly higher salaries compared to their uncertified peers.
4. Vendor-Neutral Approach
Unlike certifications tied to specific tools or vendors, CISSP focuses on broad security principles and frameworks, allowing you to adapt to various technologies and environments.
5. Continuous Learning
CISSP requires certified professionals to earn Continuing Professional Education (CPE) credits to maintain their credentials. This ensures that CISSP holders stay updated with evolving cybersecurity trends and technologies.
Who Should Pursue Cybersecurity Certification CISSP?
CISSP is an advanced-level certification tailored for professionals with a minimum of five years of work experience in relevant cybersecurity roles. This certification is ideal for individuals in the following roles:
- Security Consultants
- Information Security Managers
- IT Directors/Managers
- Security Architects
- Chief Information Officers (CIOs)
If you’re seeking to deepen your expertise and expand your job prospects in the field of cybersecurity, pursuing a cybersecurity certification CISSP is a strategic move.
The Eight CISSP Domains
The CISSP certification is built around eight domains that encompass a comprehensive range of knowledge areas. Each domain represents a critical component of effective cybersecurity practices.
1. Security and Risk Management
Learn to assess and mitigate risks while adhering to legal, regulatory, and ethical considerations.
2. Asset Security
Understand data lifecycle management and protective controls to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
3. Security Architecture and Engineering
Get equipped to design secure enterprise-grade infrastructures and implement cryptographic solutions.
4. Communication and Network Security
Gain insights into network architecture, transmission methods, and how to secure communication channels effectively.
5. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Learn to implement and manage access controls, ensuring only authorized individuals have access to critical data.
6. Security Assessment and Testing
Develop skills for monitoring systems and performing security audits to identify vulnerabilities.
