Phishing Attacks Trends Report: Analysis & Prevention Method
Cybersecurity leaders are facing a new wave of phishing tactics in 2025, driven by AI, deepfake technology, and hyper-personalized lures. What was once limited to crude mass emails is now weaponized social engineering that adapts in real time, making traditional filters and endpoint defenses nearly obsolete. The sophistication of today's attacks isn't just in their technical delivery—but in the psychological manipulation behind them. Every organization, regardless of size, is now a target.
This report dives deep into exclusive 2025 phishing data, industry-by-industry breach breakdowns, and actual attack case studies. You’ll see exactly how threat actors have adapted—and more importantly, what defensive strategies are actively working right now. We’ll also show how simulation testing, advanced email authentication protocols, and targeted employee training are being used to build phishing resilience across sectors. For those training with the ACSMI Cybersecurity & Management Certification, this report doubles as a tactical update and a real-world application guide.
How Phishing Is Evolving in 2025
Phishing in 2025 has moved beyond simplistic spoof emails and generic malware links. Today’s campaigns are crafted using real-time AI content generation, harvested personal data, and deepfake technology that mimics legitimate corporate communications with stunning precision. Threat actors are no longer sending broad campaigns; they’re targeting individuals with surgical accuracy, using behavioral analytics to predict responses.
The rise of phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platforms has made it easier than ever for non-technical cybercriminals to launch sophisticated campaigns. These platforms offer subscription-based kits with pre-built lures, obfuscation layers, and real-time dashboards, reducing the barrier to entry. As a result, phishing attempts have increased in frequency and evasion rate, slipping past traditional email security filters at alarming rates.
Another significant shift is the use of generative AI to fabricate realistic executive voices and videos. These deepfakes are embedded in phishing attempts, making them appear as urgent requests from known executives. Victims aren't just clicking on links—they're being convinced by lifelike media to initiate wire transfers, change credentials, or bypass two-factor authentication.
Let’s explore two of the biggest evolutions in phishing strategies that have emerged in 2025.
New Lure Techniques (AI/Deepfake Links)
Attackers are using AI to dynamically generate phishing content that adapts to the recipient's behavior in real time. These smart lures detect user patterns, engagement tendencies, and preferred platforms (like Slack or Teams), and deploy contextually appropriate content.
Deepfake-driven phishing involves cloned voices from past video calls or executive webinars, asking employees to approve a payment or log in urgently.
Some campaigns even trigger browser-based overlays that simulate legitimate login portals, tricking even savvy users into inputting credentials.
One advanced tactic seen in Q1 2025 includes phishing links that change destination URLs after email delivery, bypassing static security filters. These polymorphic links make detection difficult, especially when they only become malicious after triggering specific user actions.
Security teams must now treat every user interaction as a potential exploit vector, especially those that look deceptively familiar or emotionally urgent.
High-Value Targets and Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is now the default—not the exception. Attackers are investing more time in researching key decision-makers, financial officers, and infrastructure admins, often cross-referencing LinkedIn, X (Twitter), and conference speaker lists to construct believable attack narratives.
C-level impersonation has seen a 200% rise in 2025 alone, especially during high-stakes company moments like acquisitions, funding rounds, or IPO filings.
Cybercriminals are exploiting HR workflows—posing as new hires, vendors, or payroll platforms—to gain initial system access before escalating privileges.
One disturbing trend is attackers using generative AI to draft messages that match internal communication tone, mimicking sentence structures, abbreviations, and project references found in internal documents or emails stolen from other breaches. The result is a near-perfect imitation of internal language patterns.
The goal is no longer just a password—it’s persistent, invisible access that enables credential harvesting, invoice manipulation, or data exfiltration for months before detection.
Industry-Wise Threat Breakdown
Phishing in 2025 doesn’t hit all sectors equally. Attackers are focusing efforts where data volume is high, security gaps are common, and response times are slow. Based on this year’s incident analysis, industries like healthcare, finance, and government remain top targets due to the sensitivity of their data and their often outdated security infrastructures. However, small businesses have also become an easy entry point for attackers due to their low investment in cybersecurity training and infrastructure.
