As we move further into the digital age, cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, making cybersecurity more critical than ever. With the rapid evolution of technology, Cyber Tech is continuously evolving to keep up with new threats and challenges. The year 2025 is expected to bring some exciting advancements in Cyber Tech, driven by innovations like Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the increasing reliance on cloud-based services.
In this blog, we will explore the latest Cyber Tech trends in 2025 that businesses and individuals need to be aware of in order to stay ahead of cyber threats. From next-generation cybersecurity solutions to the integration of AI in defense systems, the future of cybersecurity is full of exciting possibilities.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming many industries, and one of the most critical areas they’re impacting is cybersecurity. As cyber threats become more complex and harder to detect, AI and ML are emerging as powerful tools that can help organizations stay ahead of hackers and malicious actors. In 2025, these technologies are expected to play an even more significant role in cyber defense, offering innovative ways to detect threats, analyze security data, and respond to incidents in real time.
The Role of AI in Cyber Tech
Cybersecurity is no longer just about installing antivirus software or setting up firewalls. Today, it involves advanced systems that can adapt and learn, much like human analysts—but with greater speed and accuracy. AI enhances cybersecurity by processing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and recognizing unusual behavior that could signal a cyber threat. Unlike traditional security methods, AI is not limited to rule-based detection. Instead, it evolves over time, becoming smarter with every attack it encounters.
How AI Enhances Cybersecurity
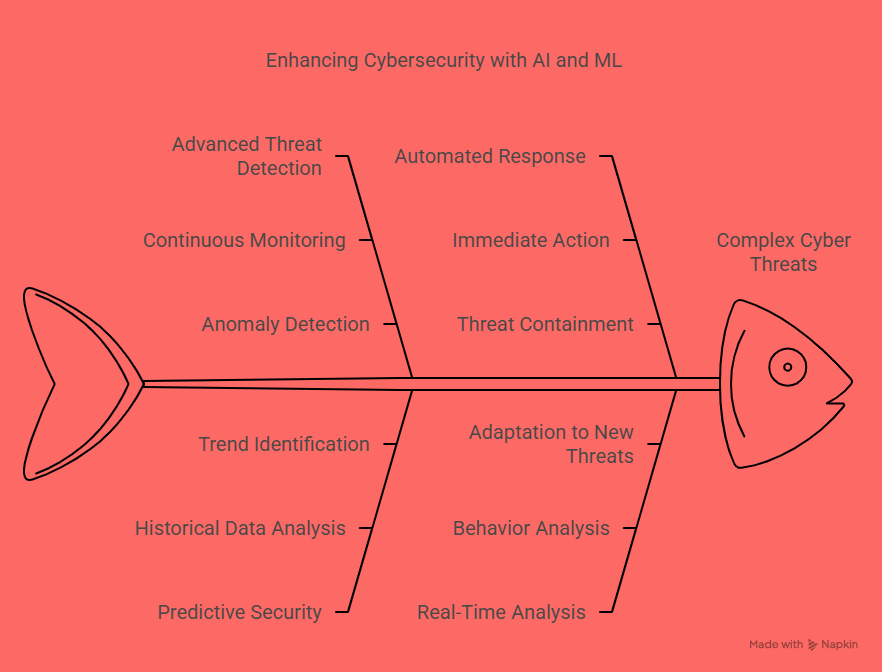
1. Advanced Threat Detection
One of the primary advantages of using AI in cybersecurity is its ability to detect threats more quickly and accurately than conventional systems. AI-powered tools can continuously monitor network traffic, user activity, and system logs to identify anomalies that deviate from normal behavior. These anomalies could be signs of malware, phishing attacks, or unauthorized access.
For example, if a user typically logs in from the United States but suddenly attempts to access the network from a foreign country at an unusual hour, AI can flag this as a potential threat. Because these systems are trained on large datasets, they can recognize subtle signals that might be missed by human analysts.
