Best Cybersecurity Companies for Retail & E-commerce: Directory
Cyberattacks in retail and e-commerce have surged, targeting point-of-sale systems, online checkouts, and customer accounts with alarming precision. With the global e-commerce market exceeding $6.3 trillion, attackers are exploiting exposed APIs, third-party plugins, and unpatched CMS platforms. Card skimming, credential stuffing, and bot-driven fraud now threaten revenue at every digital touchpoint.
The consequences are severe: GDPR fines, PCI DSS non-compliance penalties, and irreversible customer distrust. Retailers face a rapidly shifting threat landscape that demands more than generic protection. They need industry-specific solutions built for speed, uptime, and data integrity. Leading cybersecurity firms now offer real-time threat detection, bot mitigation, and SSL enforcement tailored to retail workflows. This directory highlights the key threats, top companies defending retail, and how specialized certifications equip analysts to secure fast-moving commerce environments.
Cyber Threat Landscape in Retail & E-commerce
Ransomware, Card Skimming, Account Takeovers
Retail and e-commerce platforms face a multi-layered threat model, with attackers exploiting both front-end and back-end systems. Ransomware remains the most financially damaging, often crippling inventory systems, payment gateways, and customer service operations. Retailers are especially vulnerable during high-traffic seasons — attackers time deployments when downtime is most costly, demanding ransoms to unlock business continuity.
Equally dangerous are JavaScript-based card skimming scripts, also known as Magecart attacks. These scripts silently collect payment data from checkout pages and send it to attacker-controlled servers. Even Fortune 500 retailers have been compromised this way, often through third-party integrations. The average time to detect such breaches can exceed 150 days, resulting in extensive data loss.
Then there’s account takeover (ATO) fraud. Attackers use credential stuffing bots to hijack customer accounts at scale, leveraging leaked password databases. These compromised accounts are used to make unauthorized purchases, steal loyalty points, or launder money through refund scams — all without triggering standard fraud alerts.
Regulatory Pressures: PCI DSS, GDPR, CCPA
As attacks escalate, so does regulatory scrutiny. PCI DSS compliance is mandatory for any business processing card payments — yet many small and mid-sized retailers fail to meet key encryption, logging, or segmentation standards. Fines for non-compliance can reach $500,000 per incident, excluding chargebacks or legal settlements.
The introduction of GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California further raised the stakes. These regulations require businesses to disclose breaches quickly and provide customers with control over their data. A failure to encrypt personal data, obtain proper consent, or issue timely breach notifications can trigger investigations and multi-million-dollar fines.
Retailers now face overlapping compliance frameworks, with data localization laws, consumer privacy rights, and mandatory incident disclosures shaping how cybersecurity must be implemented. Security isn’t just about protecting the network — it’s about meeting evolving legal standards that define consumer trust.
To stay compliant and competitive, e-commerce businesses must align with frameworks like NIST CSF, ISO 27001, and regional legislation — or risk losing access to markets altogether.
Top Cybersecurity Firms for Retailers
Akamai, Cloudflare, Sucuri, Palo Alto
Retailers that prioritize uptime, secure checkouts, and rapid threat mitigation turn to a small group of specialized cybersecurity firms. Akamai leads in edge-based threat protection, offering robust DDoS mitigation, bot filtering, and zero-second response times. It’s widely adopted by global e-commerce platforms for its ability to block volumetric attacks without slowing user experience.
Cloudflare dominates in the SMB and mid-market segments, delivering Web Application Firewall (WAF) capabilities, CDN services, and real-time analytics at scale. Its security ecosystem includes bot management tuned for e-commerce, shielding checkout pages and login portals from credential stuffing and fake account generation.
Sucuri, a GoDaddy company, focuses on CMS-based storefronts like WooCommerce and Magento. It specializes in malware scanning, file integrity monitoring, and website firewall configurations, especially for stores reliant on WordPress or Joomla-based setups.
Palo Alto Networks operates on the enterprise end, integrating machine learning and behavioral analytics into next-gen firewalls. With deep packet inspection and granular access control, it’s the go-to solution for retailers with distributed cloud infrastructure and complex compliance needs.
Each of these firms has engineered features with e-commerce vulnerabilities in mind — whether it’s protecting shopping cart cookies, suppressing cross-site scripting (XSS) attempts, or inspecting third-party plugin behavior.
Features: WAFs, DDoS Protection, SSL Monitoring
The most effective cybersecurity providers offer layered defenses that adapt in real-time. Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) act as the first line of defense, inspecting HTTP traffic to block malicious inputs like SQL injection and command execution attempts. In retail, WAFs also filter requests that resemble card skimming or checkout-page scraping.