Below, we break down phishing threat patterns across these sectors and compare how risk differs between large enterprises and small businesses.
Healthcare, Finance, Government Data
Healthcare continues to top the list of high-risk targets. Phishing in this sector often focuses on stealing patient portal credentials, hijacking provider logins, and deploying ransomware through email attachments disguised as electronic health records (EHRs). In 2025, multiple U.S. hospital networks faced shutdowns due to phishing-triggered ransomware, with estimated recovery costs exceeding $10 million per incident.
Many phishing emails leverage trust in electronic prescriptions and test result notifications to prompt action.
Attackers also impersonate Medicare, insurance agents, and third-party billing systems, luring administrative staff into credential submission.
In the financial sector, attackers target account managers, brokers, and auditors with spear-phishing emails disguised as internal audit requests, investor inquiries, or urgent compliance updates. These emails increasingly include deepfake videos of C-suite executives urging quick responses—especially around quarter-end or tax season.
Government agencies are not immune, especially local and regional branches. In 2025, threat actors exploited lax email validation protocols to deliver fake contractor invoice updates or inter-agency transfer approvals. These attacks often lead to backdoor installations or privilege escalation across connected systems.
Small Businesses vs Enterprise Risks
While enterprises face more targeted, prolonged phishing campaigns, small businesses remain highly vulnerable due to their lack of technical resources and policy enforcement.
Over 68% of phishing breaches in companies with under 100 employees started with a single untrained staff member clicking a fake vendor invoice.
Unlike enterprises, most small firms lack DMARC policies or routine phishing simulations, allowing attacks to go undetected for weeks.
Enterprises, on the other hand, experience more tailored attacks using internal data harvested from prior breaches. For example, attackers use actual invoice PDFs or sales contracts stolen in a past hack to craft convincing lures. These campaigns often use multi-pronged delivery methods, including WhatsApp messages, Slack impersonations, and compromised vendor portals.
Moreover, attackers are increasingly infiltrating supply chains, using small subcontractors as stepping stones into larger enterprise systems. This “phish-the-vendor” strategy has become especially effective in industries like construction, logistics, and IT support, where shared credentials or platform access is common.
The clear message in 2025: whether you're a five-person startup or a global corporation, phishing is designed to exploit your weakest human or technical link—and no sector is exempt.
| Industry | Primary Phishing Methods | 2025 Risk Factors | Example Attack Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | EHR hijacking, fake patient report links, ransomware-laced attachments | Outdated systems, staff untrained in digital threats, high-value patient data | 22,000+ records breached from IT helpdesk phishing at a regional hospital |
| Finance | Deepfake CFO requests, spoofed compliance alerts, invoice tampering | Frequent financial transfers, high-volume communication channels, urgency-driven tasks | $9.2M wire fraud loss after spoofed vendor payment request via phishing |
| Government | Spoofed inter-agency requests, fake contract approvals, credential harvesting | Slow detection response, lack of MFA, inconsistent training across departments | Multiple compromised internal accounts through a cloned procurement system |
| Small Businesses | Fake vendor invoices, spoofed payroll platforms, generic credential traps | Little to no phishing training, no DMARC or S/MIME, limited security tools | 68% of 2025 breaches began with staff clicking malicious invoice links |
| Enterprises | Executive impersonation, fake Zoom invites, polymorphic phishing via Slack/Teams | Large attack surface, complex supply chains, increased third-party exposure | Compromise of supplier credentials led to lateral movement across partner network |
Real Case Studies From 2025 Breaches
Phishing has escalated from a nuisance to a primary attack vector in 2025, with real-world consequences across multiple sectors. By analyzing recent breaches, we gain sharp insight into how phishing exploits are executed, where defenses failed, and what measures could have prevented the incidents. These aren’t theoretical attacks—they’re actual breaches from this year, involving advanced social engineering, multi-channel deception, and zero-day exploitation that bypassed enterprise-level defenses.
Let’s look at two specific examples that illustrate the sophistication of today’s phishing campaigns.