2. Predictive Security
AI doesn’t just help identify current threats—it can also predict future ones. Using machine learning algorithms, security systems can analyze historical attack data to identify patterns and trends. This predictive analysis enables organizations to take a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
For instance, if a particular type of malware has been spreading across similar companies or industries, an AI-driven system can alert a business to the likelihood of being targeted next. With this insight, companies can strengthen their defenses before an attack occurs, reducing the risk of a successful breach.
3. Automated Response
Time is critical when responding to a cyber threat. The faster a response, the lower the damage. AI dramatically shortens response times by automating certain security processes. When a threat is detected, AI systems can take immediate action—such as blocking malicious IP addresses, isolating infected devices, or shutting down compromised user accounts—without waiting for manual intervention.
This automated response not only reduces the burden on IT teams but also helps contain threats before they spread throughout a network. It’s especially beneficial in large organizations where managing thousands of endpoints manually would be impractical.
Real-Time Analysis and Adaptation
One of the most impressive aspects of AI in cybersecurity is its ability to operate in real time. Traditional methods often rely on signatures or known threat patterns, which can be ineffective against new, never-before-seen attacks. AI, on the other hand, can analyze behaviors and adapt to new threats as they emerge.
This real-time capability is crucial in today’s fast-moving digital environment, where cybercriminals are constantly changing their tactics. Whether it’s a zero-day exploit or a sophisticated ransomware attack, AI systems can respond quickly by learning on the fly and adjusting their strategies accordingly.
AI-Driven Cybersecurity for Businesses
As businesses increasingly rely on digital infrastructure, the need for robust cybersecurity solutions has never been greater. AI-driven cybersecurity tools offer a more intelligent and responsive way to protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and ensure business continuity.
These tools can be integrated into existing security architectures, providing continuous monitoring and faster threat detection. For small and medium-sized businesses, AI can offer enterprise-level protection at a fraction of the cost, reducing their exposure to costly data breaches and downtime.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI offers many advantages, it’s not without its challenges. One of the main concerns is the potential for false positives—situations where legitimate activity is incorrectly flagged as malicious. To minimize this, AI systems must be carefully trained and continuously updated.
There’s also the risk that cybercriminals could use AI for their own benefit. For example, attackers may use AI to craft more convincing phishing emails or bypass traditional defenses. This highlights the importance of staying ahead of the curve and investing in next-generation cybersecurity technologies.
Another key consideration is data privacy. AI systems require access to large amounts of data to function effectively, raising concerns about how that data is stored, used, and protected. Organizations must ensure that their AI-driven cybersecurity solutions comply with privacy regulations and industry standards.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
Looking ahead, AI and machine learning will become even more embedded in cybersecurity strategies. As the technology evolves, we can expect more advanced threat-hunting capabilities, improved threat intelligence sharing, and better integration with other security tools.
Organizations that embrace AI-powered cybersecurity will be better positioned to defend themselves against both known and unknown threats. The combination of speed, accuracy, and adaptability makes AI an indispensable ally in the ongoing battle against cybercrime.
To learn more about how AI is transforming cybersecurity, check out our article on How Does Cyber Tech Protect You From Cyber Threats?
2. Zero-Trust Security Architecture
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, traditional cybersecurity models are no longer sufficient to protect organizations from sophisticated and persistent cyber threats. The conventional approach to security—built around a strong, well-defined network perimeter—was once effective when most employees worked from fixed locations and company resources were stored on-premises. However, the rise of cloud computing, remote work, mobile technology, and third-party service integrations has significantly blurred the boundaries of corporate networks. As a result, businesses are shifting towards a more adaptive and resilient model: zero-trust security architecture.
