In the world of rapidly advancing technology, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a driving force across various industries, and security is no exception. As cyber threats become more sophisticated and complex, traditional security measures are no longer enough to keep up with these evolving risks. AI's ability to analyze vast amounts of data, detect anomalies, and make real-time decisions has positioned it as a game changer in the Evolution of Security Technology.
This blog delves into the role of AI in security, focusing on how it is transforming both cybersecurity and physical security technologies. From predictive threat detection to automating incident responses, AI is revolutionizing security operations across sectors. As we look ahead to 2025 and beyond, this guide will explore how AI continues to enhance security and how businesses and individuals can leverage AI-powered security solutions for better protection.
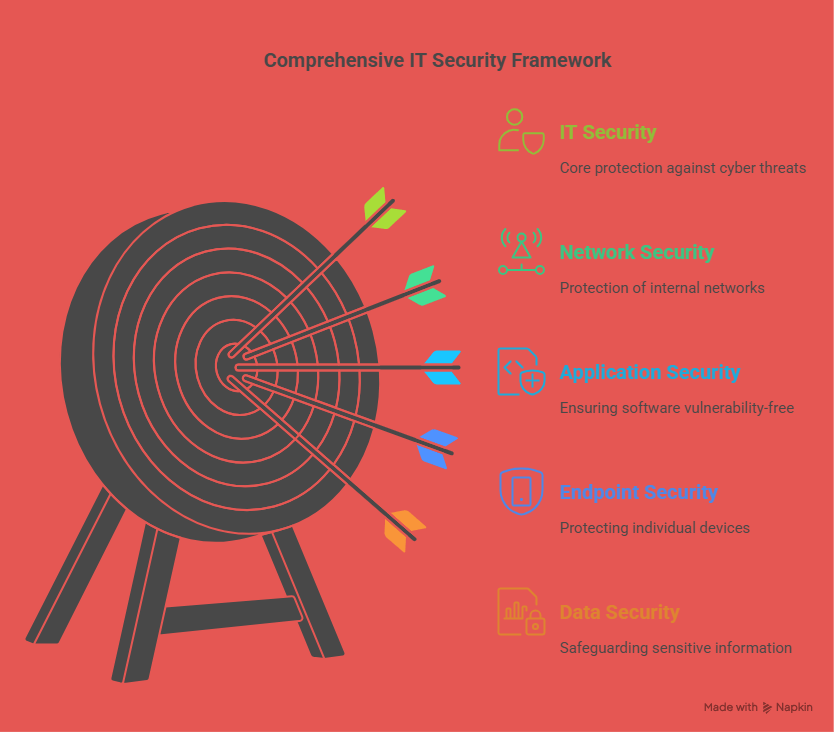
The Intersection of AI and Security Technology
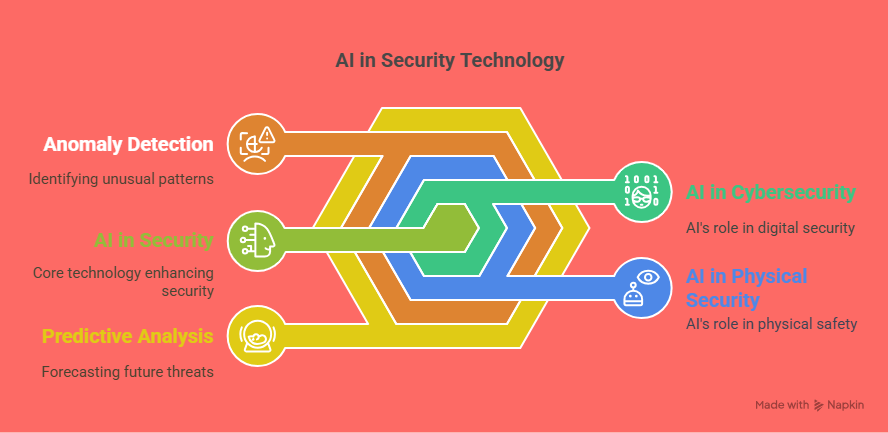
AI in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a primary area where AI is making significant strides. As the volume and complexity of cyberattacks continue to rise, AI’s ability to analyze large datasets and detect abnormal patterns is crucial in preventing breaches. Traditional cybersecurity systems are often reactive, addressing threats after they’ve been detected. In contrast, AI-powered systems enable predictive threat detection, allowing organizations to stop attacks before they cause damage.
