In today's increasingly regulated world, organizations face constant pressure to comply with a variety of laws and industry-specific regulations. Security management plays a crucial role in ensuring that businesses meet these compliance and legal requirements, protecting both the organization and its clients from legal consequences, financial penalties, and reputational damage.
From data protection laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to industry-specific regulations like HIPAA in healthcare and PCI DSS for payment card data, effective security management is essential for meeting legal obligations and minimizing risk. In this blog, we’ll explore how security management affects compliance, why it’s critical for legal protection, and how businesses can implement a security management system that supports both security and regulatory requirements.
For more details on how security management impacts broader business practices, check out our blog on what is security management.
1. Understanding the Role of Security Management in Compliance
In today's complex regulatory environment, security management plays a critical role in ensuring organizations remain compliant with industry standards, legal requirements, and best practices. It forms the foundation of any robust compliance program, going far beyond simply following a checklist of rules. Instead, security management involves a proactive, strategic approach to safeguarding information, mitigating risk, and building a culture of accountability and awareness across the organization.
Compliance is often associated with adhering to specific regulations—such as HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI-DSS—but at its core, it’s about more than just meeting baseline requirements. It's about demonstrating a consistent commitment to protecting data, ensuring operational integrity, and maintaining trust with customers, partners, and regulators. That’s where security management comes in.
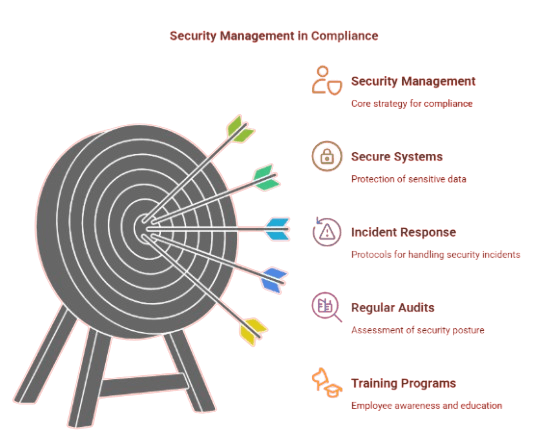
A well-structured security management system ensures that an organization has:
-
Secure systems for managing sensitive data: Protecting customer and organizational data is non-negotiable. Security management involves implementing strong access controls, data encryption, firewalls, and secure storage practices. These measures help prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of data breaches.
-
Protocols in place for incident response: Despite best efforts, incidents can still occur. A key element of security management is having a clear and effective incident response plan. This plan outlines how the organization will detect, respond to, recover from, and report security incidents—minimizing damage and ensuring timely remediation.
-
Regular audits to ensure compliance: Auditing and monitoring processes help organizations assess their security posture and compliance status. Internal and external audits identify gaps, vulnerabilities, or deviations from policy, enabling prompt corrective action. Security management ensures these audits are conducted regularly and thoroughly.
-
Training and awareness programs for employees: Human error is one of the leading causes of security breaches. Security management emphasizes the importance of training employees to recognize threats like phishing, handle sensitive data responsibly, and understand the consequences of non-compliance. Regular awareness programs keep security top-of-mind.
Beyond these key components, effective security management also includes risk assessments, the development of security policies and procedures, and continuous improvement initiatives. It’s a dynamic, ongoing process that evolves with the changing threat landscape and regulatory requirements.
By creating and maintaining a comprehensive security management system, organizations position themselves to remain resilient in the face of both internal and external challenges. More importantly, they minimize the risk of non-compliance, which can lead to severe penalties, reputational harm, and operational disruption.
In essence, security management is not just an IT or compliance responsibility—it’s a business-wide priority. When integrated into daily operations, it supports a culture of security, fosters transparency, and builds confidence among stakeholders. Whether you’re a startup or a large enterprise, investing in strong security management practices is essential for long-term success in a compliance-driven world.
2. Key Regulations and Standards That Impact Security Management
There are several laws and industry standards that directly impact security management. These regulations ensure that businesses protect sensitive data and maintain security standards to prevent data breaches and other security incidents.
Key regulations include:
-
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): A regulation in the European Union that focuses on data protection and privacy. It requires businesses to implement specific security measures to protect personal data and provides individuals with greater control over their personal information.
-
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): This US law mandates that healthcare organizations protect the privacy and security of health information. Healthcare entities must implement physical, technical, and administrative security measures to safeguard patient data.
