Cybersecurity is one of the most critical areas of expertise in today’s rapidly advancing digital world. With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals has surged. Whether you’re new to the field or already working in it, obtaining cybersecurity certifications can provide a competitive edge, enhance career prospects, and keep you updated with the latest industry trends. In this blog, we’ll explore the numerous benefits of pursuing cybersecurity certifications.
Related Blog: Top Cyber Security Certifications
Benefits of Cyber Security
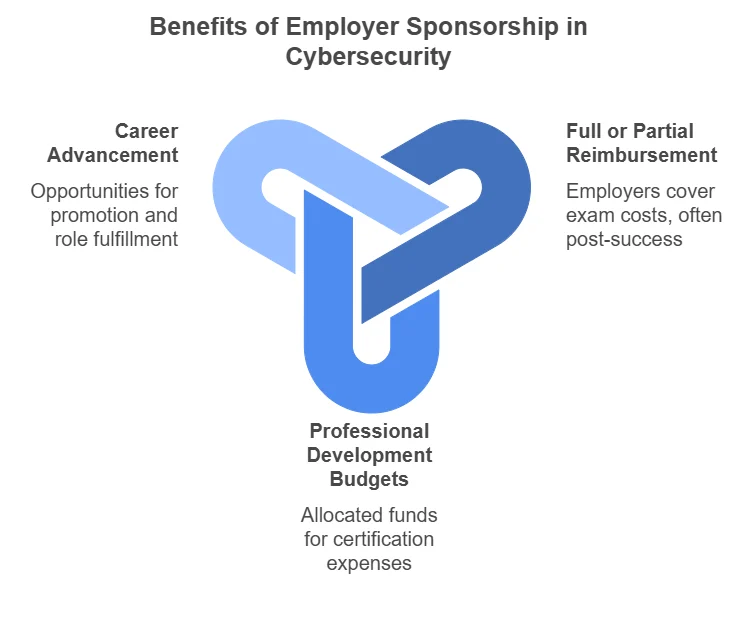
Career Advancement
Cybersecurity certifications are powerful tools for career advancement. By gaining certifications, you prove your knowledge and commitment to the field, which can lead to a range of career benefits. Here’s how:
- Promotions: Certifications signal to employers that you are prepared for more responsibility and leadership roles. With a certification, you demonstrate that you have the skills and expertise to take on more complex tasks and higher-level positions, making you an ideal candidate for promotions.
- Salary Increases: Cybersecurity certifications are often linked to higher earning potential. Studies show that certified professionals can earn more than their non-certified peers. For example, certified professionals often qualify for roles that offer higher salaries due to their specialized knowledge and skills.
- Greater Job Security: In an ever-changing and high-demand field like cybersecurity, certifications provide an extra layer of job security. By proving that you have up-to-date skills, you make yourself invaluable to your employer, reducing the chances of being laid off. Employers are more likely to retain professionals who bring high levels of expertise to the organization.

