Table of Contents
Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing fields, with businesses worldwide investing heavily in protecting their data and networks. Whether you’re an aspiring cybersecurity professional or an experienced IT expert looking to advance, you may wonder: Should I pursue a Cybersecurity Certification Without Experience or a degree? Both options have unique advantages and drawbacks, and the best choice depends on your career goals, budget, and time constraints.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the benefits of Cybersecurity Certification Without Experience and degrees, compare their career prospects, and help you decide the best path for your future.
Why Choose a Cybersecurity Degree?
A cybersecurity degree is a formal education program offered by universities and colleges. It provides an in-depth understanding of cybersecurity concepts and practical skills.
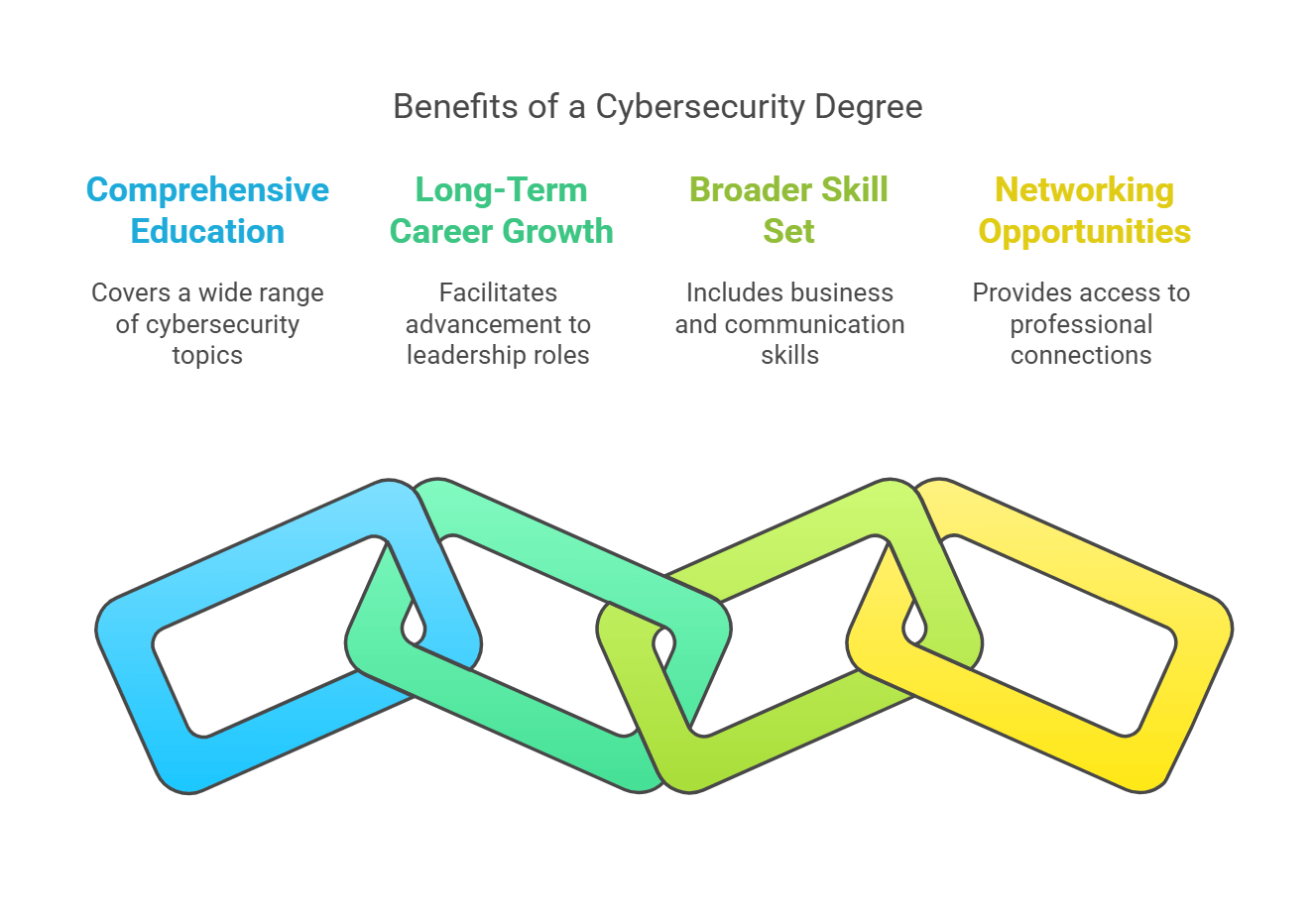
Advantages of a Cybersecurity Degree
1. Comprehensive Education
A degree covers a broad range of topics, including coding, ethical hacking, risk management, and cryptography. It provides both theoretical knowledge and practical application.