Incident 1: Financial Sector Attack
In February 2025, a multinational investment firm experienced a $9.2 million fraud loss due to a phishing attack that targeted a senior accounts officer. The lure was a highly convincing internal email thread—recreated using data from a 2024 supply chain breach—that referenced a legitimate vendor invoice and included a cloned signature of the CFO.
The phishing email was embedded with a link to a deepfake video, allegedly from the CFO, asking the officer to “expedite payment due to audit deadlines.”
The video, powered by generative AI, matched the executive’s voice and mannerisms and even referenced a real meeting from the previous week.
The accounts officer completed the wire transfer to what appeared to be the vendor’s new banking details—unaware that the domain had one character replaced and was registered 48 hours prior.
Following the attack, forensic investigation revealed that the attacker had previously infiltrated the vendor’s email system and monitored threads for over six weeks, timing the strike for when the real CFO was out of the country.
This incident prompted the firm to immediately roll out mandatory multi-person approval for vendor payment changes, implement real-time domain reputation checks, and tighten DMARC enforcement for both incoming and outgoing emails.
Incident 2: Healthcare Credential Leak
In April 2025, a regional hospital system in the U.S. Midwest suffered a catastrophic credential leak affecting over 22,000 patient records. The breach originated from a phishing email sent to the hospital’s IT helpdesk, disguised as an internal password reset request from the head of the radiology department.
The email used the hospital’s branding, correct internal jargon, and referenced specific imaging software used by the department.
The link redirected the helpdesk to a cloned single sign-on (SSO) portal, where they unknowingly entered admin credentials.
Once inside, attackers gained access to Active Directory and exported login credentials for over 120 clinicians. These accounts were used to download patient imaging files, lab results, and internal memos over a 72-hour window before detection.
The attackers also created ghost admin accounts with persistent backdoor access, bypassing basic password changes. Fortunately, a behavioral anomaly was flagged by the EHR’s user analytics engine, prompting deeper investigation.
The breach cost the hospital over $4.6 million in compliance penalties and remediation, not to mention reputational damage. They have since adopted real-time identity verification for internal requests, endpoint detection solutions tied to user behavior analytics, and a full revamp of phishing simulation programs across all departments.
| Case | Attack Vector | Exploit Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Investment Firm Fraud | Deepfake Video Phishing | Impersonated CFO via AI-generated video requesting urgent wire transfer; cloned invoice and email thread. | $9.2M fraud loss, vendor email compromise, security protocol overhaul |
| Hospital Credential Leak | SSO Portal Clone via Phishing | Helpdesk staff redirected to fake login page; admin credentials stolen and used to exfiltrate EHR data. | 22,000+ patient records exposed, $4.6M in penalties, full training revamp |
| Municipal Payroll Scam | Spoofed Internal HR Email | Fake HR update redirected employees to a malicious site; payroll details altered and payments rerouted. | Loss of employee salaries, breach of public trust, implementation of MFA |
| Cloud Vendor Breach | Third-Party Developer Account Compromise | Attacker gained access via weak password reuse; sent phishing emails from a trusted vendor domain. | Credential theft, access to multiple client environments, vendor terminated |
| University Enrollment Attack | Compromised Professor Account | Attacker sent fake class registration forms; harvested student credentials through cloned portal. | Mass credential reset, incident response overhaul, restricted faculty access |
Prevention Tactics That Work Now
As phishing attacks become more sophisticated, prevention requires more than just spam filters and firewall rules. In 2025, organizations succeeding at phishing mitigation are those using layered security models, combining email authentication protocols with behavior-driven detection, employee resilience training, and real-time visibility into social engineering attempts. Static controls no longer suffice—adaptive security is essential.
Below are the two most effective modern defense strategies that are proving successful today.
