As businesses grow and evolve, so too do their security needs. From protecting sensitive customer data to preventing unauthorized access to critical systems, security management has become a cornerstone of business operations. One of the most important aspects of maintaining a secure environment is choosing the right security management tools.
With the vast number of available tools—each offering different features, functionalities, and levels of protection—selecting the right ones can be a daunting task. In this blog, we’ll explore the factors you should consider when choosing security management tools, the features that make a security tool effective, and some of the best options available on the market today.
To understand more about security management, you can check out our blog on how security management prevents cyber threats.
Understanding Security Management Tools
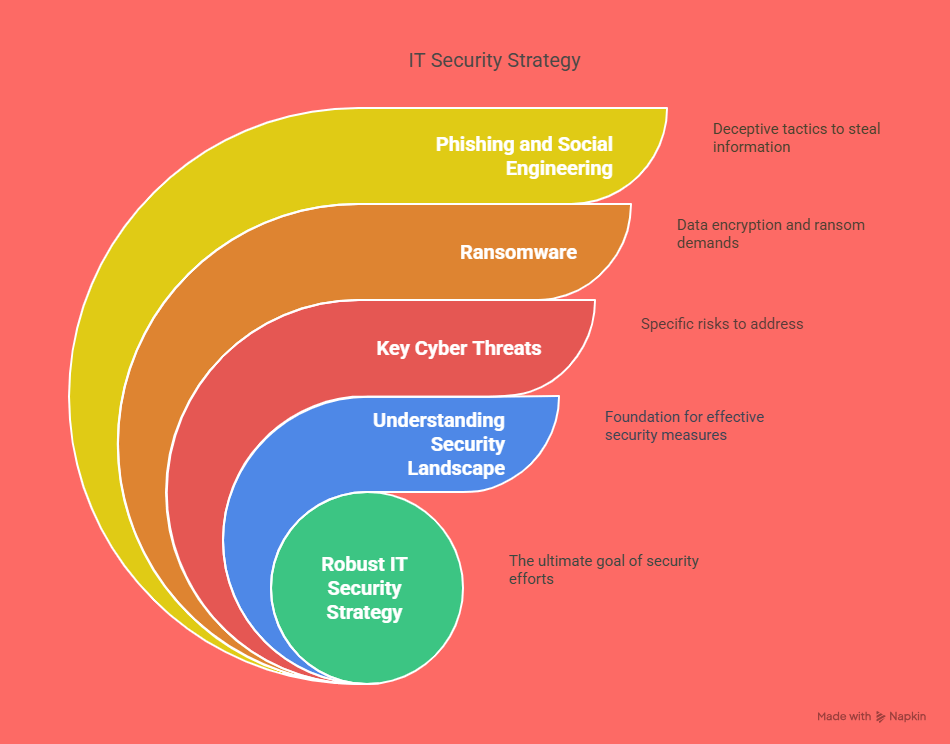
In today’s ever-evolving threat landscape, businesses must prioritize both digital and physical security to protect their assets, data, employees, and customers. Whether you’re a small business owner or part of a large corporation, implementing the right security solutions is critical. Before diving into how to choose the right tools, it's important to understand what security management tools are, how they function, and why they are essential in today’s business environment.