Marketability
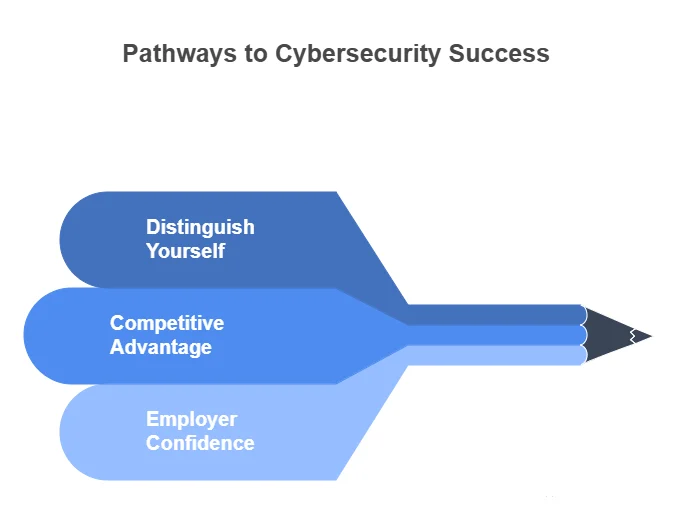
The cybersecurity job market is highly competitive. There are thousands of skilled professionals vying for top positions, and a certification can make you stand out. Here’s how certifications enhance your marketability:
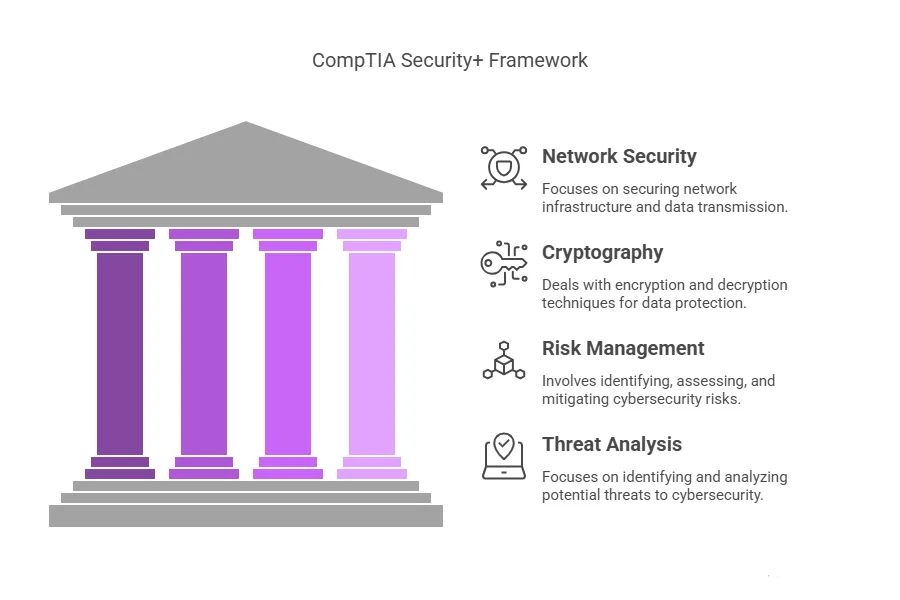
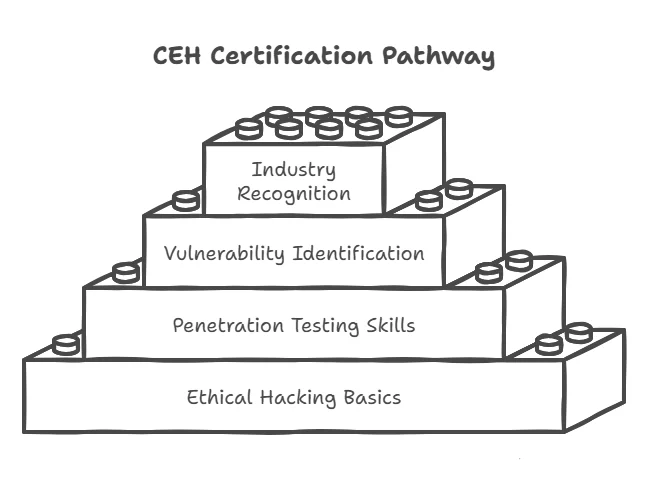
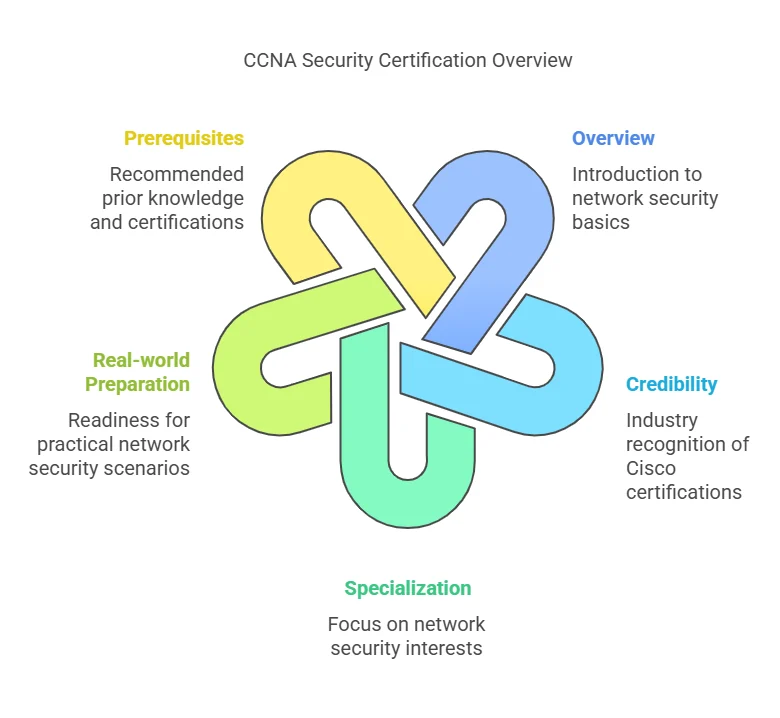
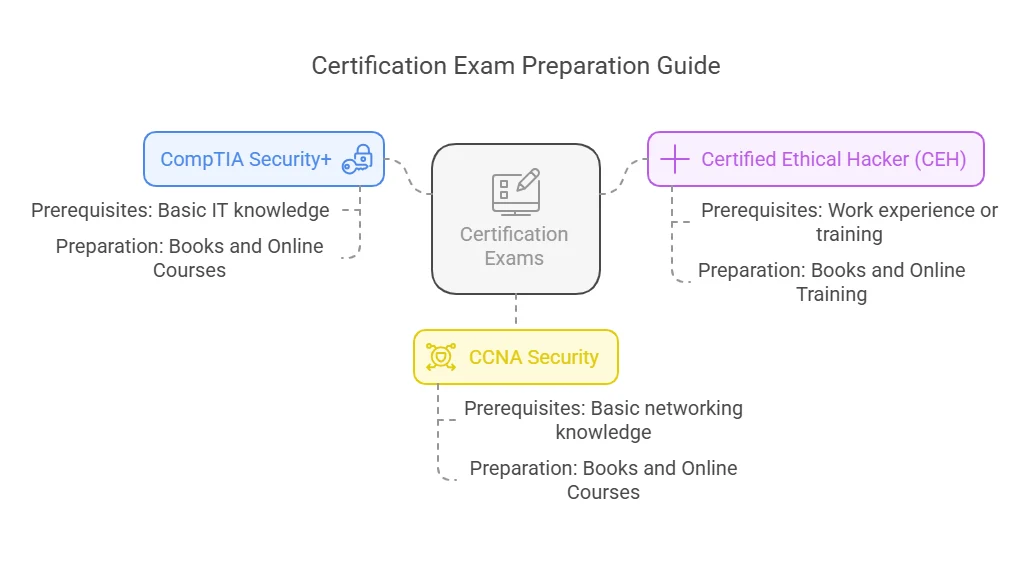
- Distinguish Yourself: Certifications like CISSP, CEH, or CompTIA Security+ are recognized globally and serve as a testament to your knowledge and dedication. They highlight your credibility in the eyes of recruiters and employers, giving you an edge over other applicants without certifications.
- Competitive Advantage: Certifications give you an advantage in a saturated job market. When a company is looking to hire for a cybersecurity role, certified candidates are often prioritized because they’ve already demonstrated expertise in critical areas.
- Employer Confidence: Hiring a certified professional gives employers confidence that the individual possesses the technical skills needed to protect their organization from cyber threats. This is why many companies explicitly request specific certifications in their job postings.