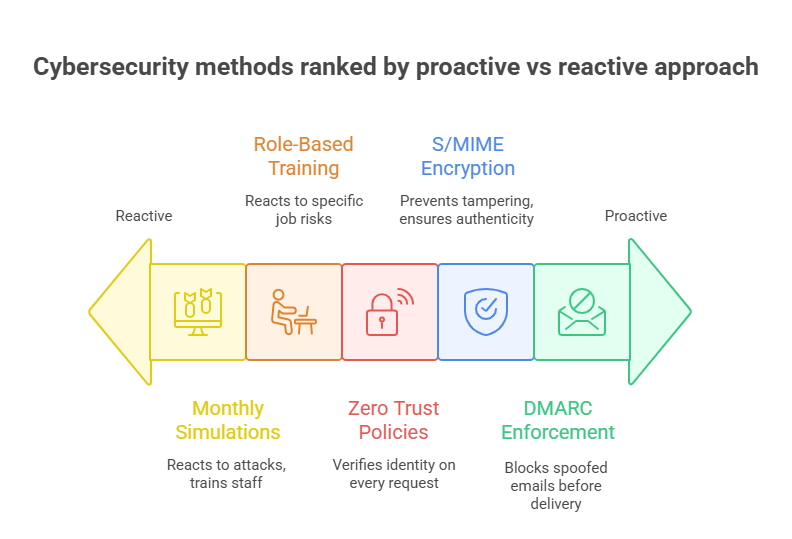
DMARC, S/MIME, Anti-Phishing Kits
Advanced email authentication is now foundational. Three protocols lead the charge:
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) ensures emails sent from a domain are authorized by its administrators. In 2025, companies using enforced DMARC policies saw up to 85% reduction in spoofed phishing emails.
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) adds encryption and digital signatures to verify the authenticity of senders and message integrity.
Anti-phishing kits, often bundled with email security gateways, use machine learning to analyze sender behavior, detect polymorphic URLs, and quarantine suspicious attachments. The best ones now simulate phishing environments in real time before allowing the message to hit the inbox.
However, implementation isn’t enough. What’s working now is aggressive monitoring of DNS records, instant alerts for policy failures, and integration with zero-trust architecture to validate not just the message, but the messenger’s device, location, and login behavior.
Employee Training Protocols
Human error is still the leading cause of phishing success. In 2025, organizations investing in targeted, monthly phishing simulations saw a 63% reduction in real-world phishing click-through rates. But effective training isn’t just about “spotting fake emails”—it’s about replicating real attack conditions and measuring how staff respond.
The most effective programs include industry-specific lures, personalized content (e.g., HR policy changes or performance review requests), and deepfake-based simulations that train users to distrust urgency without verification.
Modern platforms provide immediate micro-feedback when a user clicks a simulation, explaining what gave the email away, and tracking improvement over time.
What’s changed in 2025 is the move away from generic training toward role-based phishing resilience plans. Admins, C-suite staff, and frontline employees all face different attack types—so their training must reflect those realities. Top-performing companies now tie simulation results into quarterly performance reviews, making security behavior a measurable metric.
Measuring Phishing Resilience
In 2025, phishing resilience isn’t just a training checkbox—it’s a quantifiable performance indicator. The most secure organizations now treat it like any other core KPI, using real-time metrics and behavioral analytics to assess risk posture, simulate breaches, and adapt defenses. Effective measurement isn't about blocking emails—it's about proving your people, tools, and protocols can hold up under real pressure.
Phishing Simulation Metrics
Phishing simulations remain the frontline tool for resilience testing, but the way they're being used has evolved significantly. High-performing organizations are no longer just measuring click rates—they’re building multi-tier dashboards that track each stage of the simulated attack chain:
Email open rate – how many employees engaged with the message.
Click-through rate – who clicked, and how quickly.
Credential submission rate – the most critical, showing how many users went all the way and entered login data.
Report rate – percentage of users who flagged the phishing email appropriately.
The gold standard is now “Time to Report” (TTR)—the average time it takes for the first employee to report a phishing simulation. Companies with sub-15-minute TTR windows are dramatically reducing lateral attack windows in real incidents.
Additionally, simulation data is being correlated with department, role, and location, giving security teams visibility into hotspots of vulnerability. Some organizations now gamify resilience by publishing monthly phishing scores internally, rewarding teams that detect and report threats fastest.
Behavioral Indicators and Tools
Beyond simulations, modern phishing defense depends on passive, behavior-based monitoring. AI-driven security platforms now watch for:
Unexpected login locations or time zones
Unusual email forwarding patterns
Abnormal download volumes or permissions changes
Unusual cross-platform activity across work apps
These tools use behavioral baselines to trigger alerts when deviations occur—flagging compromised accounts even if no malware is detected. In 2025, many security stacks now combine phishing simulation scores with real-time endpoint telemetry, giving a complete picture of human and system-level readiness.