2. Long-Term Career Growth
A degree helps you advance to leadership roles in cybersecurity. Many senior positions, such as Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), require a formal education background.
3. Broader Skill Set
Unlike certifications, degrees cover additional subjects like business management, communication, and IT governance, making graduates suitable for multidisciplinary roles.
4. Networking Opportunities
Universities provide access to alumni networks, industry conferences, and internships, helping students build valuable professional connections.
Drawbacks of a Cybersecurity Degree
1. High Cost
Tuition fees for cybersecurity degrees can range from $20,000 to over $100,000, making them a significant financial investment.
2. Time Commitment
A degree program typically takes 2-4 years to complete, delaying entry into the workforce compared to certifications.
3. Delayed ROI (Return on Investment)
While degrees offer long-term career growth, it may take years to reach high salary levels and leadership roles.
Why Choose a Cybersecurity Certification?
Certifications validate your expertise in specific cybersecurity domains such as network security, ethical hacking, or cloud security. If you’re considering expanding your knowledge, it’s important to factor in the Google Cybersecurity Certification Price when planning your next steps. These certifications are ideal for professionals looking to upskill quickly.
Advantages of a Cybersecurity Certification
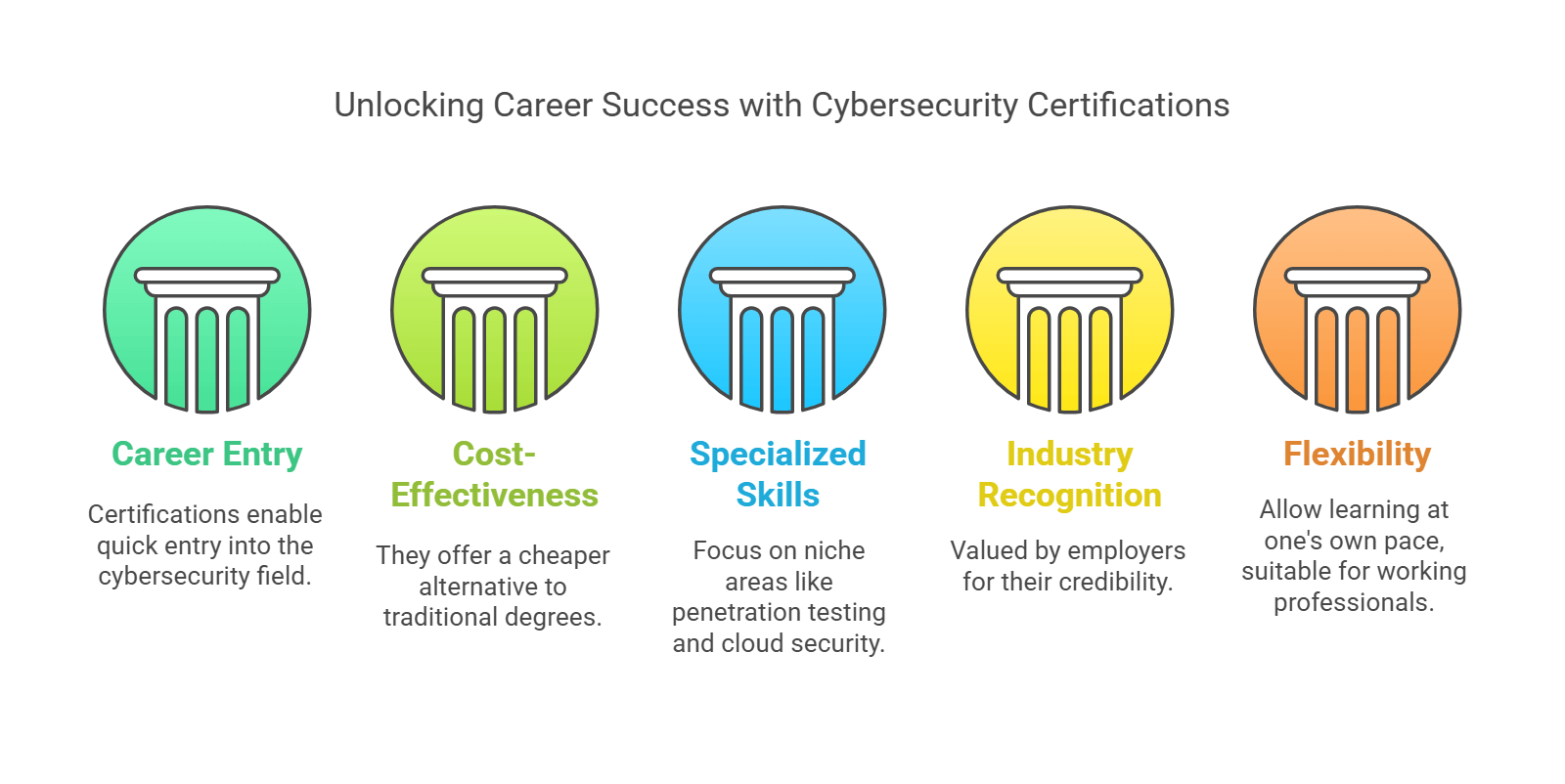
1. Faster Career Entry
Certifications can be completed in months, making them ideal for those who want to enter the cybersecurity industry quickly.
2. Cost-Effective Option
Compared to degrees, certifications are significantly cheaper, usually costing between $500 and $2,000.
3. Specialized Skills for Niche Roles
Certifications focus on specific areas like penetration testing, cloud security, or incident response, making you a specialist in those fields.
4. Industry Recognition
Many certifications, such as Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) or Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), are highly valued by employers.
5. Flexibility for Working Professionals
Online certification programs allow you to learn at your own pace while maintaining a full-time job.
6. Stay Updated with Industry Trends
Certifications evolve to keep up with the latest cybersecurity threats, tools, and best practices.
7. Increased Employability
Employers recognize certifications as proof of practical expertise, helping you stand out in job applications.
8. Continuous Learning Opportunities
Many certifications have multiple levels and require ongoing education, ensuring you remain competitive in the field.
Drawbacks of Cybersecurity Certifications
1. Limited Breadth of Knowledge
Certifications focus on specific skills but may lack the broader understanding provided by a degree.
2. Recertification Requirements
Many certifications require renewal every few years, adding to long-term costs.
3. Less Emphasis on Soft Skills
Unlike degrees, certifications do not typically include courses on leadership, teamwork, or communication.