7. Security Operations
Understand how to manage and respond to incidents, including designing strategies for disaster recovery and business continuity.
8. Software Development Security
Learn secure coding principles and how to incorporate robust security measures right from the software development process.
Mastering these diverse domains ensures you’re well-rounded and prepared for real-world challenges.
How Cybersecurity Certification CISSP Compares to Other Certifications
CISSP is widely regarded as one of the most prestigious certifications in the cybersecurity world. However, it’s not the only option for professionals looking to validate their expertise. Depending on your career goals, other certifications might suit your needs just as well—or even better. Here’s a detailed look at how CISSP stacks up against other popular cybersecurity certifications.
CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional)
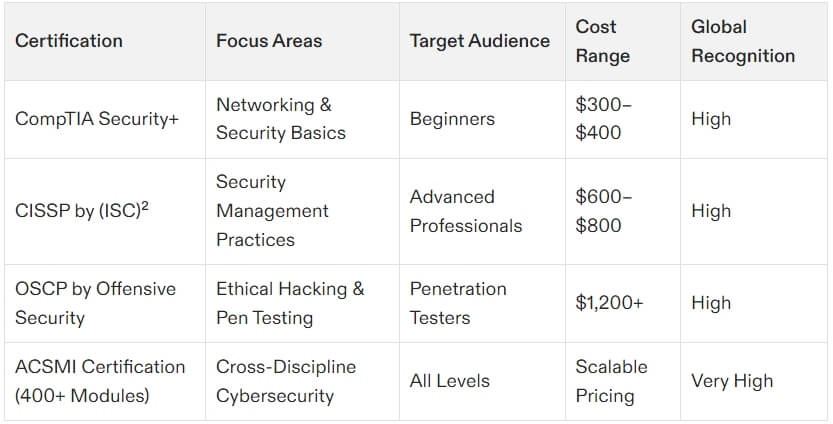
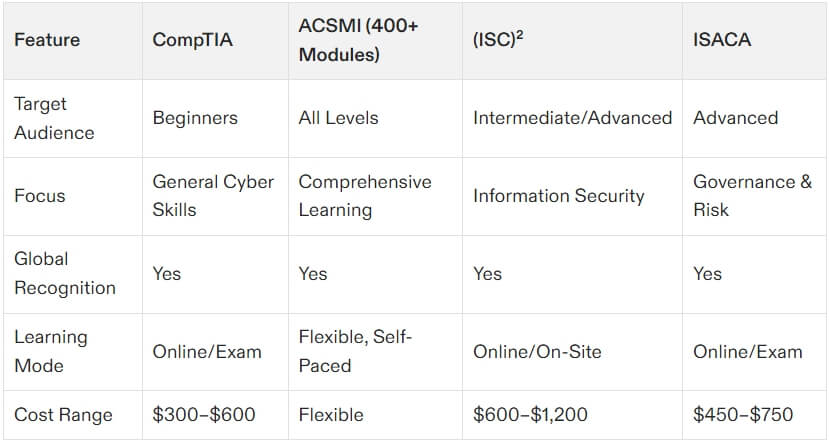
CISSP is designed for seasoned professionals looking to showcase their mastery over a wide range of cybersecurity domains. It’s perfect for those aiming for leadership or managerial roles, such as Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or Security Architect. Covering eight domains, CISSP takes a comprehensive, vendor-neutral approach, making it suitable for diverse industries and roles. However, it’s not an easy feat to accomplish. With a requirement of five years of work experience and a rigorous exam, CISSP demands thorough preparation and advanced-level expertise.
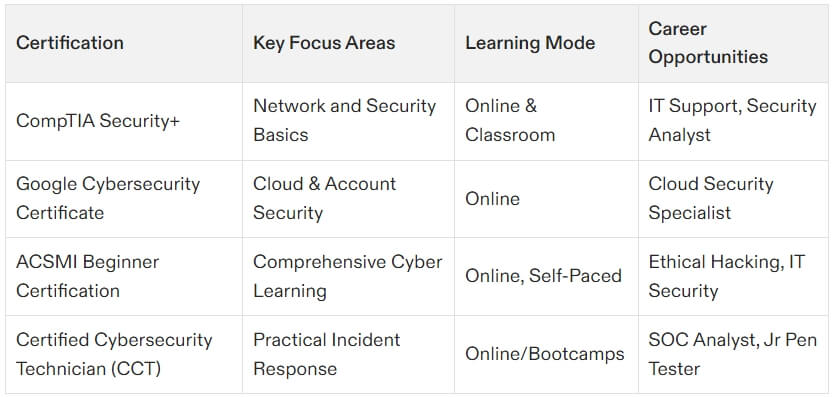
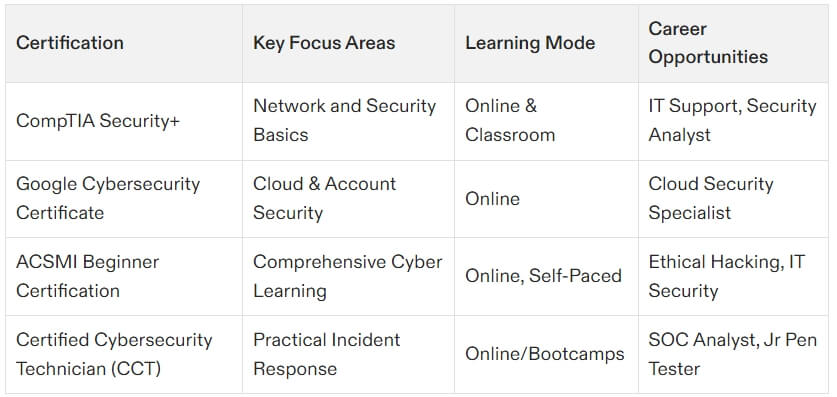
CompTIA Security+
For those just starting their cybersecurity careers, CompTIA Security+ is often the go-to certification. It provides foundational knowledge of core security concepts, such as risk management and threat detection. Unlike CISSP, Security+ requires little to no prior experience, making it ideal for beginners or entry-level IT professionals. However, because of its broader and more basic syllabus, it’s not as highly valued for advanced positions.