Some companies are also deploying resilience scoring frameworks, assigning phishing preparedness scores to individuals or teams based on simulation history, training engagement, and risky behavior indicators. These scores feed directly into risk dashboards monitored by CISOs and are increasingly used to prioritize security investments and tabletop exercises.
In short, phishing resilience in 2025 is data-driven, personalized, and proactive—not reactionary.
ACSMI Cybersecurity Certification Includes Phishing Defense
The ACSMI Cybersecurity & Management Certification is built not just to teach technical concepts—but to equip professionals with real-world, frontline defense capabilities against phishing. As phishing evolves in 2025, static knowledge isn’t enough. That’s why ACSMI’s program integrates phishing detection, simulation handling, and social engineering defense across its core curriculum, labs, and testing modules.
Simulation Labs + Social Engineering Modules
ACSMI’s certification includes hands-on phishing simulation labs where learners navigate real attack scenarios: polymorphic links, cloned login portals, executive impersonation, and deepfake requests. These aren’t static quizzes—they’re live simulation environments that track behavior, flag mistakes, and provide feedback in real time.
Labs mimic actual inboxes, communication channels (e.g., Slack, Microsoft Teams), and internal ticketing systems, teaching how to spot context-based phishing across platforms.
Learners are required to perform domain lookups, link dissections, and email header analysis using forensic tools built into the lab.
The certification also simulates business email compromise (BEC) attacks, where candidates must detect and halt fraudulent payment requests or credential harvesting attempts.
Each module includes real-world breach breakdowns, showing how successful phishing campaigns were constructed and what red flags were missed. Students don’t just study examples—they reverse-engineer real attacks, learning both the technical and psychological mechanics.
Social engineering modules go further, teaching recognition of manipulative language, urgency traps, authority-based deception, and emotion-driven calls to action. These are the soft skills most cybersecurity pros lack, but attackers rely on. Learners are trained to deploy adaptive questioning techniques, flag inconsistencies, and escalate internal warnings based on behavioral cues—not just content.
This dual focus on technical skill and human insight is what differentiates ACSMI from static training platforms or lecture-only certs. It prepares candidates to defend both the machine and the mind.
Ready to Lead Phishing Defense? Enroll at ACSMI
What makes ACSMI’s certification uniquely suited for today’s phishing landscape is its integration of live threat modeling, behavior-based detection strategies, and business continuity planning. It doesn’t stop at individual protection—it teaches candidates how to build phishing-resistant systems and teams.
By the end of the program, candidates will know how to:
Configure and enforce DMARC, SPF, and DKIM protocols
Integrate zero-trust logic into access controls and messaging layers
Launch and interpret monthly phishing simulations
Design role-based awareness training plans for executives, admins, and frontline staff
Use threat intel platforms to track emerging phishing lures and actor behavior
This is why leading organizations are choosing ACSMI graduates to spearhead phishing defense programs across industries. They’re not trained for past threats—they’re equipped to neutralize the evolving phishing threats of 2025 and beyond.
To learn how you can become one of these elite cybersecurity professionals, visit the official ACSMI Cybersecurity & Management Certification page and enroll now. The sooner you start, the sooner you can lead your team in resisting today’s most dangerous cyber threat.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Phishing attacks in 2025 have become significantly more dangerous due to the use of generative AI, deepfake technology, and real-time data harvesting. Attackers now create highly personalized, multi-channel lures that mirror internal communications, making detection extremely difficult. Deepfake audio and video impersonations of executives add urgency and credibility, increasing click-through and credential submission rates. Moreover, phishing-as-a-service platforms have lowered the technical barrier for launching attacks, leading to a surge in targeted campaigns across industries. These threats aren’t just email-based—they appear in Slack, SMS, WhatsApp, and fake portals. As a result, phishing is now a leading cause of data breaches and financial fraud across all sectors.