DDoS protection is critical for retailers operating during peak sale periods. Cloudflare and Akamai lead with globally distributed scrubbing centers that can absorb attacks exceeding 100 Tbps without service interruption. More importantly, their systems identify low-and-slow application-layer DDoS attacks — which traditional tools often miss.
SSL certificate monitoring ensures encrypted sessions aren’t being spoofed or redirected. Top firms automatically renew, validate, and rotate certificates across e-commerce domains, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks that could compromise credit card details or login credentials. Some platforms offer real-time alerts for certificate expiry or misconfigurations, reducing the chances of a security lapse going unnoticed.
Together, these capabilities build a security perimeter optimized for the speed, complexity, and volume of modern retail traffic.
| Company | Specialization | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Akamai | Edge security, DDoS mitigation, bot management | Large-scale e-commerce platforms |
| Cloudflare | WAF, CDN, API security, bot protection | SMBs and mid-market online retailers |
| Sucuri | Malware cleanup, CMS firewall, file integrity monitoring | WordPress/WooCommerce storefronts |
| Palo Alto Networks | Next-gen firewalls, ML-powered detection, policy control | Enterprise-level retail infrastructure |
How These Companies Prevent Data Leaks & Downtime
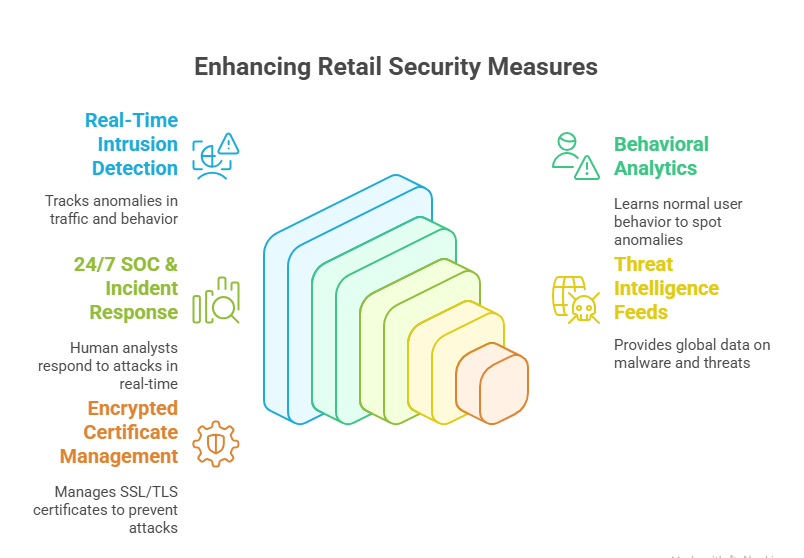
Real-Time Intrusion Detection
The top cybersecurity firms in retail don’t just react to attacks — they predict and neutralize them in real time. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for anomalies and signatures tied to known threats. These systems are integrated directly into CDNs, firewalls, and cloud APIs, allowing for sub-second detection of malicious activity.
For e-commerce, this means catching an injected skimmer script the moment it modifies a checkout page or flagging a suspicious admin login from an untrusted IP. Providers like Palo Alto and Cloudflare use behavioral baselines — tracking normal activity per region, device type, or time of day — and immediately raise alerts on deviations.
Retailers benefit from event correlation engines that combine data from firewalls, endpoint logs, and web servers. These engines pinpoint the source of a breach before it spreads laterally across inventory databases or customer support platforms. Unlike traditional log monitoring, this approach surfaces zero-day exploits and multi-vector attacks in real time, not after damage is done.
24/7 Incident Response & Threat Intel
Even the best preventive systems need human backup. That’s why firms like Akamai and Palo Alto offer 24/7 Security Operations Center (SOC) support, giving retailers direct access to trained analysts during live incidents. When an attack is detected, analysts can isolate servers, redirect traffic, and implement patches — often without requiring customer-side action.
Global threat intelligence plays a critical role. These companies maintain real-time feeds on ransomware strains, phishing kits, and botnet command centers, allowing them to recognize emerging attack patterns before they go mainstream. For example, a phishing domain that targets one retailer in Asia is often blocked in the U.S. hours later — proactively protecting clients worldwide.
Incident response teams also handle forensics and compliance documentation, ensuring that if a breach occurs, it’s resolved cleanly with a full audit trail. This includes memory dumps, log chain-of-custody, and legal-ready incident reports — vital for meeting GDPR and PCI DSS disclosure rules.