cybersecurity Certification vs. Degree: Key Considerations
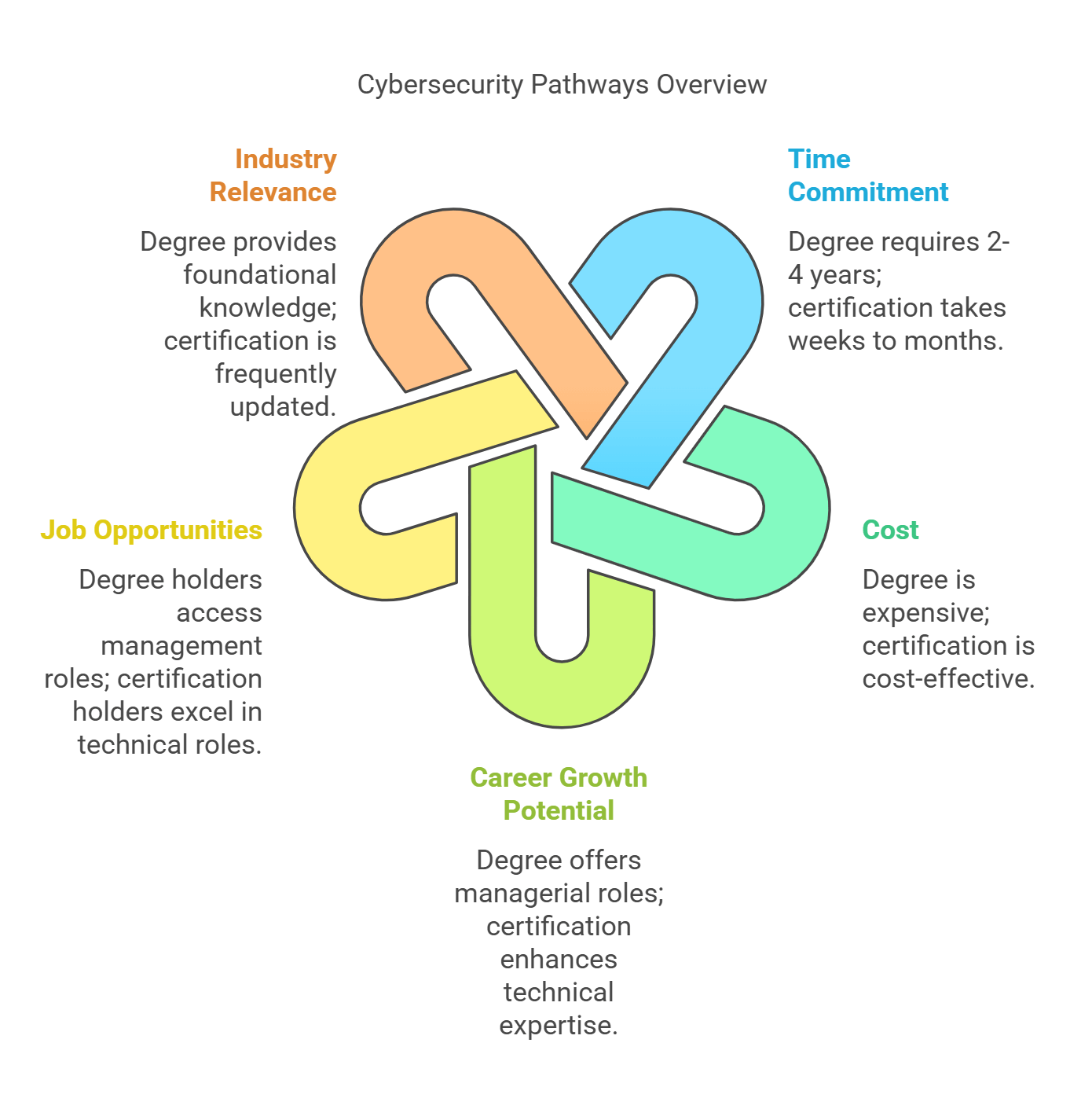
1. Time Commitment
-
Cybersecurity Degree: Pursuing a degree in cybersecurity requires a significant time investment, typically ranging from two to four years. This duration includes coursework, practical lab sessions, projects, and internships, all designed to provide students with an in-depth understanding of cybersecurity concepts. The structured learning approach helps develop theoretical knowledge along with practical application.
-
Cybersecurity Certification: Certifications are a faster alternative, often taking a few weeks to several months to complete, depending on the program’s complexity. They are ideal for professionals who want to gain specific skills quickly and enter the workforce or upskill while working a full-time job. Certifications offer flexibility, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace.
2. Cost
-
Cybersecurity Degree: Obtaining a cybersecurity degree can be expensive, with tuition fees ranging from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the institution. Additional expenses may include books, learning materials, lab fees, and accommodation if studying on campus. Many students take out loans to finance their education, which can result in long-term financial commitments.