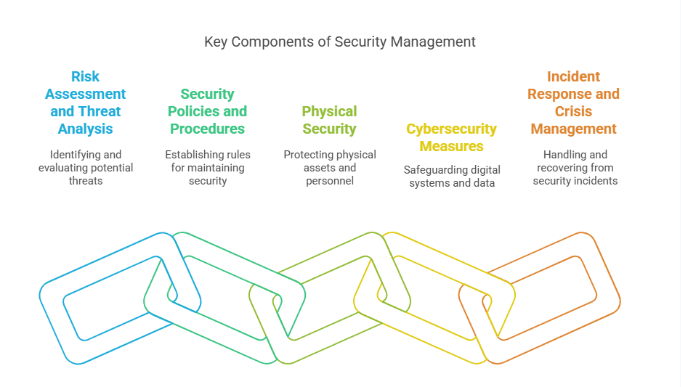
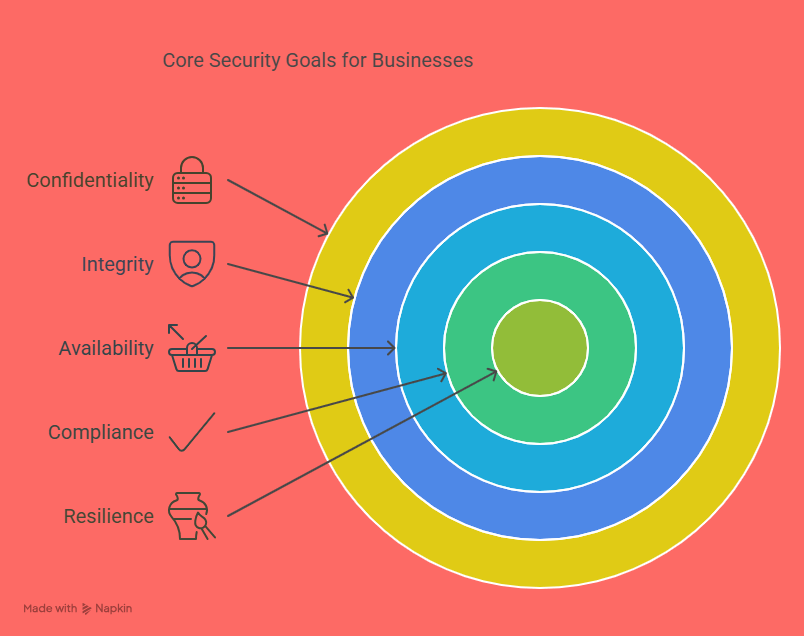
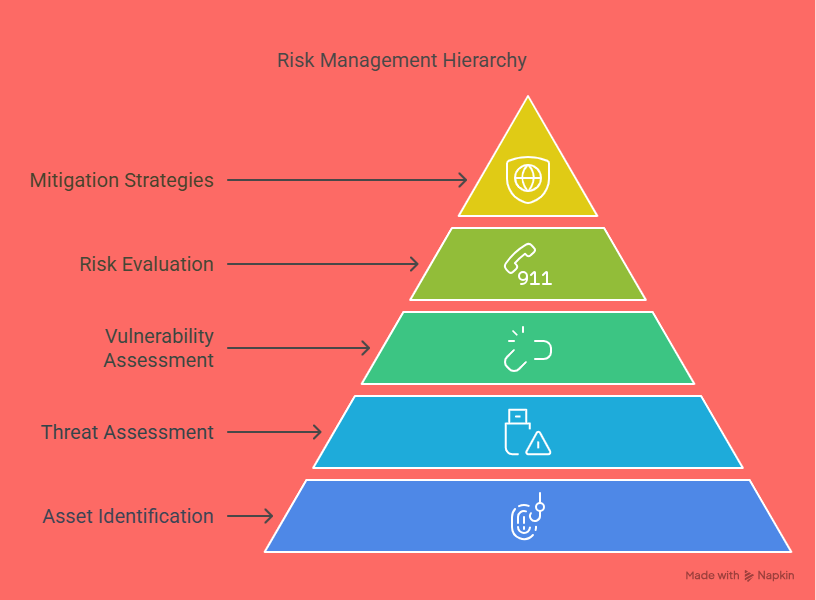
Security management tools refer to a broad range of software and hardware systems used to monitor, control, and protect business environments from various threats. These threats can range from cyberattacks and data breaches to unauthorized physical access and emergencies. Security tools help organizations proactively manage risks, respond to incidents more effectively, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Let’s break down some of the most common categories of security management tools and explore their importance in greater detail.