-
Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms can learn the normal behavior patterns of a system or network. If there is any deviation from this behavior—such as unusual login times or data access patterns—AI triggers an alert, providing early warning signs of potential security threats.
-
Predictive Analysis: By continuously analyzing data, AI can predict emerging threats. This predictive ability helps in preventing cyberattacks that have not yet been identified by traditional methods, such as zero-day threats.
AI in Physical Security
AI is also having a profound impact on physical security systems. Through innovations such as AI-powered surveillance cameras, security systems can now autonomously monitor and identify threats in real time. These systems use computer vision and deep learning to continuously analyze video footage, allowing them to identify suspicious activities or threats without human intervention.
-
Facial Recognition: AI algorithms are used to compare individuals' facial features against large databases in real-time. This is particularly useful for identity verification and access control in high-security environments such as airports, government buildings, or financial institutions.
-
Crowd Monitoring: AI systems can analyze crowds, detect unusual behavior, and identify individuals who may be engaging in suspicious activities. These systems can automatically flag incidents for further investigation, improving response times and reducing reliance on human monitoring.
How AI is Revolutionizing Cybersecurity
1. Predictive Threat Detection
AI is a game changer in threat detection because of its ability to predict attacks before they occur. Traditional security measures typically rely on detecting known threats, but this leaves systems vulnerable to new and unknown attacks. AI, on the other hand, can analyze patterns of behavior and detect potential threats by identifying unusual activity before it turns into a full-blown attack.
-
Behavioral Analytics: One of the key components of AI’s predictive power is behavioral analytics. AI learns the normal activity patterns of users and devices within a network. When there is a deviation from the norm, such as a user accessing sensitive data at odd hours or from an unfamiliar location, AI can flag this behavior as a potential threat.
-
Real-time Threat Detection: AI-powered systems can analyze network traffic in real time, detecting potential threats based on traffic anomalies. This allows businesses to respond quickly, reducing the potential damage caused by cyberattacks.
2. Automated Threat Response
AI is not just about detecting threats—it's also about responding to them quickly and efficiently. Traditional security systems often require human intervention to respond to threats, which can cause delays. AI can automate response protocols, neutralizing threats much faster than humans could.
-
Incident Containment: In the event of a detected threat, AI can immediately take action by isolating affected systems or devices, thereby containing the threat and preventing it from spreading. This quick response reduces the risk of widespread damage to networks or systems.
-
Automated Decision Making: AI can automatically determine the best course of action based on real-time data. For example, if AI detects an ongoing DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service) attack, it can automatically initiate countermeasures like traffic filtering or rate-limiting to minimize the impact.
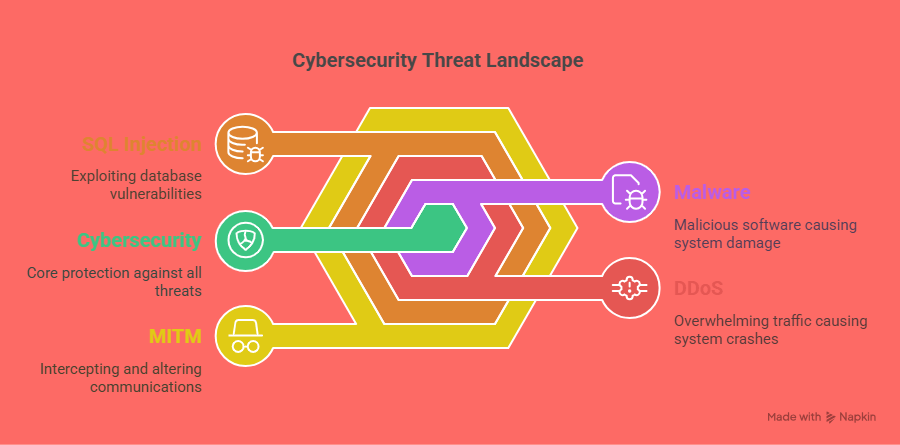
3. Advanced Malware Detection
Malware detection is another critical area where AI is making a significant impact. Traditional methods of malware detection rely on known malware signatures to identify and block attacks. However, this method is ineffective against zero-day malware, which is newly created and lacks a signature.
-
Behavioral Malware Detection: AI can identify malware based on its behavior, even if the specific variant is not previously known. For instance, AI may recognize patterns such as file encryption or unauthorized file access, which are indicative of malware activity. This ability to detect unknown threats is invaluable in preventing advanced cyberattacks.
