In today’s digital age, businesses face constant threats to their data and infrastructure. With cyberattacks becoming more sophisticated, building a robust IT security strategy is crucial for protecting your organization's sensitive information. A solid strategy helps you mitigate risks, comply with regulations, and respond effectively to cyber threats. In 2025, cyberattacks are expected to evolve, requiring companies to stay ahead of emerging risks through Technology Security Certifications and proactive measures.
This blog will guide you through the process of creating an effective IT security strategy, from identifying your risks and defining security goals to implementing cutting-edge technologies and maintaining an ongoing security posture.
What is Information Technology Security?
Information Technology Security refers to the policies, procedures, and tools designed to protect data, networks, and devices from cyber threats. Its goal is to preserve the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization’s data. Given the evolving nature of digital threats, IT security strategies are crucial to ensuring business continuity and protecting against unauthorized access, theft, and destruction of sensitive information.
A robust IT security strategy is a combination of several key elements:
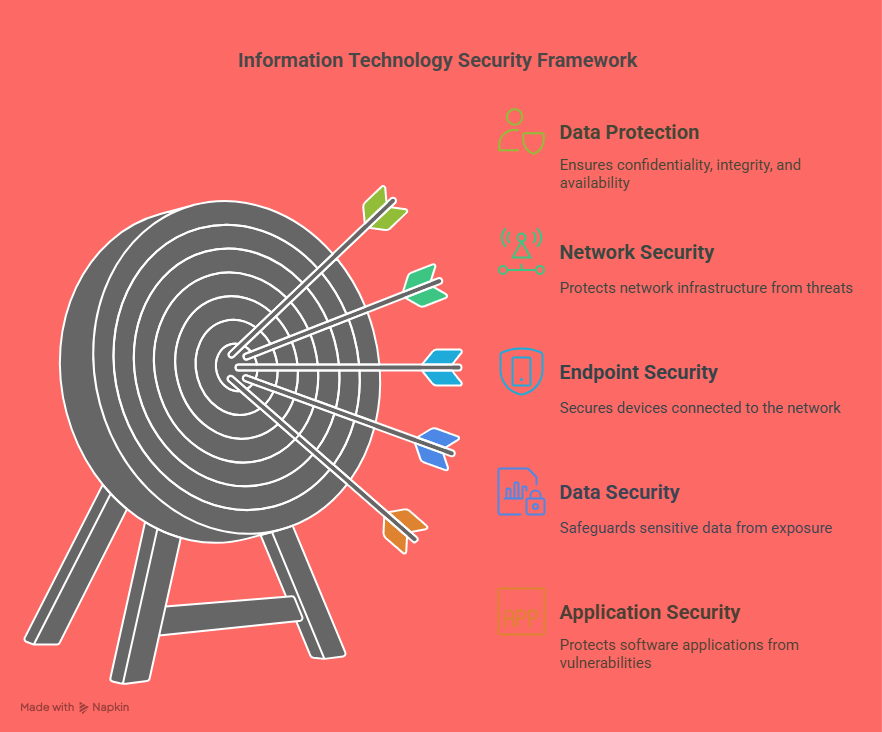
-
Network Security: Protecting the network infrastructure from unauthorized access and attacks.
-
Endpoint Security: Ensuring devices connected to the network (laptops, mobile phones, etc.) are secure.
-
Data Security: Safeguarding sensitive data from exposure, theft, or corruption.
-
Application Security: Protecting software applications from vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
-
Identity and Access Management: Ensuring only authorized individuals can access certain systems and data.
Step 1: Understand the Security Landscape
The first step in building a robust IT security strategy is understanding the threat landscape your business faces. Threats in 2025 are evolving, and cybercriminals are increasingly using sophisticated methods to bypass traditional security systems. By understanding the risks, you can better prepare your business for the challenges ahead.