Related Blog: Cyber Security Certifications for Beginners
Skill Validation
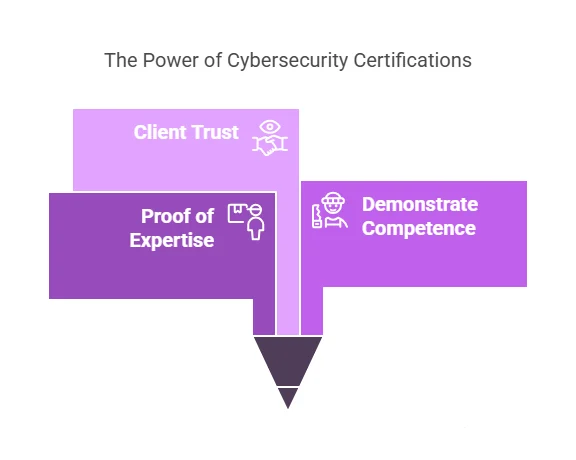
One of the most valuable aspects of cybersecurity certifications is that they validate your expertise. Certifications are a clear and objective way for employers and clients to assess your competency. Here’s why:
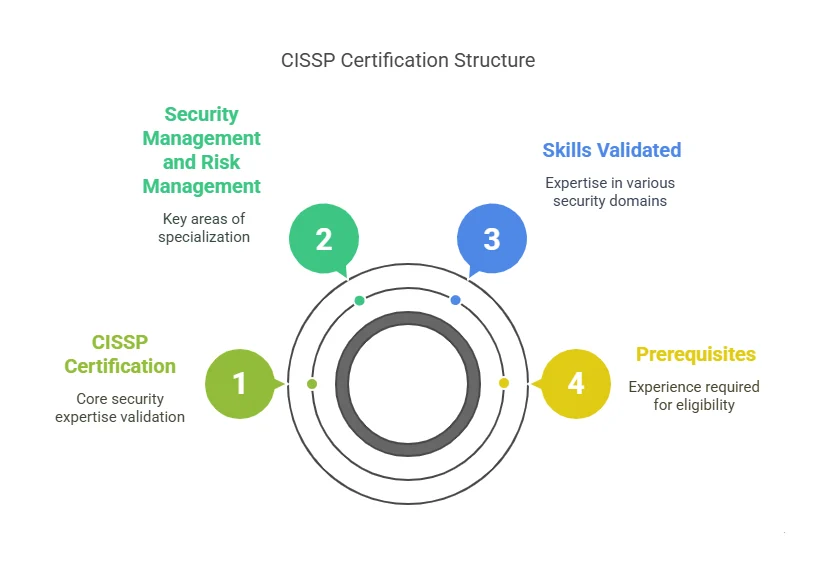
- Proof of Expertise: Certifications such as CISSP or Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) validate that you have a solid understanding of cybersecurity principles, practices, and technologies. They are often used as a benchmark to gauge a candidate’s knowledge.
- Demonstrate Competence: Having a certification proves that you are competent in the key areas of cybersecurity, such as risk management, threat analysis, and security protocols. It reassures employers that you have the necessary skills to manage and mitigate security risks effectively.
- Client Trust: For consultants or those in freelance roles, certifications can help build trust with potential clients. Clients are more likely to trust professionals with certifications because they know these individuals have undergone rigorous training and testing.
Networking Opportunities
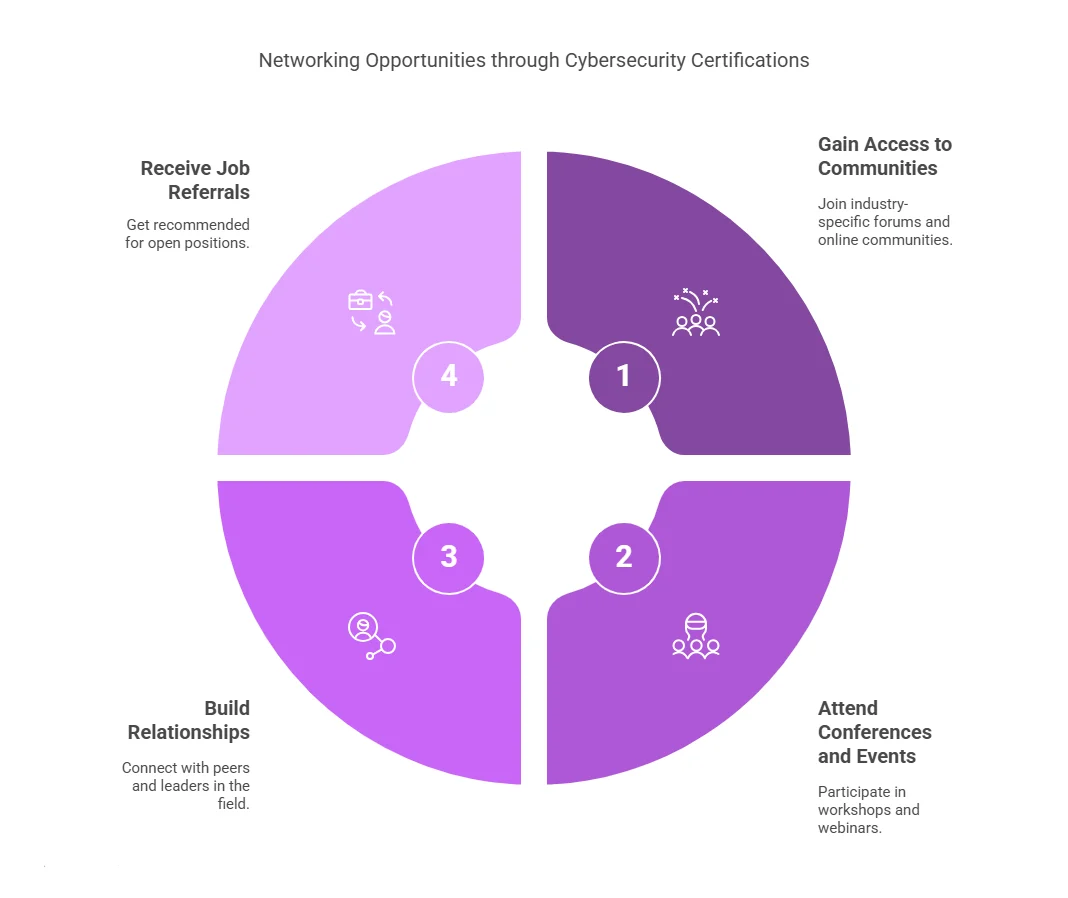
Cybersecurity certifications can open doors to various networking opportunities. Through your certification, you gain access to exclusive professional communities, events, and conferences. Here’s how:
- Access to Communities: Certifications often provide access to industry-specific forums and online communities. For example, as a Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), you can join the EC-Council community, where professionals share knowledge and collaborate on projects.