-
Cybersecurity Certification: Certifications are a cost-effective option compared to degrees. They typically cost between $500 and $2,000, making them an affordable choice for individuals looking to gain specialized knowledge without incurring significant debt. Some employers may even cover certification costs, recognizing their value in the industry.
3. Career Growth Potential
-
Cybersecurity Degree: Holding a cybersecurity degree can significantly enhance long-term career prospects, opening doors to executive and managerial positions. Organizations often prefer degree holders for leadership roles such as Cybersecurity Manager, Security Architect, or Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). A degree provides a well-rounded education, including business and management skills, which are crucial for career advancement.
-
Cybersecurity Certification: Certifications focus on technical expertise and specialization, making them valuable for professionals aiming for hands-on roles in cybersecurity. Certifications can lead to positions such as Penetration Tester, Security Analyst, or Incident Response Specialist. While certifications alone may not guarantee a leadership role, they can complement a degree or extensive work experience to boost career growth.
4. Job Opportunities
-
Degree Holders: Graduates with a cybersecurity degree often have access to a wider range of job opportunities, particularly in management and strategy-oriented roles. Common positions include:
Cybersecurity Manager: Oversees security teams and develops cybersecurity strategies. -
Security Architect: Designs secure IT systems and infrastructure.
-
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): Leads an organization’s cybersecurity initiatives and ensures compliance.
-
Certification Holders: Professionals with cybersecurity certifications are well-suited for highly technical roles that require specific expertise. Popular job titles include:
-
Penetration Tester: Conducts ethical hacking to identify security vulnerabilities.
-
Security Analyst: Monitors security threats and protects an organization’s digital assets.
-
Incident Response Specialist: Investigates and mitigates cybersecurity breaches.
5. Industry Relevance
-
Cybersecurity Degree: A degree provides a strong foundational knowledge in cybersecurity, covering various topics such as cryptography, network security, risk management, and ethical hacking. However, technology and threats evolve rapidly, and professionals may need additional certifications to stay up to date with the latest trends and security practices.
-
Cybersecurity Certification: Certifications are designed to be industry-relevant and updated frequently, ensuring that professionals remain knowledgeable about current cybersecurity challenges. Certifications such as Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), CompTIA Security+, and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) are widely recognized and demonstrate expertise in specific domains of cybersecurity.
Conclusion
Choosing between a cybersecurity certification and a degree depends on your career goals, budget, and time availability. Certifications provide quick, affordable, and targeted skills, making them ideal for technical roles. Degrees offer a comprehensive foundation, networking opportunities, and pathways to leadership roles.
For the best career growth, consider a combination of both earning certifications to gain specialized skills while pursuing a degree for long-term advancement. Whichever path you choose, cybersecurity is a rewarding and high-demand career field with numerous opportunities for growth.
Understanding the differences between certifications and degrees is essential when planning your cybersecurity career. ACSMI Certification offers a specialized credential that can help you focus on specific areas within the field. Use this table as a guide to identify which path aligns best with your goals and resources, ensuring you make the choice that’s right for you.
FAQs: Cybersecurity Certification vs. Degree
1. Is a cybersecurity degree better than a certification?
Both have their advantages. A degree provides a broader foundation and leadership skills, while certifications offer specialized, job-ready skills.
2. Can I start with a certification and pursue a degree later?
Yes! Many professionals earn certifications first to gain experience before investing in a degree.
3. Are certifications enough to secure a job?
Yes, especially for entry-level roles. Many companies hire candidates with certifications and hands-on experience.
4. Do cybersecurity certifications expire?
Some certifications require renewal through continuing education or exams.
5. Can I combine both a degree and certifications?
Absolutely! Having both a degree and certifications can maximize your career opportunities.
6. What are the most recognized cybersecurity certifications?
Some top certifications include CISSP, CEH, CompTIA Security+, and CISM.
7. How do employers view cybersecurity certifications vs. degrees?
Employers value both but often prioritize certifications for technical roles and degrees for leadership positions.
8. Which path is better for a career switch into cybersecurity?
Certifications are the best way to switch careers quickly, as they provide industry-recognized skills in a shorter time frame.

Leave a Reply