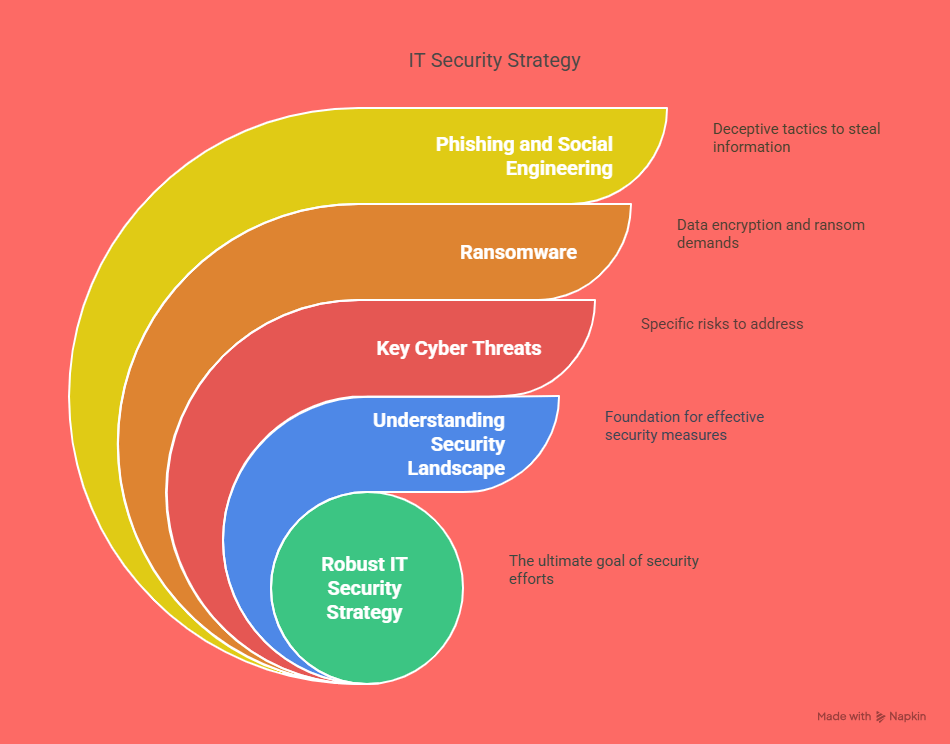
Key Cyber Threats to Watch in 2025
-
Ransomware: Attackers encrypt your data and demand a ransom to release it. This type of attack is particularly dangerous for small and medium-sized businesses.
-
Phishing and Social Engineering: Cybercriminals trick employees into revealing sensitive information through fake emails or websites.
-
Insider Threats: Employees or contractors may unintentionally or maliciously compromise security, putting your business at risk.
-
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): These long-term, targeted attacks typically aim to steal sensitive data over time, often remaining undetected.
-
Cloud Vulnerabilities: As more businesses move to the cloud, the risk of poor configuration or insufficient security measures increases.
Understanding these risks allows you to identify your business’s most valuable assets and prioritize your security efforts accordingly.
Step 2: Define Your Security Goals
Once you've understood the landscape, it's time to set clear and measurable security goals. Your security goals should align with your business objectives and be tailored to the specific risks your business faces. The goal of any IT security strategy is to protect critical assets, prevent breaches, ensure compliance, and reduce downtime in case of an attack.