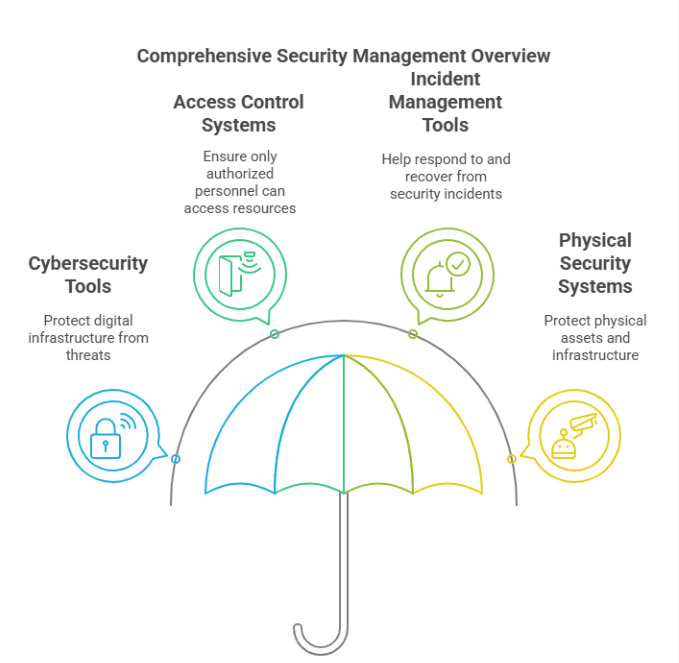
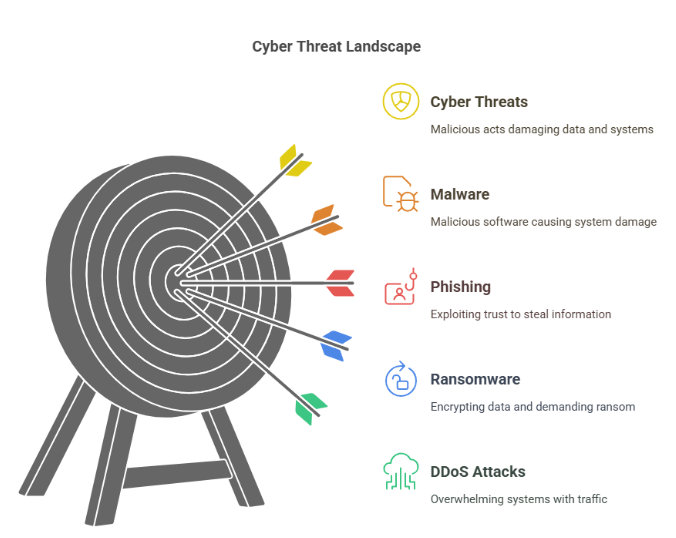
Cybersecurity Tools
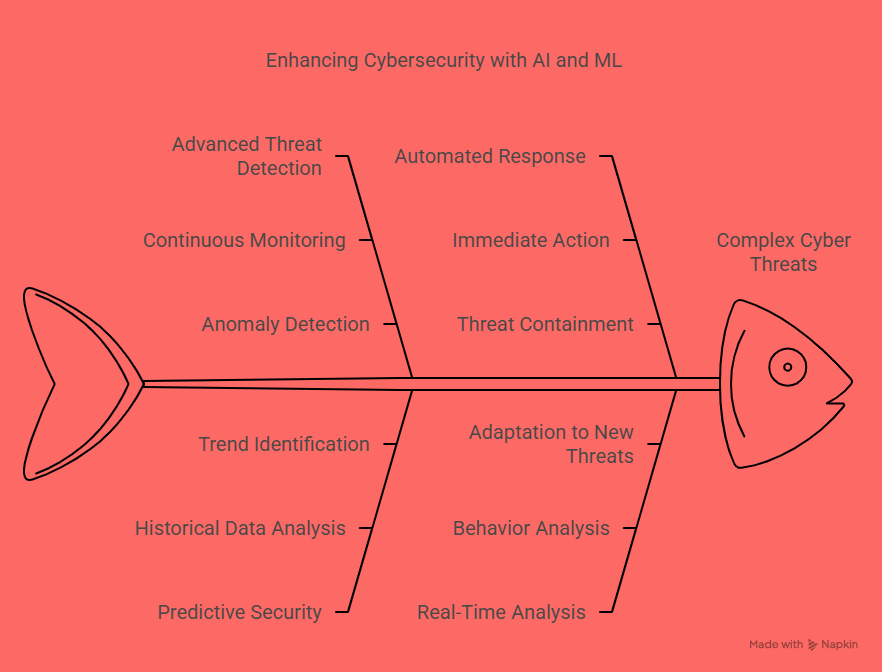
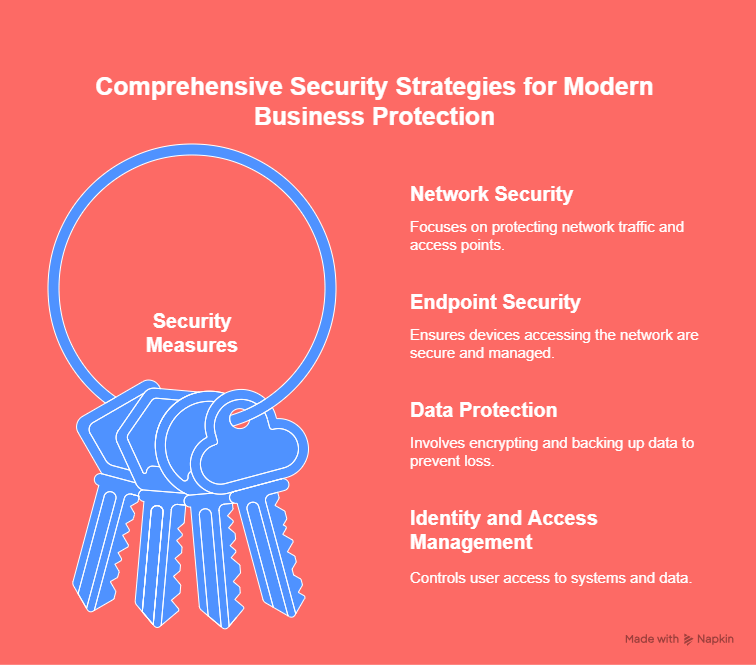
Cybersecurity tools are vital components of any business’s security framework. These tools are designed to protect your company’s digital infrastructure—such as networks, servers, databases, and employee devices—from both internal and external threats. Common cybersecurity tools include firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), endpoint protection platforms (EPP), and encryption solutions.
With the rise in remote work, cloud computing, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices, the digital attack surface of businesses has expanded significantly. This makes cybersecurity tools more important than ever. These tools not only defend against threats like malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks but also provide ongoing monitoring and analytics to detect unusual behavior before it becomes a major issue.
Investing in advanced cybersecurity tools enables your IT team to detect vulnerabilities in real time, enforce security policies, and maintain the integrity of sensitive business data.
Access Control Systems
Another essential component of security management is controlling who can access what. Access control systems help ensure that only authorized personnel can enter specific areas of a building or access certain digital resources. These systems can be physical (like key cards and biometric scanners) or logical (such as role-based access controls for software platforms).
Physical access control is crucial for protecting confidential areas like data centers, executive offices, or storage rooms containing sensitive materials. On the digital side, access control limits who can view or manipulate important data, helping to prevent insider threats and accidental breaches.