- Conferences and Events: Many certification bodies host conferences, workshops, and webinars. These events bring together cybersecurity professionals, offering opportunities to exchange ideas, learn from experts, and build relationships. Networking with peers and leaders in the field can lead to career opportunities, collaborations, and mentorship.
- Job Referrals: Networking with other certified professionals can also lead to job referrals. When you become part of a certification community, you increase your visibility within the industry, and other professionals may recommend you for open positions or consulting gigs.
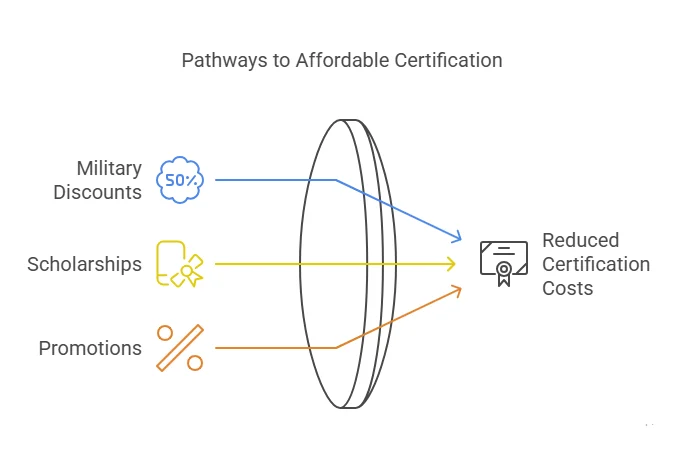
Related Blog: Cost of Cybersecurity Certifications
Access to Better Job Opportunities
One of the most tangible benefits of cybersecurity certifications is the access to better job opportunities. Many roles in cybersecurity, particularly in leadership or consulting, require specific certifications. Here’s how certifications provide access to exclusive roles:
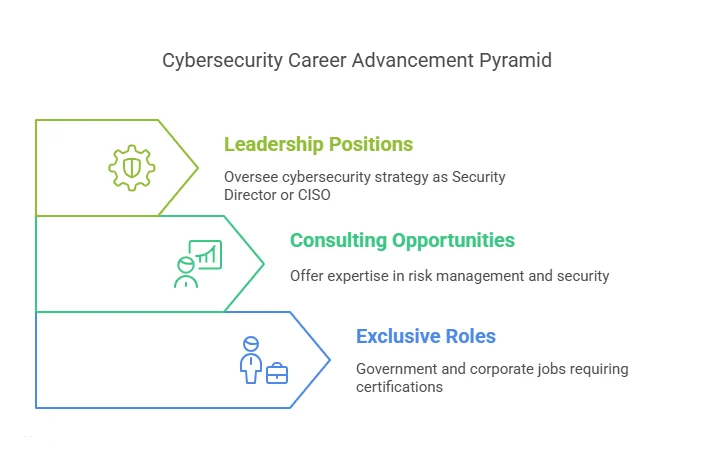
- Exclusive Roles: Some job positions, especially those in government and large corporations, are only available to individuals who hold specific certifications. For instance, government contracts or positions in cybersecurity often require CISSP certification.
- Consulting Opportunities: Cybersecurity certifications can unlock doors to consulting opportunities. As a certified professional, you can offer services to organizations looking for expertise in areas such as risk management, network security, or ethical hacking.
- Leadership Positions: Many leadership roles in cybersecurity, such as Security Director or Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), often require advanced certifications. These roles involve overseeing a company’s entire cybersecurity strategy, and employers prefer candidates with proven knowledge and experience through certifications.
Staying Current with Industry Trends