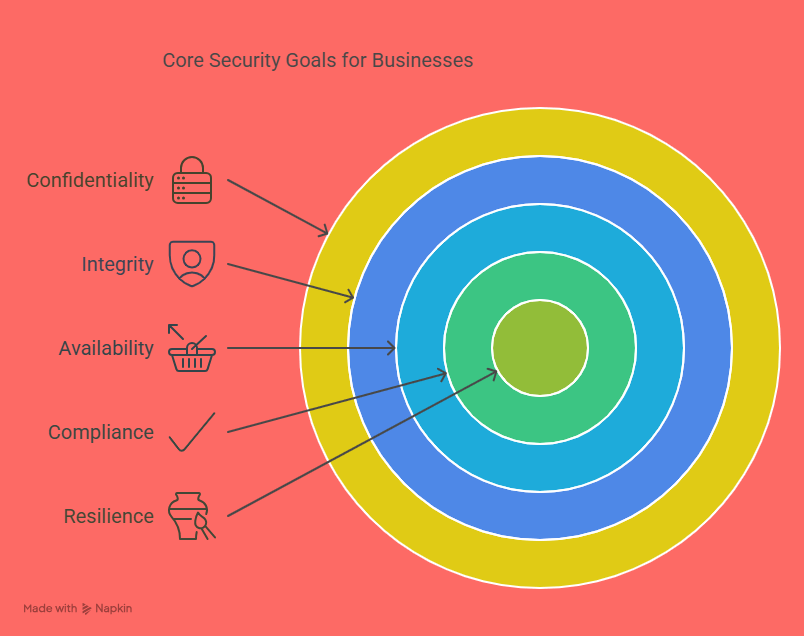
Core Security Goals for Any Business
-
Confidentiality: Ensure that sensitive data, such as customer information, financial records, and intellectual property, is only accessible to authorized personnel.
-
Integrity: Protect the integrity of your data by preventing unauthorized modifications or corruption.
-
Availability: Ensure that critical systems and data are always available and accessible to authorized users, even in the face of a cyberattack.
-
Compliance: Ensure your security practices comply with industry-specific regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS).
-
Resilience: Build systems and processes that can quickly recover from an attack, minimizing the disruption to business operations.
By setting these goals, you can create a structured approach to IT security that directly supports your business’s needs.
Step 3: Develop a Comprehensive Risk Management Plan
Risk management is the cornerstone of any IT security strategy. A risk management plan outlines how to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. This plan will also define your organization’s approach to incidents, ensuring that your team can respond quickly and effectively to minimize damage during a breach. The Evolution of Security Technology plays a vital role in shaping these plans, allowing organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats and adopt more efficient protective measures.
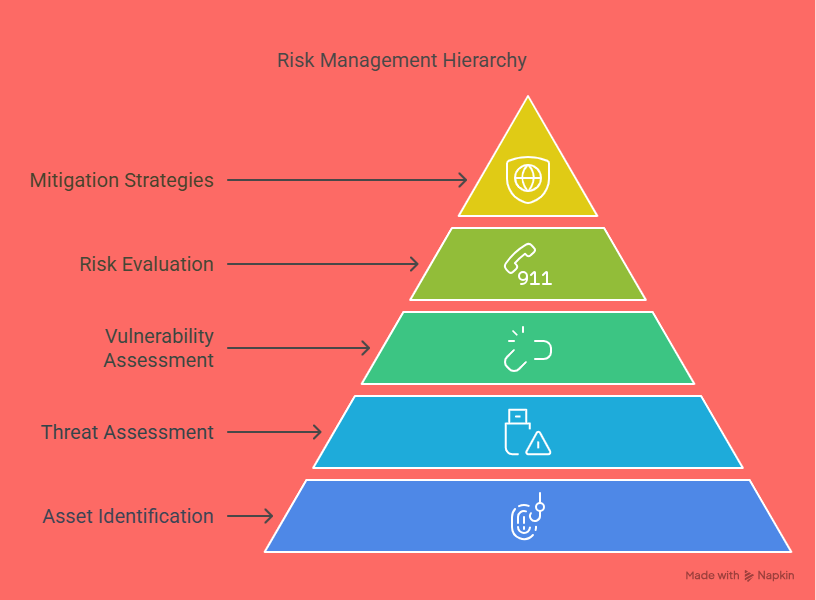
Components of a Risk Management Plan
-
Asset Identification: List your digital assets, including hardware, software, data, and intellectual property. This will help you determine which assets need the most protection.
-
Threat Assessment: Identify potential threats to your assets, such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or employee negligence.
-
Vulnerability Assessment: Identify weaknesses in your infrastructure, such as outdated software, unsecured endpoints, or lack of employee training.
-
Risk Evaluation: For each identified risk, assess its potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. Prioritize these risks to allocate resources effectively.
-
Mitigation Strategies: Develop strategies to minimize the risks, such as implementing encryption, firewall protection, or intrusion detection systems.