Modern access control systems are often integrated with identity and access management (IAM) solutions, allowing businesses to manage permissions and track user activity seamlessly. These systems also contribute to audit readiness by logging every access attempt, whether successful or denied.
Incident Management Tools
No matter how strong your security posture is, incidents can and do happen. When they do, having a structured response plan is essential. That’s where incident management tools come into play. These tools help organizations prepare for, detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents effectively.
Incident management software typically includes features for ticketing, real-time alerts, escalation procedures, forensic analysis, and post-incident reporting. It allows security teams to document each stage of the incident, communicate with stakeholders, and ensure that nothing falls through the cracks during a crisis.
By using incident management tools, companies can minimize the impact of breaches, reduce downtime, and learn from each event to improve future response efforts. Some platforms even integrate with other tools in your security stack to automate incident workflows and response protocols.
Physical Security Systems
While much of today’s focus is on cybersecurity, physical security is just as important—especially in industries like manufacturing, retail, education, and healthcare. Physical security systems protect people, assets, and infrastructure from theft, vandalism, unauthorized access, and other physical threats.
These systems include surveillance cameras (CCTV), intrusion alarms, motion sensors, and security gates or turnstiles. Modern physical security tools are often IP-based, meaning they can be monitored remotely and integrated with other IT systems. For example, video surveillance footage can be linked to access control logs to identify who entered a building at a specific time.