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving with new threats, tools, and technologies. Certifications ensure that you stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends and advancements. Here’s why it’s important:
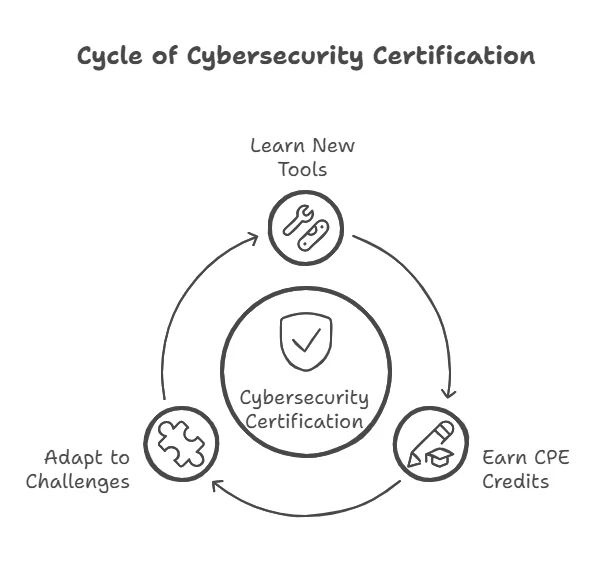
- Latest Tools and Technologies: As new cybersecurity tools and technologies emerge, certification programs incorporate them into their curriculum. For example, the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) certification keeps professionals updated on cloud security practices, an area of growing importance in cybersecurity.
- Ongoing Learning: Many certifications, such as CISSP, require professionals to earn Continuing Professional Education (CPE) credits to maintain their credentials. This encourages continuous learning, ensuring that certified professionals remain experts in the field and are prepared to handle emerging threats.
- Adaptation to New Challenges: Cybersecurity threats are constantly changing. A certification can help you learn how to address new and evolving challenges. For example, certifications in ethical hacking teach professionals how to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in new technologies, which is crucial for staying ahead of cybercriminals.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cybersecurity certifications provide an invaluable array of benefits for professionals in the field. From career advancement and marketability to skill validation and access to better job opportunities, certifications are a powerful tool to boost your career in cybersecurity. They not only help you stay relevant in the fast-evolving cybersecurity industry but also open doors to new career paths and professional networks. If you’re looking to advance your career in cybersecurity, pursuing a certification is a great investment.