CISM (Certified Information Security Manager)
CISM, offered by ISACA, is tailored for individuals transitioning into managerial roles. While CISSP focuses on a balance of technical and managerial aspects, CISM is much more niche, emphasizing governance, risk management, and system auditing. It’s ideal for project managers or IT leaders looking to specialize in these areas. Both certifications are highly respected, but CISSP is often favored in roles requiring a blend of technical expertise and leadership, whereas CISM is a stronger choice for governance and compliance-driven roles.
CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker)
CEH is another well-known certification but focuses on offensive security rather than the defensive or managerial approach CISSP offers. Tailored for penetration testers and ethical hackers, CEH teaches professionals how to think like attackers, covering topics such as vulnerability exploitation and system breaching methods. While both CISSP and CEH are advanced certifications, CISSP holders often lead the teams in charge of infrastructure security, while CEH specialists work as part of red teams for organizations performing active tests on defenses.
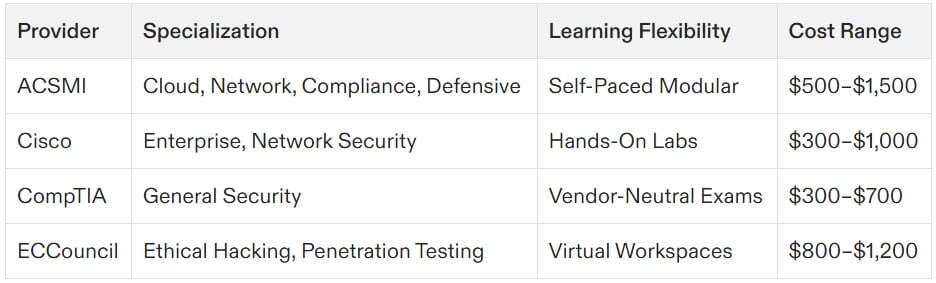
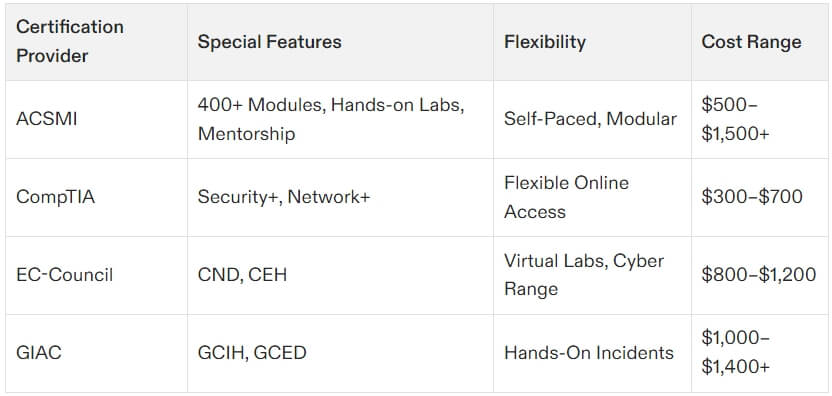
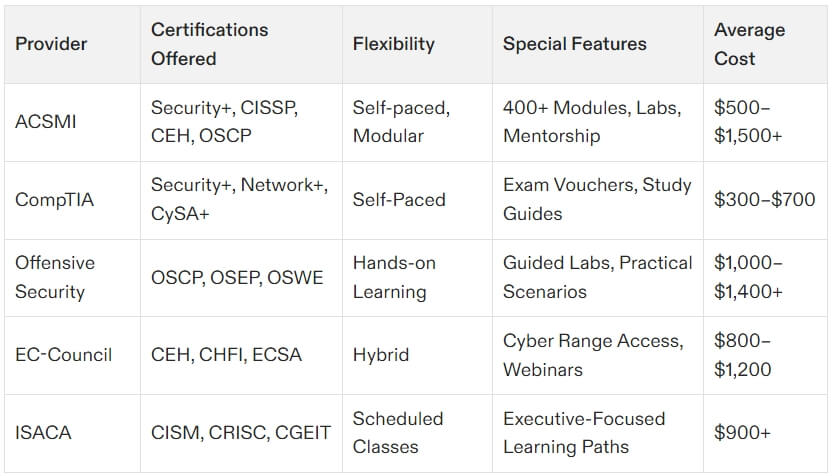