Physical security also includes environmental monitoring tools such as fire detection systems, water leak sensors, and temperature control units—critical in data centers and storage facilities. Integrating physical security with digital tools provides a more holistic view of your organization’s risk landscape.
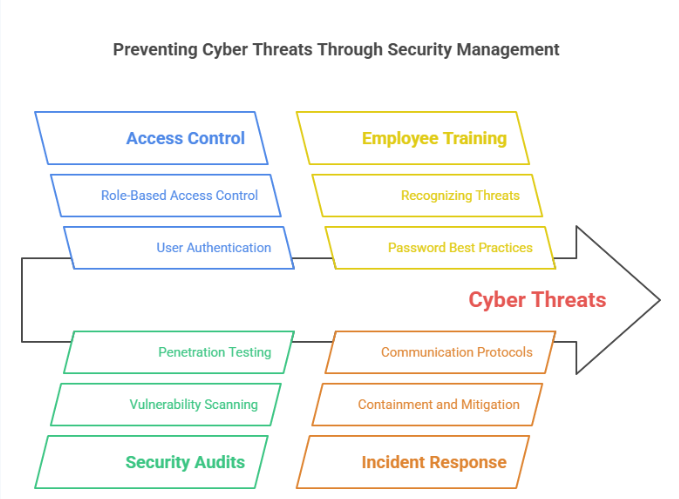
The Value of an Integrated Approach
A well-rounded security management system doesn’t rely on a single tool. Instead, it integrates multiple tools across different domains—digital, physical, and operational—to form a unified defense strategy. This integrated approach is often referred to as converged security, and it allows for improved data sharing, faster threat detection, and more coordinated responses.
For instance, if a breach is detected on a server, your incident management system can trigger an automatic alert, restrict access via your access control system, and notify security personnel to investigate. This kind of automated, cohesive response reduces the time it takes to contain and resolve threats.
In addition, integrated security management systems often provide centralized dashboards where security teams can monitor all activity in one place. This visibility helps identify patterns, anticipate risks, and optimize overall security protocols.
A well-rounded security management system integrates multiple tools to address various aspects of security, both physical and digital.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Security Management Tools
In today’s digital landscape, businesses of all sizes face a growing range of cybersecurity threats. To effectively protect sensitive data, intellectual property, and critical systems, selecting the right security management tools is essential. However, with countless options available, making the right choice can be overwhelming. This guide explores the key factors you should consider to ensure the tool you choose aligns with your business needs, enhances your security posture, and supports long-term growth.
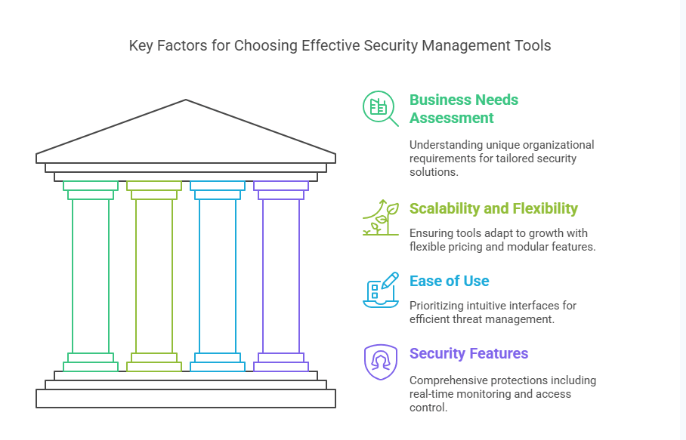
1. Assess Your Business Needs
The first and most important step in selecting a security management tool is understanding your organization's unique requirements. No two businesses are the same, and your security solution should reflect your specific environment and goals.
Here are some aspects to evaluate:
-
Size of your organization: The needs of a small startup differ significantly from those of a multinational enterprise. A small company may need a lightweight, easy-to-use tool, while a large organization might require a robust, scalable solution that can support multiple departments and locations.
-
Industry-specific requirements: Different industries face different threats and have varying compliance standards. For example, healthcare providers must protect patient records under HIPAA, while financial institutions need to comply with regulations like GLBA or SOX. Understanding your industry's standards is crucial to ensuring your tools provide the required safeguards.
-
Type of data and assets: Identify the assets that are most critical to your business, such as customer data, intellectual property, or internal communications. Some tools are better suited for protecting specific types of information, so it’s important to choose accordingly.