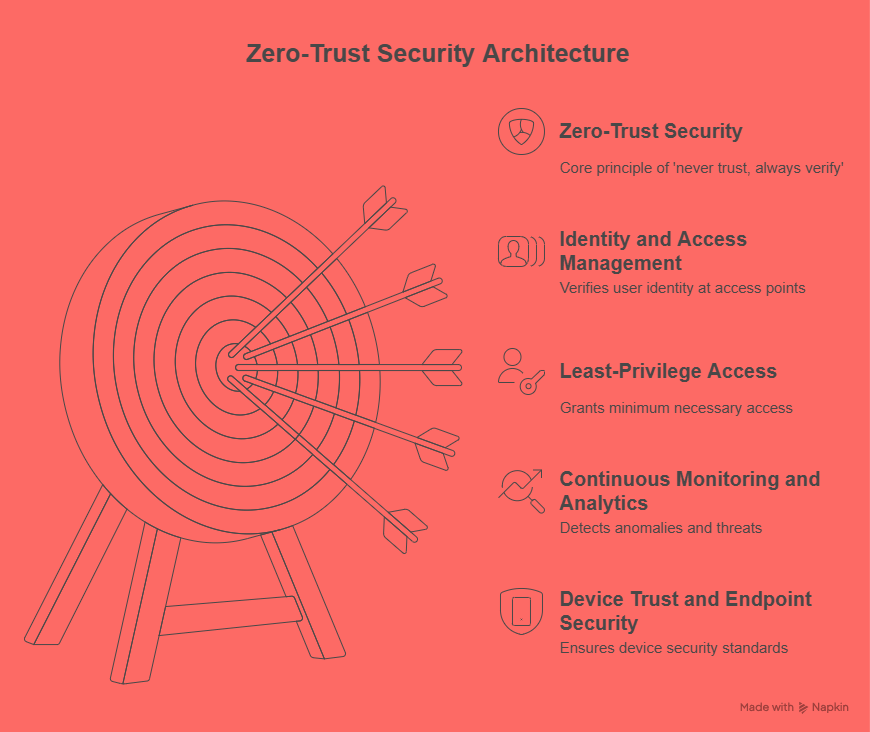
Zero-trust is a security framework based on the principle of "never trust, always verify." Unlike traditional models that implicitly trust users or devices within the network perimeter, zero-trust assumes that every access request—whether it originates from inside or outside the network—could be a potential threat. Therefore, verification is required every time a user, device, or application attempts to access corporate resources.
Key Components of Zero-Trust Security Architecture
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM):
At the heart of zero-trust lies strong identity verification. IAM ensures that only authenticated and authorized users gain access to sensitive data and systems. This includes multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and robust password policies. By verifying user identity at every point of access, organizations can prevent unauthorized entry and reduce the risk of data breaches.
2. Least-Privilege Access:
Zero-trust advocates for the principle of least privilege, meaning users are granted the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job functions. This limits exposure to sensitive information and helps contain potential damage in the event of a breach. For instance, a marketing professional doesn’t need access to financial systems—restricting such access reduces risk.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Analytics:
In a zero-trust environment, security is not a one-time event but a continuous process. Organizations must constantly monitor user activity, network traffic, and access patterns to detect anomalies that could indicate a security incident. Real-time analytics and automated threat detection tools play a crucial role in identifying and responding to suspicious behavior swiftly.
4. Device Trust and Endpoint Security:
Zero-trust also considers the security posture of devices. Just because a device is being used by a verified user doesn’t mean it should be trusted blindly. Devices must meet security standards—such as up-to-date software and active antivirus protection—before they’re granted access to the network.
5. Micro-Segmentation:
To limit lateral movement within a network, zero-trust uses micro-segmentation. This involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated zones and applying granular access controls between them. Even if an attacker breaches one segment, they can’t move freely throughout the network.
The Future of Cybersecurity
As more businesses transition to hybrid work environments and embrace cloud-based operations, the traditional network perimeter will continue to dissolve. Zero-trust security architecture offers a forward-thinking solution that focuses on protecting users, data, and devices regardless of location. By adopting zero-trust principles, organizations can build a resilient security posture that keeps pace with modern threats and operational needs.
3. Quantum Computing and Its Impact on Cybersecurity
Quantum computing is a breakthrough technology that promises to revolutionize many fields, including Cyber Tech. By harnessing the power of quantum mechanics, quantum computers can perform calculations at speeds that are currently impossible for classical computers. This could have a profound impact on encryption and data security.