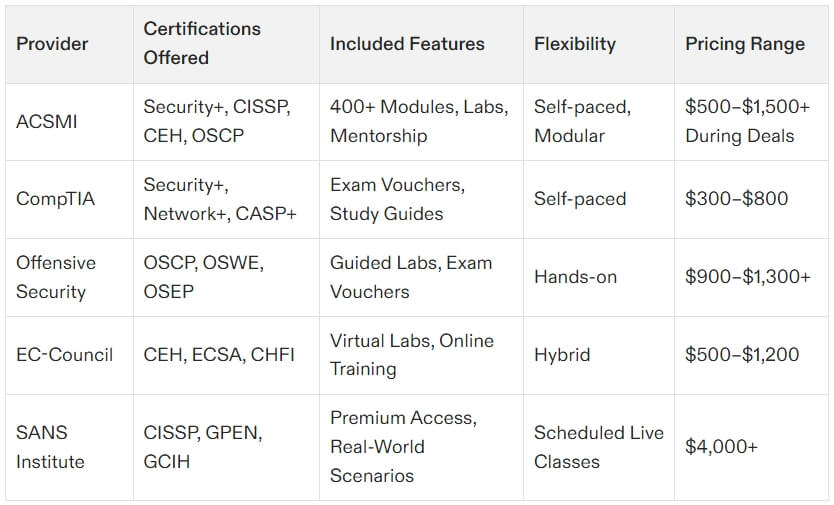
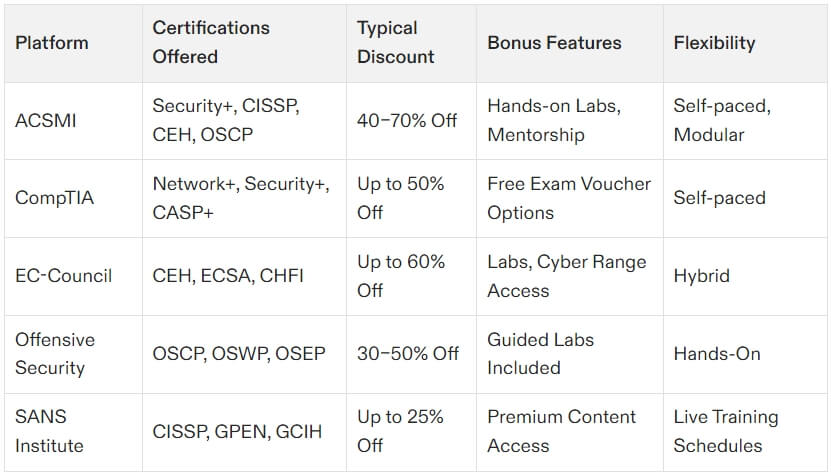
ACSMI Certifications
For a broader learning experience beyond the eight CISSP domains, platforms like ACSMI provide training through customizable 400+ modules. These certifications target various aspects of cybersecurity, from network security and cloud architecture to penetration testing and compliance management. ACSMI offers flexibility with self-paced, modular learning, making it ideal for professionals wanting to explore areas outside CISSP’s managerial focus. Explore ACSMI certifications here.
Each certification has strengths tailored to different career paths. While CISSP remains unmatched for individuals aiming to lead large-scale cybersecurity programs, other credentials like Security+, CISM, and CEH excel in their specialized niches. Carefully consider your career aspirations and current experience level when deciding which certification is the right fit.
Benefits of Obtaining Cybersecurity Certification CISSP
1. Enhanced Knowledge
CISSP enables you to develop a deeper understanding of complex cybersecurity principles, particularly in leadership and strategic roles.
2. Industry Recognition
With CISSP, you become part of an elite group of professionals trusted worldwide to lead enterprise security efforts.