At ACSMI, we understand the importance of certifications in today’s professional landscape. That’s why we offer comprehensive medical scribe certifications, ensuring that you have the skills and credentials to thrive in your career.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What cybersecurity certifications are the most in-demand?
Some of the most in-demand certifications include CISSP, CEH, CompTIA Security+, and Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP).
How long does it take to get certified in cybersecurity?
The time required to obtain a certification varies. For example, CompTIA Security+ can take a few months, while advanced certifications like CISSP may take longer due to the experience requirements.
Do I need prior experience to get a cybersecurity certification?
Some certifications require prior experience in cybersecurity, while others, like CompTIA Security+, are suitable for beginners.
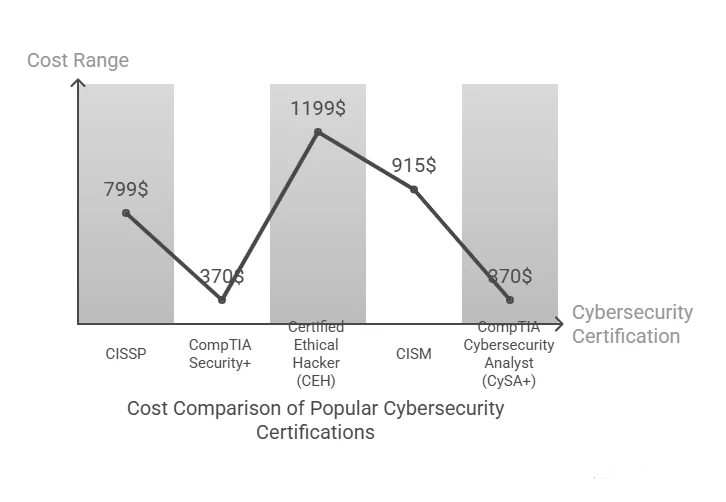
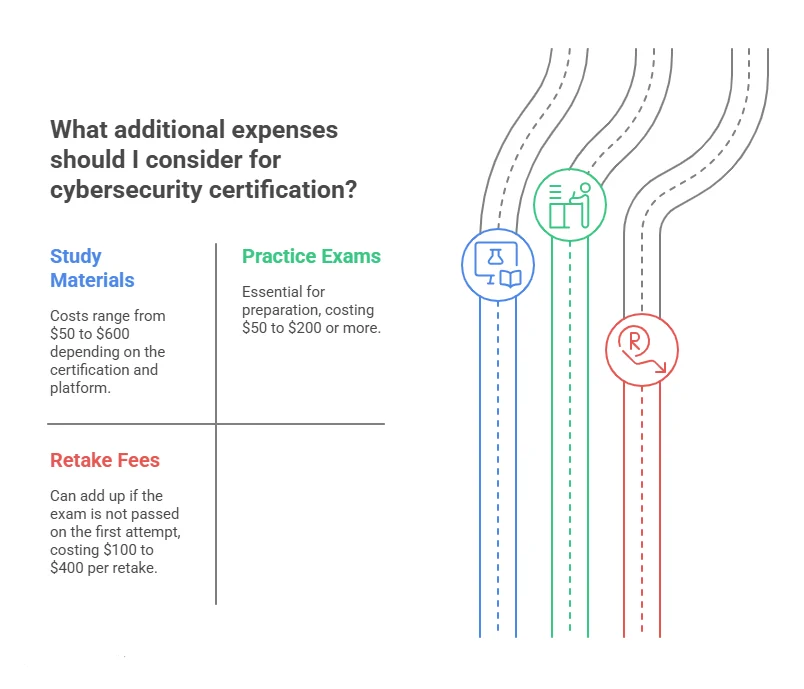
How much does a cybersecurity certification cost?
The cost of a cybersecurity certification can vary. For example, CompTIA Security+ may cost around $350, while CISSP can cost over $700.
How can certifications improve my job security in cybersecurity?
Certifications provide proof of your expertise and competence, which can make you a more valuable employee. This enhances job security, as employers are more likely to retain certified professionals.