The Challenges Quantum Computing Poses:
-
Breaking Traditional Encryption: Current encryption methods, such as RSA and AES, rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. Quantum computers could potentially break these encryption systems in a fraction of the time it would take classical computers.
-
Post-Quantum Cryptography: As quantum computing advances, cybersecurity professionals are working on developing new encryption methods that can withstand attacks from quantum computers. Post-quantum cryptography is a new field that aims to create encryption algorithms that are resistant to quantum attacks.
In 2025, businesses and governments will likely begin to prepare for the era of quantum computing by adopting quantum-resistant encryption methods, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure.
4. Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
As businesses move towards more complex IT environments, the need for integrated cybersecurity solutions has grown. Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is an emerging Cyber Tech trend that integrates various security tools into a unified platform for enhanced detection, analysis, and response.
How XDR Works:
XDR integrates data from multiple sources, including endpoints, networks, and cloud environments, to provide a holistic view of an organization’s security posture. By combining traditional security tools like antivirus and firewalls with newer technologies like AI and machine learning, XDR can detect threats that may have evaded individual security solutions.
Key benefits of XDR:
-
Faster Threat Detection: XDR provides a centralized platform for monitoring, making it easier to detect and respond to cyber threats.
-
Improved Incident Response: With integrated security tools, XDR can automate responses to threats, reducing the time it takes to contain and mitigate attacks.
-
Comprehensive Security: By connecting endpoints, networks, and cloud environments, XDR offers a more complete security solution, ensuring that all aspects of an organization’s infrastructure are protected.
As businesses continue to deploy more advanced security tools, XDR will become an essential part of their cybersecurity strategy.
5. Cloud Security and the Rise of Cloud-Native Security Tools
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations manage their infrastructure, data, and operations. By offering unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, it has become an integral part of digital transformation strategies across industries. However, with this shift to the cloud comes a new wave of cybersecurity concerns. As businesses increasingly migrate sensitive data and mission-critical applications to cloud platforms, ensuring robust security becomes a top priority. In 2025, cloud security continues to evolve, with a growing focus on advanced tools and strategies that are tailored to modern cloud environments.
Cloud Security Trends in 2025
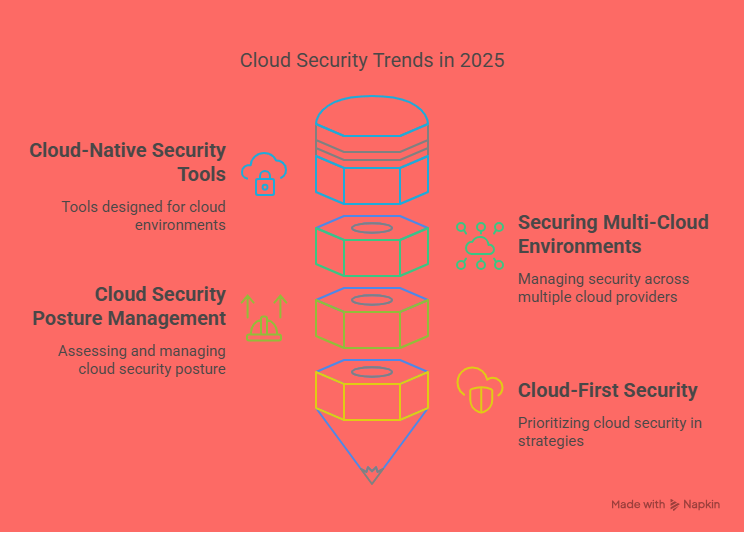
Cloud-Native Security Tools
Traditional security tools often fall short in protecting dynamic and distributed cloud environments. That’s why cloud-native security tools are gaining traction. These tools are designed specifically for cloud-based infrastructure and applications, offering features like automated threat detection, continuous monitoring, real-time compliance checks, encryption, and identity and access management (IAM). What sets cloud-native tools apart is their ability to scale with cloud deployments and adapt to changes in real-time. In 2025, businesses are investing heavily in these tools to strengthen their cloud defenses and respond quickly to potential threats.