3. Versatility
CISSP certification equips you to work across different industries, from healthcare and finance to governmental sectors.
4. Professional Networking
CISSP holders gain access to an exclusive (ISC)² member community that fosters collaboration and career advancement.
5. Higher Earning Potential
According to leading industry surveys, CISSP-certified professionals earn significantly more, with an average salary increase of 25–30%.
Career Paths with Cybersecurity Certification CISSP
Professionals with a CISSP certification often take on critical roles in cybersecurity, such as:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): A top-level executive tasked with overseeing an organization’s cybersecurity strategy.
- Security Architect: Responsible for designing robust cybersecurity frameworks to protect IT infrastructure.
- Information Security Manager: Ensures security policies and systems align with both organizational and regulatory needs.
- Senior Security Consultant: Advises businesses on improving their cybersecurity posture.
- Incident Response Manager: Manages cybersecurity incidents, from detection to resolution.
FAQs About Cybersecurity Certification CISSP
1. What is the CISSP certification?
CISSP, offered by (ISC)², is an advanced-level certification focused on eight domains that collectively cover the breadth of cybersecurity practices.
2. Is CISSP difficult to earn?
Yes, earning a CISSP certification requires significant preparation and expertise in the field. However, the difficulty underscores its high value and recognition.
3. How much experience is required for CISSP?
CISSP candidates need at least five years of cumulative, paid work experience in cybersecurity-related roles.
4. Why choose CISSP over other certifications?
CISSP provides a holistic, vendor-neutral approach to cybersecurity and is ideal for leadership and managerial roles.
5. How does ACSMI complement CISSP?
ACSMI provides extensive training programs, with 400+ modules, offering a broader scope that complements CISSP’s focus areas.
Learn more about ACSMI certifications here.
6. How long does it take to prepare for CISSP?
On average, candidates spend three to six months preparing, depending on their prior knowledge and study schedule.
7. Are remote exams available for CISSP?
Yes, (ISC)² offers remote proctoring for CISSP exams to accommodate professionals worldwide.
8. What is the passing score for the CISSP exam?
Candidates need to score at least 700 out of 1,000 points to pass.
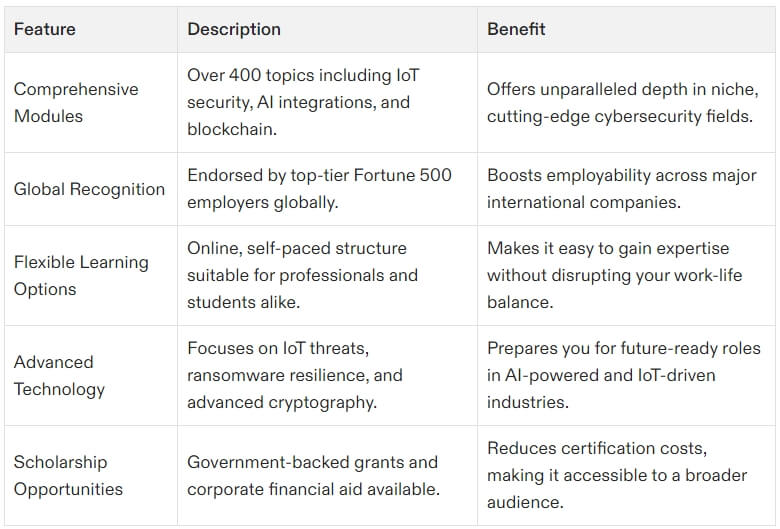
Highlighting ACSMI Certification
 Final Thoughts
Final Thoughts
The cybersecurity certification CISSP is a world-class credential that establishes you as a trusted expert capable of handling sophisticated security challenges. Its robust curriculum, comprehensive domains, and global recognition make it a must-have for seasoned professionals.
For broader, self-paced learning options, platforms like ACSMI offer tailored certifications with 400+ modules, ideal for complementing CISSP and expanding your skill set.
Start your ACSMI learning path today and take the next big step in your cybersecurity career!