This comprehensive approach ensures that all aspects of your business are considered, reducing vulnerabilities and improving your overall security posture.
Step 4: Implement Security Measures
Once your risk management plan is in place, it's time to implement security measures to protect your assets. The specific measures you choose should align with your risk assessment and security goals. In 2025, businesses must be proactive in deploying both traditional security solutions and emerging technologies to stay ahead of cyber threats.
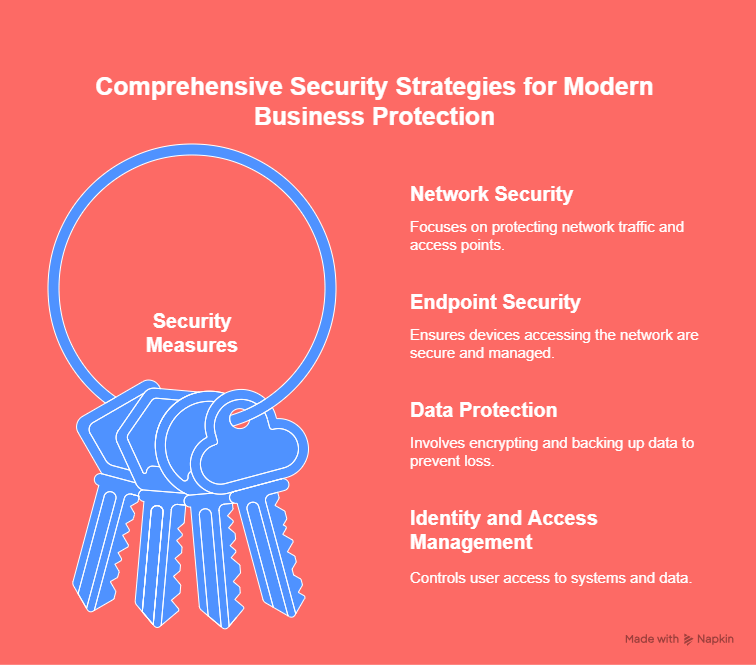
Key Security Measures to Implement
-
Network Security
-
Firewalls: A first line of defense that filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules.
-
Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and automatically block potential threats.
-
Virtual Private Network (VPN): VPNs provide secure remote access to your business network by encrypting data transmitted over the internet.
-
-
Endpoint Security
-
Antivirus Software: Protect endpoints (laptops, mobile devices) from malware and viruses.
-
Mobile Device Management (MDM): MDM solutions ensure that all mobile devices accessing your network are secured with encryption, password protection, and remote wipe capabilities.
-
-
Data Protection
-
Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit (when moving between systems) and at rest (when stored on servers or devices) to protect it from unauthorized access.
-
Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up your critical data and test recovery processes to ensure data can be restored in case of a disaster or attack.
-
-
Identity and Access Management
-
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using more than just a password.
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC ensures that users only have access to the systems and data necessary for their role.
-
Step 5: Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training
Humans are often the weakest link in a business’s security defense. Employees may inadvertently fall for phishing emails or neglect basic security practices, creating vulnerabilities within your organization. Regular security awareness training ensures that your employees understand the risks and know how to prevent security breaches.
Key Training Areas
-
Phishing and Social Engineering: Teach employees how to recognize phishing emails and social engineering tactics used by cybercriminals to steal sensitive information.
-
Password Management: Encourage strong password policies and educate employees on the importance of using unique passwords and enabling MFA.
-
Secure File Sharing: Train employees on how to securely share files, using encrypted methods and trusted file-sharing platforms.
-
Reporting Suspicious Activity: Ensure employees know how to report potential security issues, such as strange emails or suspicious network activity.
Security awareness training should be an ongoing process, with quarterly refreshers and simulated phishing tests to assess employee readiness.
Step 6: Monitor, Evaluate, and Improve Security
In 2025, cyber threats evolve at a rapid pace. Your IT security strategy must be dynamic and adaptable to keep up with emerging risks. Continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential to maintaining a strong security posture.