-
Machine Learning Models: AI’s machine learning algorithms can continuously improve over time by learning from new data. This makes AI more effective at identifying sophisticated malware and evolving threats, ensuring that cybersecurity systems stay ahead of attackers.
AI in Physical Security and Surveillance
1. Smart Surveillance Systems
AI-powered surveillance systems are changing the landscape of physical security. By leveraging computer vision and deep learning, these systems can autonomously monitor video feeds and detect threats in real time. These systems can recognize faces, identify objects, and even detect suspicious activities like loitering or unauthorized access to restricted areas.
-
Real-Time Threat Detection: AI-powered surveillance systems continuously analyze video footage in real-time. Unlike traditional systems that rely on human operators to monitor video feeds, AI systems can autonomously flag suspicious activities and provide alerts, improving response times and reducing the risk of security lapses.
-
Accuracy and Efficiency: AI-based systems are more accurate than human operators at detecting potential threats. They can work 24/7 without fatigue, ensuring that every video feed is analyzed for security risks without interruption.
2. AI-Powered Access Control
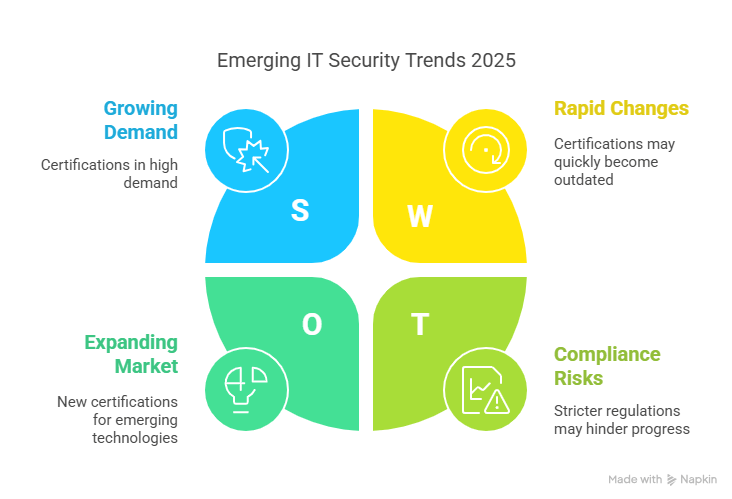
AI is also being integrated into access control systems to enhance security. Traditional access control methods, such as keycards or PINs, can be bypassed or stolen. AI-powered systems, however, use biometric authentication methods such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning to ensure that only authorized individuals can gain access to sensitive areas. These advancements align with the growing demand for Information Technology Security Certifications, as professionals need to stay updated with modern security technologies and protocols.
-
Facial Recognition: AI systems use facial recognition to identify individuals in a crowd or at access points. These systems compare the individual’s face against a database of authorized personnel to ensure that access is granted only to those who are permitted.
-
Voice Recognition: AI can also use voice recognition technology to verify the identity of individuals, making it an additional layer of security for areas where face recognition may not be applicable.
AI’s Role in Fraud Prevention
Fraud prevention is an area where AI is having a profound impact. In industries such as finance, retail, and e-commerce, AI is used to detect and prevent fraudulent activities in real-time by analyzing transaction data, user behavior, and patterns.
1. Fraud Detection Systems
AI systems can analyze transactions in real time, identifying patterns that indicate fraudulent behavior. These systems can flag suspicious transactions, such as unusually large purchases, changes in spending habits, or transactions from unfamiliar locations, and prevent them from going through.
-
Real-Time Fraud Detection: By continuously analyzing transaction data, AI-powered systems can spot fraudulent activities as they happen. This allows businesses to block fraudulent transactions before they affect customers or businesses.
-
Machine Learning Models: AI fraud detection systems use machine learning algorithms to identify new types of fraud. As these models are exposed to more data, they improve their ability to detect new fraud patterns, making them more effective over time.
2. Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
AI is also used in anti-money laundering efforts to track and detect suspicious financial activities. By analyzing large datasets from multiple sources, AI can identify patterns indicative of money laundering, such as the movement of large sums of money between accounts or across borders.
-
Pattern Recognition: AI-powered AML systems are trained to recognize patterns associated with money laundering activities. This helps financial institutions comply with regulations and avoid penalties by identifying potential money laundering activities before they become a problem.