-
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): A set of security standards designed to protect card payment data. Organizations that store, process, or transmit credit card information must adhere to PCI DSS requirements.
-
Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA): This U.S. law requires federal agencies and contractors to secure information systems and data against cyber threats. It mandates regular risk assessments and security controls.
3. The Connection Between Security Management and Risk Mitigation
One of the primary goals of security management is to minimize risks—whether they involve data breaches, cyberattacks, insider threats, or physical security breaches. Effective security management aligns risk mitigation strategies with legal requirements, ensuring that companies:
-
Identify risks that could lead to non-compliance, such as outdated software, weak access controls, or inadequate employee training.
-
Implement proactive controls to address those risks, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and firewalls.
-
Monitor systems continuously to detect vulnerabilities and security threats that could violate compliance standards.
-
Respond quickly to security incidents, minimizing the damage and ensuring that regulatory requirements for breach notification are met.
By managing risk effectively, organizations can stay compliant with laws and avoid costly penalties.
4. The Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to meet security management and legal requirements can result in significant negative consequences for organizations, both in the short and long term. Non-compliance not only affects a company’s financial standing but also its reputation, legal standing, and ability to function efficiently. Understanding these risks is essential for businesses that aim to maintain trust, avoid penalties, and ensure operational continuity.
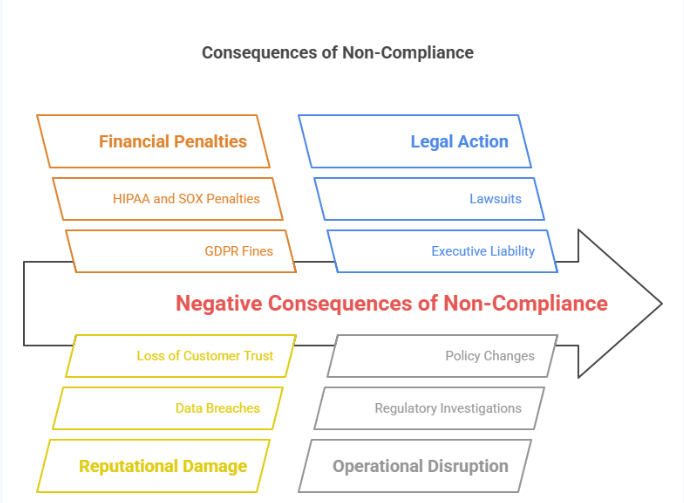
Financial Penalties
One of the most immediate and tangible consequences of non-compliance is the financial impact. Regulatory bodies across various industries have established strict data protection and security standards, and they have the authority to enforce compliance through substantial fines. For instance, under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, organizations found guilty of non-compliance can face penalties of up to 4% of their global annual revenue or €20 million—whichever is higher. In the U.S., regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) also impose considerable fines for security and reporting violations. These financial repercussions can be especially devastating for small to medium-sized enterprises, often threatening their very survival.
Reputational Damage
Non-compliance often results in data breaches, unauthorized access, or misuse of sensitive information, all of which can erode a company’s reputation. Trust is a critical factor in customer relationships, and once lost, it is incredibly difficult to regain. When an organization is publicly identified as being negligent in protecting user data, customers may choose to take their business elsewhere. Additionally, media coverage of compliance failures spreads quickly, further amplifying the damage. This kind of reputational harm can also impact partnerships, investments, and long-term growth opportunities, as stakeholders may view the business as a liability.
Legal Action
Another serious risk tied to non-compliance is legal liability. Companies that fail to follow established laws and regulations may face lawsuits from consumers, employees, or regulatory agencies. These lawsuits can result in lengthy court proceedings, expensive settlements, and even more fines. Moreover, legal battles can divert a company’s resources and focus away from core operations, adding to the overall cost of non-compliance. In extreme cases, executives or board members may be held personally liable, further complicating the legal implications.
Operational Disruption
Non-compliance can also disrupt an organization’s operations. Regulatory investigations and audits often require significant time and resource allocation, and sanctions may force companies to halt certain business activities until issues are resolved. This can cause project delays, reduced productivity, and lost revenue. Furthermore, businesses may need to implement rapid changes to policies, infrastructure, or staff training programs to meet compliance standards, often at a high cost and under tight deadlines.