-
Compliance requirements: Regulatory compliance is not just about avoiding fines—it’s about maintaining trust with your customers and partners. Tools that help you stay compliant with frameworks like GDPR, PCI-DSS, or ISO/IEC 27001 can simplify audits and reduce legal risks.
Taking time to map out these requirements will help you filter out solutions that don’t meet your criteria and focus on the ones that align closely with your business goals.
To explore compliance topics in more detail, check out our post on security compliance and legal requirements.
To learn more about compliance requirements, check out our post on security compliance and legal requirements.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
As your company grows, your security demands will increase and likely change. It’s essential to invest in a security management tool that not only meets your current needs but can also adapt as your business evolves.
Key features to look for include:
-
Flexible pricing: Many vendors offer pricing models based on the number of users, data volume, or the number of assets being protected. Choose a tool that can scale cost-effectively, so you’re not paying for more than you need—or stuck without features when you need them most.
-
Modular scalability: The best tools are modular, meaning you can add features or capabilities as needed without overhauling the entire system. This is especially useful when expanding to new markets or adding new departments.
-
Integration with existing infrastructure: Your security tools should work seamlessly with your current IT ecosystem, including firewalls, cloud services, and identity management systems. Strong integration capabilities ensure you get a unified view of your organization’s security without gaps or overlaps.
Planning for growth not only saves you from future headaches but also ensures your security infrastructure remains robust and relevant.
3. Ease of Use and User Interface
Even the most advanced security tools are ineffective if they’re too complicated to use. A solution that’s difficult to navigate or overly technical can slow down your team and lead to errors.
Look for tools that prioritize user experience, such as:
-
Intuitive dashboards: Your team should be able to see the most important security metrics and alerts at a glance. Visual dashboards help reduce response times and support faster decision-making.
-
Customization options: Every organization has different workflows. A good tool allows you to tailor alerts, reports, and permissions to match your internal processes.
-
Ease of deployment: Ideally, the tool should be simple to install, configure, and maintain—whether you’re operating in the cloud, on-premises, or in a hybrid environment. Some solutions also offer managed services or onboarding support to help you get started quickly.
An easy-to-use interface empowers your team to manage threats more efficiently and ensures high user adoption across your organization.
4. Security Features and Capabilities
Not all security management tools are created equal. When comparing options, pay attention to the core features and technologies that each tool provides. A robust solution should include a comprehensive suite of protections to address multiple threat vectors.
Some essential capabilities include:
-
Real-time monitoring and alerts: You should be able to identify unusual activity as it happens—not after damage has occurred. Tools with AI-driven analytics and automatic alerts can significantly reduce response time and limit the impact of threats.
-
Access control and identity management: Role-based access controls (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and user behavior analytics are crucial for ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
-
Encryption and data protection: Ensure the tool supports strong encryption methods for data at rest and in transit. Features like data masking and secure file sharing also help prevent leaks and breaches.
-
Incident response and reporting: When a security event occurs, you need tools that support rapid investigation and resolution. Automated incident response workflows and comprehensive audit logs are critical for managing incidents effectively.
-
Compliance tracking and auditing: For companies subject to regulation, tools that offer built-in compliance reporting and audit support can simplify your compliance efforts and reduce the time spent preparing for assessments.
Choosing a tool with a comprehensive feature set ensures you're protected against current threats and prepared for emerging risks.