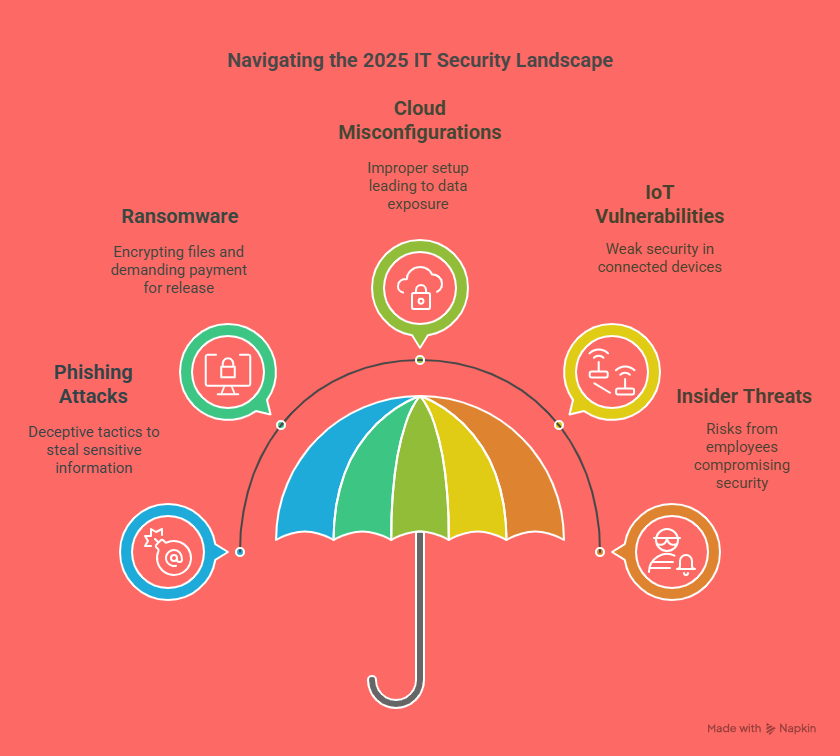
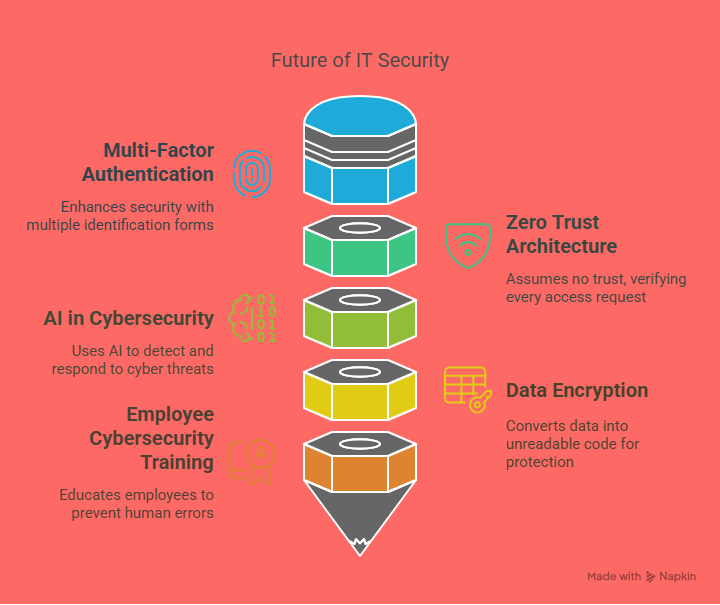
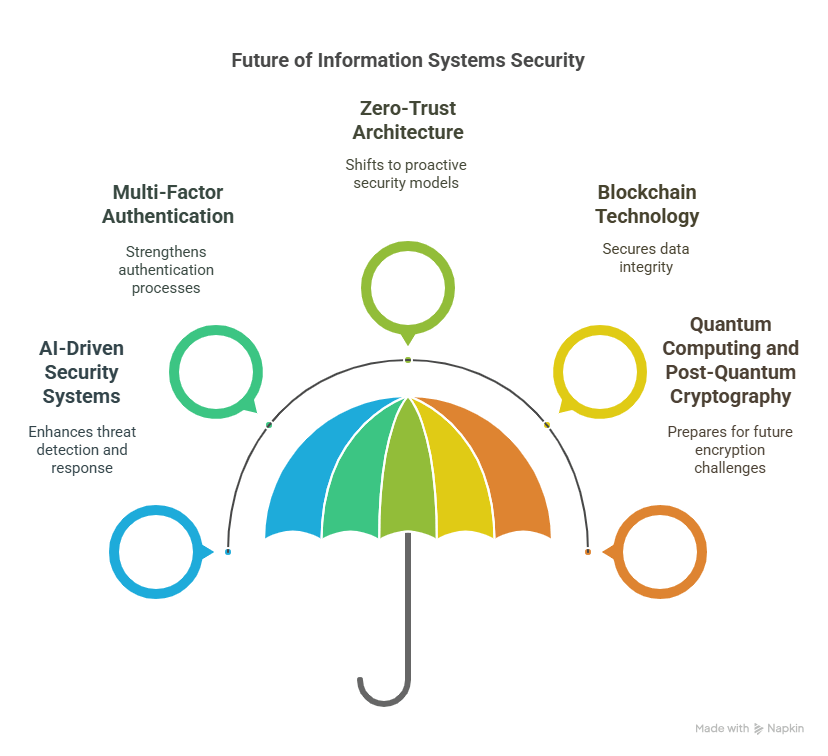
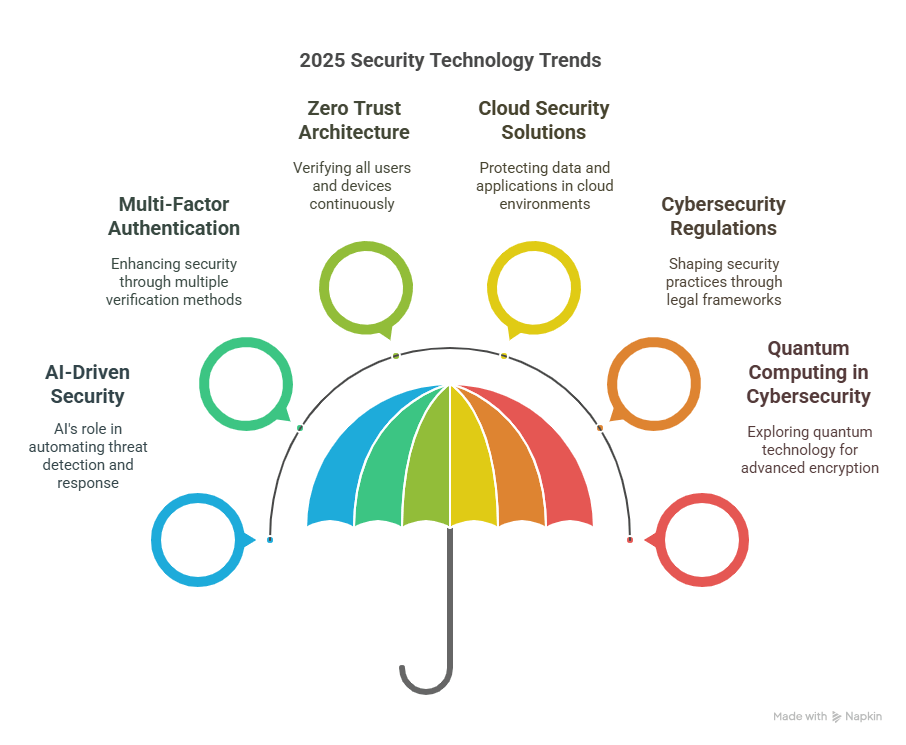
The Future of AI in Security Technology: What’s Next?
1. AI-Powered Threat Intelligence
In 2025, AI will continue to evolve as a central component of threat intelligence. AI will be able to analyze data from multiple sources, such as global threat feeds, internal security logs, and even social media, to provide real-time insights into emerging threats. These systems will continuously learn and adapt, improving their predictive capabilities and staying ahead of cybercriminals.
-
Real-Time Global Threat Analysis: AI-powered threat intelligence platforms will provide security teams with real-time alerts about emerging threats, allowing them to respond faster and more effectively.
-
Collaborative Intelligence: AI will also enable the sharing of threat intelligence across organizations and industries. By pooling data from various sources, AI systems will be able to detect and mitigate threats that may have otherwise gone unnoticed.