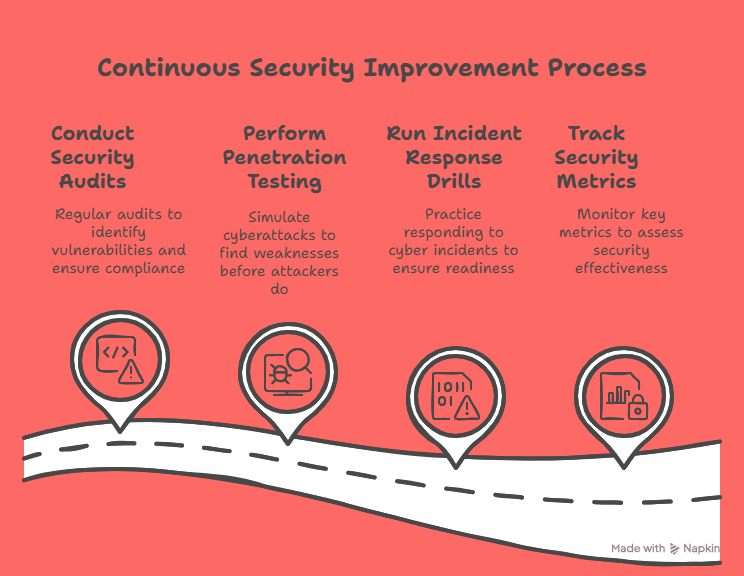
Key Actions for Continuous Improvement
-
Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities, ensure compliance, and assess the effectiveness of your security measures.
-
Penetration Testing: Hire ethical hackers to simulate cyberattacks and identify weaknesses in your infrastructure before malicious attackers can exploit them.
-
Incident Response Drills: Run incident response drills to ensure your team can act quickly and efficiently in the event of a real attack.
-
Security Metrics: Track key security metrics such as threat detection rates, incident response times, and the number of vulnerabilities patched.
By continually evaluating and updating your security measures, you can ensure that your business remains protected from the latest cyber threats.
10 Lesser-Known Facts About IT Security
-
AI and machine learning are being integrated into firewalls to detect and stop advanced threats.
Source -
60% of data breaches in 2025 will involve insider threats, making employee training essential.
Source -
Zero-day vulnerabilities are responsible for 30% of attacks in 2025.
Source -
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) reduces the risk of account takeovers by 99.9%.
Source -
80% of all cyberattacks exploit known vulnerabilities, many of which are avoidable by patching systems.
Source -
Data loss costs businesses an average of $3.9 million annually.
Source -
Phishing attacks are the most common way for hackers to gain access to corporate networks.
Source -
The average time to identify a data breach is 206 days.
Source -
By 2025, over 80% of businesses will use cloud security platforms for risk management.
Source -
Small businesses are the target of 43% of cyberattacks, despite often having fewer resources for security.
Source
Conclusion
Building a robust IT security strategy is critical to protecting your business in the digital age. By understanding the risks, setting clear goals, and implementing the right technologies and practices, you can safeguard your company’s assets and reduce the risk of a costly data breach.
At ACMSI, we understand the importance of secure systems and data, especially in healthcare. That’s why we offer Medical Scribe Certifications, equipping professionals with the skills needed to protect sensitive medical information securely.
FAQs
1. What is a risk assessment in IT security?
A risk assessment identifies potential vulnerabilities and threats to your organization’s data and systems, helping prioritize security measures.
2. How often should a business update its IT security strategy?
IT security strategies should be reviewed and updated annually or whenever there is a significant change to your systems, infrastructure, or business operations.
3. What is multi-factor authentication (MFA)?
MFA is a security process that requires users to provide two or more verification methods—such as a password and a one-time code—before gaining access to systems.
4. Why is employee training essential for IT security?
Employees often unknowingly become the target of cyberattacks. Regular training helps them recognize threats like phishing and adopt secure practices.
5. How can AI enhance IT security?
AI enhances IT security by enabling predictive threat detection, automating incident responses, and continuously learning from new data to stay ahead of cybercriminals.

Leave a Reply