Securing Multi-Cloud Environments
It's common for modern businesses to utilize multiple cloud service providers—such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud—to meet different operational needs. While this multi-cloud approach enhances flexibility and resilience, it also introduces complex security challenges. Each provider has its own tools, policies, and configurations, making it harder to maintain consistent security across all platforms. In 2025, organizations are increasingly turning to unified multi-cloud security solutions that offer centralized visibility, governance, and control. These platforms enable security teams to detect anomalies, enforce policies, and manage risks more effectively across all cloud environments.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
As misconfigurations continue to be one of the leading causes of cloud security breaches, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools have become essential. CSPM solutions automatically assess cloud environments for misconfigurations, compliance violations, and potential vulnerabilities. By providing real-time visibility into security posture, these tools help organizations detect and remediate issues before they lead to data breaches or non-compliance. In 2025, CSPM adoption is on the rise, especially among enterprises subject to strict regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
A Growing Focus on Cloud-First Security
As more businesses adopt cloud-first strategies, cloud security is no longer optional—it’s critical. The focus has shifted from reactive security to proactive risk management, leveraging automation and artificial intelligence to anticipate and neutralize threats before they cause harm. In the realm of Cyber Tech in 2025, cloud security stands out as a top priority, driving innovation in security architectures and prompting collaboration between cloud service providers and cybersecurity vendors.
Organizations that invest in modern cloud security tools and practices will be better equipped to protect their assets, maintain customer trust, and stay resilient in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Conclusion:
The future of Cyber Tech in 2025 is full of innovation and promise. From AI-driven cybersecurity solutions to the adoption of zero-trust architecture and quantum-resistant encryption, the landscape of cybersecurity is evolving rapidly. Businesses that embrace these trends will be better equipped to protect themselves from cyber threats and stay ahead of cybercriminals.
At ACSMI, we understand the importance of staying current with the latest Cyber Tech trends, especially in sectors like healthcare, where data protection is paramount. As new technologies continue to emerge, we remain committed to providing the best tools and certifications to help professionals excel in the cybersecurity field.
FAQs
1. What is the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity in 2025?
In 2025, Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a major role in enhancing cybersecurity by automating threat detection, predicting future attacks, and responding to security incidents in real-time. AI will analyze large volumes of data, detect anomalies, and learn from new threats to provide faster and more accurate protection against cyberattacks. This will enable businesses to stay ahead of evolving threats and reduce the impact of cyber incidents.
2. What is Zero-Trust Security, and why is it important in 2025?
Zero-Trust Security is a security model that assumes no user or device is trusted by default, whether inside or outside the network. Every access request is continuously verified before granting access to any resource. In 2025, Zero-Trust Security is crucial due to the rise of cloud computing, remote work, and the increasing complexity of network environments. It ensures better protection by minimizing the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access.
3. How will Quantum Computing impact cybersecurity in 2025?
Quantum computing poses both challenges and opportunities for cybersecurity. Quantum computers have the potential to break current encryption methods, which could compromise sensitive data. In response, post-quantum cryptography will emerge to develop new encryption algorithms resistant to quantum attacks. By 2025, businesses will need to adopt quantum-resistant security solutions to protect their data from the capabilities of quantum computing.
4. What is Extended Detection and Response (XDR) and how will it change cybersecurity in 2025?
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is an integrated security solution that combines multiple security tools into a single platform to provide comprehensive visibility and faster response to threats. In 2025, XDR will become more essential as businesses face complex IT environments. By streamlining security efforts, XDR will help detect, analyze, and respond to cyber threats more effectively, reducing the time and resources required to address security incidents.
5. How will cloud security evolve by 2025?
As more businesses migrate to the cloud, cloud security will continue to evolve to address new risks. By 2025, cloud-native security tools will be widely adopted to provide better protection for cloud environments. These tools will offer automated threat detection, encryption, and identity management. Additionally, Multi-Cloud Security and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) will become critical to ensure businesses maintain control and visibility across various cloud platforms.

Leave a Reply