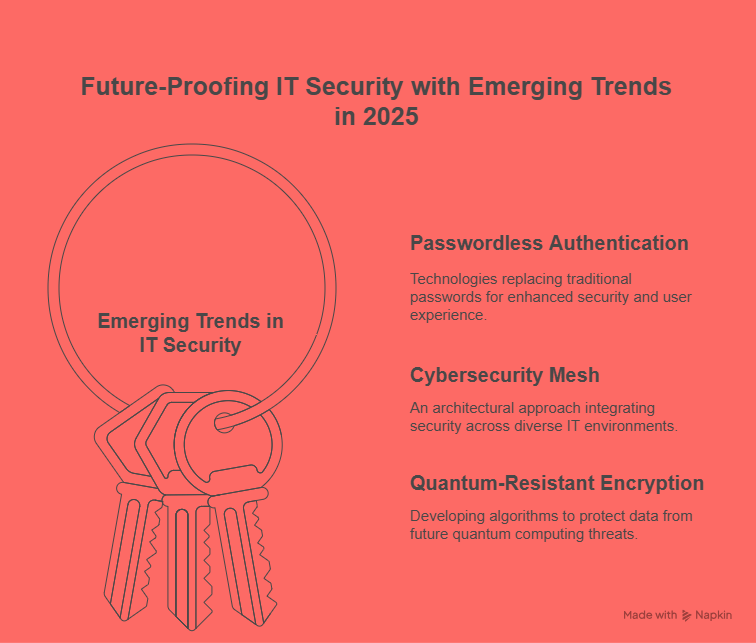
2. AI and Quantum Computing
The rise of quantum computing presents new challenges for cybersecurity. Traditional encryption methods may become obsolete as quantum computers become more powerful. AI will play a crucial role in developing new quantum-resistant encryption algorithms to protect data in the age of quantum computing.
-
Post-Quantum Cryptography: AI will be used to develop cryptographic techniques that can withstand the power of quantum computers, ensuring that data remains secure in the future.
3. AI-Integrated Cyber Defense Systems
In the future, AI will be deeply integrated into cyber defense systems, working alongside human security teams. AI systems will not replace human expertise, but they will complement and enhance security operations, automating routine tasks and providing advanced threat detection capabilities.
10 Lesser-Known Facts About AI in Security Technology
-
AI-powered security systems can predict cyberattacks based on historical data and global trends.
Source -
AI can autonomously block cyberattacks by isolating compromised systems and preventing further damage.
Source -
AI is capable of identifying deepfake videos with high accuracy, helping to prevent misinformation and fraud.
Source -
AI in surveillance systems is now being used to identify potentially dangerous behaviors in crowds.
Source -
AI-powered systems have reduced false alarm rates in security monitoring by up to 75%.
Source -
AI can track and predict the spread of ransomware attacks, helping companies prevent data loss.
Source -
AI has the ability to analyze both structured and unstructured data, giving it an edge over traditional systems.
Source -
AI’s application in fraud prevention has reduced financial losses from fraud by over 30% in some sectors.
Source -
AI-based facial recognition technology is now used in over 30% of global airports for passenger identification.
Source
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is undoubtedly a game changer in security technology. By enhancing both cybersecurity and physical security, AI offers innovative solutions to counter evolving threats and mitigate potential risks. With its ability to analyze massive datasets, predict future threats, and respond autonomously to incidents, AI is transforming the way businesses and individuals protect their data and assets.
At ACSMI, we understand the critical importance of security in healthcare. That’s why we offer Medical Scribe Certifications to ensure professionals are equipped with the skills needed to navigate the complexities of healthcare documentation with a strong emphasis on data security and privacy.
FAQs
1. How does AI improve cybersecurity?
AI enhances cybersecurity by enabling faster threat detection, automating responses, and providing predictive insights into potential vulnerabilities.
2. What is AI-powered surveillance?
AI-powered surveillance uses computer vision and deep learning to analyze live video feeds, detect threats, and flag suspicious activities automatically.
3. Can AI prevent fraud in financial systems?
Yes, AI can analyze transaction patterns, detect fraud in real time, and block suspicious transactions before they can cause harm.
4. What is quantum-resistant encryption?
Quantum-resistant encryption refers to encryption methods that are designed to withstand the computational power of quantum computers, which threaten traditional cryptographic techniques.
5. How does AI complement human security experts?
AI enhances human security efforts by automating routine tasks, providing real-time insights, and improving threat detection accuracy, but human expertise remains essential for critical decision-making.