5. How to Ensure Your Security Management System Supports Compliance
Maintaining compliance with ever-evolving legal and regulatory standards is a critical responsibility for businesses in today’s digital landscape. An effective security management system (SMS) should not only defend against cyber threats but also ensure that all compliance obligations are consistently met. Here’s how organizations can structure their SMS to support and strengthen compliance efforts:
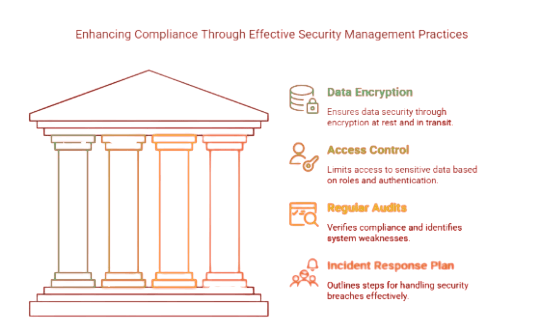
1. Data Encryption
Data encryption is a foundational component of any compliance-oriented security system. To protect sensitive information, businesses must encrypt data both at rest (stored data) and in transit (data being transferred). This ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized users, it remains unreadable and secure. Many regulations—such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS—mandate encryption to protect personally identifiable information (PII) and other critical data. Ensuring proper key management and using strong, industry-standard encryption protocols can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches.
2. Access Control
Implementing robust access control measures is essential for maintaining compliance. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) allows organizations to assign permissions based on an individual's job role. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access by limiting exposure to sensitive data and systems only to those who need it. RBAC supports the principle of least privilege, which is a key requirement in many compliance frameworks. In addition, integrating multi-factor authentication (MFA) can further enhance access security and satisfy regulatory expectations.
3. Regular Audits
Compliance isn’t a one-time event—it requires ongoing verification. Regular internal and external audits help organizations assess whether their current security practices align with applicable laws and standards. Audits also help identify gaps or weaknesses in the system, providing an opportunity to make necessary adjustments before they result in violations or penalties. Comprehensive documentation of audit findings and remedial actions can serve as proof of due diligence in the event of an investigation or legal inquiry.
4. Incident Response Plan
A well-structured incident response plan is crucial for timely and effective action during a security breach or cyber incident. The plan should outline clear steps for identifying, reporting, containing, and recovering from security events. It should also include specific roles and responsibilities, communication strategies, and post-incident evaluation processes. Regulatory bodies often require evidence that a company can respond effectively to incidents. By documenting and testing your response plan regularly, you can meet these obligations and reduce the potential impact of security incidents.
5. Employee Training
Human error is one of the leading causes of data breaches and compliance failures. Regular security training ensures that employees understand their responsibilities and are familiar with best practices for protecting sensitive data. Training should include how to recognize phishing attempts, report suspicious activities, handle data securely, and comply with relevant regulations. A well-informed workforce is a company’s first line of defense in maintaining both security and compliance.
By proactively managing security and adhering to these best practices, organizations can not only stay compliant but also create a culture of security that extends across the entire organization.
Conclusion
Security management is the cornerstone of any successful compliance strategy. By integrating security controls into your organization's operations, you can ensure that legal requirements are met, reduce risks, and avoid costly penalties. Organizations that embrace security management are better equipped to face evolving threats while staying compliant with industry regulations.
At ACSMI, we understand the importance of compliance in security management. We offer medical coding and billing certifications, ensuring professionals have the expertise to comply with industry regulations and safeguard sensitive data. We also provide a variety of snacks online to fuel your team as they maintain and improve your security systems.
FAQs
How does security management support compliance?
Security management helps organizations implement necessary security controls, monitor systems for threats, and ensure that compliance standards are met, reducing the risk of legal consequences.
What are the key regulations that impact security management?
Key regulations include GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and FISMA, each of which mandates specific security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure privacy.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with security regulations?
Non-compliance can lead to financial penalties, reputational damage, legal action, and operational disruption, all of which can harm an organization.
How can I make sure my security management system is compliant with regulations?
Implement data encryption, access controls, conduct regular audits, and ensure employee training on security best practices and regulatory requirements.
Why is employee training important for compliance?
Employees are often the first line of defense. Regular training ensures they understand how to follow security protocols and avoid actions that could lead to non-compliance or security breaches.

Leave a Reply