Popular Security Management Tools on the Market
Now that we’ve outlined the factors to consider when selecting security management tools, let’s explore some of the most popular and widely used solutions available in today’s market. These tools play a crucial role in helping businesses protect their systems, data, and digital environments against evolving security threats. From endpoint protection to identity management and incident tracking, here are five tools that stand out:
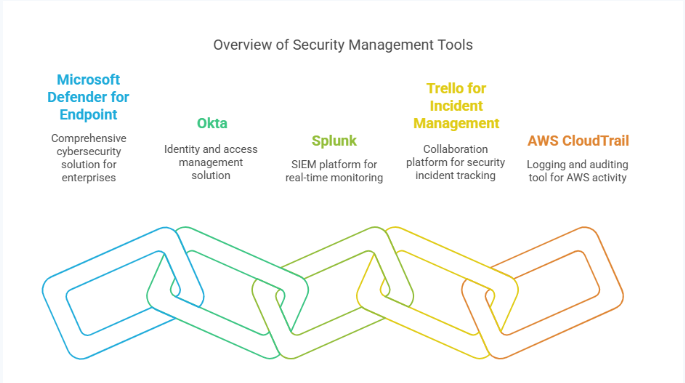
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is a comprehensive cybersecurity solution designed for enterprise environments. It offers advanced threat protection by providing real-time monitoring, behavioral analysis, and automated investigation and response capabilities. This tool helps detect, prevent, investigate, and respond to advanced attacks across devices. With integration into Microsoft 365 and seamless cloud compatibility, it delivers centralized security management and deep visibility into threats. Defender for Endpoint also includes features such as threat intelligence, attack surface reduction, endpoint detection and response (EDR), and vulnerability management.
Okta
Okta is a leading identity and access management (IAM) solution trusted by businesses to control and secure user access to applications, systems, and data. It supports single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and lifecycle management for users across cloud and on-premises environments. By verifying and managing identities, Okta minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. It's especially useful for organizations with remote or hybrid workforces, providing secure and seamless access to tools and platforms. Okta’s integration with thousands of applications makes it a flexible choice for businesses of all sizes.
Splunk
Splunk is a powerful Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platform that enables real-time monitoring, searching, and analysis of machine-generated data across an organization’s IT infrastructure. It helps security teams detect suspicious activities, analyze logs, correlate events, and respond to incidents efficiently. With built-in machine learning and analytics, Splunk can identify anomalies and predict potential threats before they cause damage. It’s highly scalable and is used across various industries to maintain security compliance and improve operational intelligence.
Trello for Incident Management
While Trello is not a traditional security tool, it’s a versatile collaboration platform that can be adapted for security incident management. Organizations use Trello boards, lists, and cards to track security events, assign tasks to response teams, document investigation steps, and ensure transparency in the incident resolution process. Its simple, visual interface makes it easy for teams to stay organized and informed during high-pressure situations. When paired with other tools, Trello becomes a valuable part of a well-rounded security management workflow.
AWS CloudTrail
For organizations leveraging Amazon Web Services (AWS), CloudTrail is an essential security tool that provides logging, monitoring, and auditing of AWS account activity. It records API calls and changes to infrastructure, helping organizations detect unusual activity, troubleshoot operational issues, and ensure compliance with internal policies or external regulations. CloudTrail provides visibility into user activity and simplifies governance, making it easier to respond to security events in a cloud-native environment.
The Role of Integration in Choosing Security Management Tools
An often-overlooked factor when choosing security tools is their ability to integrate with your existing systems. As businesses rely on a variety of software solutions for operations, selecting tools that can seamlessly integrate with each other is vital.
For example, your access control system should integrate with your incident management tools to ensure that security breaches are addressed immediately. Similarly, your cybersecurity tools should work together with your data backup and recovery systems to protect critical data from cyber threats.
Conclusion
Choosing the right security management tools is critical to safeguarding your business against a variety of risks, from cyber threats to physical breaches. By assessing your specific needs, considering scalability, ease of use, and the security features offered by each tool, you can build a robust security management system that provides comprehensive protection.
At ACSMI, we understand the importance of securing your digital and physical assets. We provide medical coding and billing certifications to ensure professionals can handle sensitive data securely. We also offer a range of snacks online to keep your team energized while managing your security needs.
FAQs
How do I choose the right security management tool for my business?
Start by assessing your business's security needs, scalability, integration capabilities, and the specific features offered by each tool.
What is the importance of integration in security management tools?
Integration ensures that your tools work together seamlessly, providing comprehensive protection and improving efficiency.
Can small businesses benefit from enterprise-level security management tools?
Yes, many enterprise-level security tools offer scalable pricing options, making them accessible for small businesses as well.
What are some essential features in a security management tool?
Essential features include real-time monitoring, access control, data encryption, incident response, and compliance tracking.
How can security management tools help ensure compliance with regulations?
Security tools can help track compliance with industry regulations, provide reports for audits, and maintain the necessary security standards.