-
Defending against deepfake phishing requires a multi-layered strategy. First, organizations must enforce authentication protocols like DMARC, SPF, and DKIM to reduce spoofing. Next, all staff—especially executives—should receive specific training on deepfake awareness, including examples of manipulated audio and video. Out-of-band verification for financial or high-risk requests is now mandatory—no sensitive action should be taken without voice or in-person confirmation. AI detection tools that scan voice, syntax, and behavioral anomalies can help flag deepfake content. Lastly, simulation labs and phishing tests that include deepfake scenarios can strengthen detection instincts across all departments and roles.
-
Both healthcare and finance store sensitive, high-value data—from patient records to banking credentials—making them top targets. Healthcare systems often run on outdated infrastructure and lack real-time monitoring, while finance teams are bombarded with legitimate requests daily, making fake ones harder to detect. In healthcare, phishing is used to exfiltrate EHR access or deploy ransomware. In finance, attackers mimic compliance notices or executive instructions to trigger fraudulent wire transfers. These sectors also face strict regulatory penalties, so a breach can cost millions beyond the immediate damage. The combination of urgency, complexity, and value makes them prime phishing targets in 2025.
-
The best phishing simulations in 2025 go beyond click rates. Key metrics include email open rate, link click rate, credential submission rate, and most importantly, time to report (TTR)—how quickly someone flags the phishing email. A fast TTR means reduced attacker dwell time in a real incident. Segmenting results by department or role helps pinpoint vulnerable user groups, while trend tracking shows if awareness is improving. Also critical are post-click actions—did the user attempt to reset their password, or report the attempt through proper channels? Organizations that use these layered metrics see faster breach detection and reduced compromise rates.
-
Yes—especially now, when cloud-based email security platforms and phishing simulation tools have become more affordable. Many vendors offer tiered pricing for small teams, including DMARC enforcement, link scanning, and real-time simulation. Free or low-cost options like Google Workspace phishing alerts or Microsoft Defender email rules can provide basic protection. What small businesses often overlook is employee training, which can be done through short monthly modules and simulation emails. Even a 15-minute monthly training can significantly reduce breach risk. With phishing responsible for over 60% of SMB breaches in 2025, inaction is more expensive than protection.
-
The ACSMI Cybersecurity & Management Certification includes extensive training in phishing recognition, simulation response, and incident handling. Candidates complete hands-on labs that replicate advanced phishing scenarios like deepfake executive requests, polymorphic links, and business email compromise. The program also teaches forensic analysis of phishing headers, payload inspection, and how to configure anti-phishing defenses like S/MIME and DMARC. More importantly, learners are trained in social engineering identification, so they can recognize manipulation techniques used in spear phishing. Graduates of the program are equipped to design organization-wide defense strategies, run simulations, and respond effectively to real-world phishing incidents.
-
Post-breach behavioral anomalies are critical indicators. These include sudden login attempts from new locations, unexpected credential changes, and unusual download or sharing activity—especially outside business hours. Other red flags include email forwarding to unknown accounts, permissions changes without ticket logs, or re-authentication prompts across unrelated systems. Security platforms using UEBA (User & Entity Behavior Analytics) can detect these shifts quickly, flagging compromised accounts before widespread damage occurs. Monitoring failed login patterns, repeated access to restricted files, and new API integrations without approval can also indicate attacker movement. Behavioral surveillance, not just perimeter defense, is now essential to breach detection.
Our Verdict
Phishing in 2025 is no longer a basic scam—it’s a sophisticated, multi-channel operation driven by AI, psychology, and organizational blind spots. From deepfake impersonations to polymorphic links and credential harvesting embedded in business workflows, the attack surface is expanding faster than ever. Organizations that still rely on outdated filters or annual awareness sessions are simply unprepared for today’s threat landscape.
The good news? Resilience is measurable, trainable, and scalable. Whether you’re securing a healthcare network, managing financial transfers, or overseeing remote teams, your ability to resist phishing now depends on behavioral training, real-time metrics, and tool integration—not luck. Certifications like the ACSMI Cybersecurity & Management Certification are built around these modern challenges, arming professionals with both technical skills and strategic awareness to neutralize threats.