Ultimately, the combination of real-time detection and rapid response reduces mean time to resolution (MTTR), preventing revenue loss, customer churn, and compliance failures.
Choosing the Right Cybersecurity Partner
Vendor Vetting Criteria
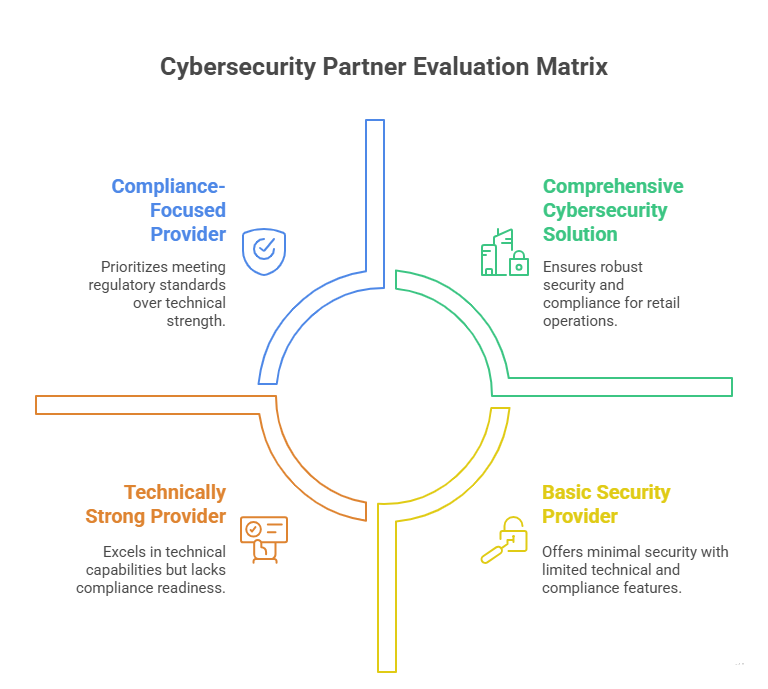
Selecting a cybersecurity vendor isn’t about chasing brand names — it’s about choosing a partner whose tools and response times align with your business model. Retailers must vet vendors across five critical dimensions: threat detection speed, integration flexibility, vertical experience, uptime guarantees, and compliance readiness.
Start with technical capability. Ask whether the vendor offers API-based integration with your current platforms — Shopify, Magento, Salesforce, or custom stacks. Incompatible tools lead to blind spots. Next, evaluate their e-commerce threat intelligence coverage. Does the provider actively track retail-specific threats like Magecart, automated gift card fraud, and fake inventory crawlers?
Retailers should demand SOC 2 or ISO 27001 certification, penetration testing reports, and details on their incident escalation procedures. A red flag: any vendor that can’t articulate their disaster recovery timeframes or how quickly they can sandbox a compromised asset.
References also matter. Ask for proof of success in defending retailers with similar transaction volumes, geographic presence, and tech stacks. Case studies and SLAs should clearly show how they reduce dwell time and maintain checkout speeds under load.
Support Levels & SLAs
Retail operates 24/7 — your security support should too. Enterprise-grade cybersecurity firms offer multiple support tiers, often including dedicated incident response teams, real-time dashboards, and direct access to senior engineers. Look for guaranteed response times under 15 minutes for critical events and named security analysts familiar with your stack.
An SLA without teeth is just marketing. Ensure that your agreement includes financial penalties for missed thresholds, such as DDoS mitigation lag, false positive rates, or downtime windows. Top vendors don’t shy away from SLA enforcement — they use it to prove their platform's reliability.
Support must also be proactive. Does your vendor schedule quarterly security posture reviews, threat simulation exercises, or policy audits? Are patching protocols and change logs shared in real time? If not, you’re flying blind when your business depends on visibility.
Finally, look for tooling that enhances your internal team's workflow. Portals should provide multi-tenant access, audit logs, escalation triggers, and compliance dashboards — not just alerts. The more aligned the vendor is with your operational rhythm, the faster you can identify, respond to, and neutralize threats before they hit revenue.
Future Trends in Retail Cybersecurity
AI-Based Threat Hunting
Cybercriminals now use automation to launch bot-driven attacks, fake login attempts, and even dynamic skimming scripts — all designed to bypass traditional defenses. To counter this, cybersecurity vendors are embracing AI-powered threat hunting as a frontline strategy. Unlike signature-based detection, AI systems analyze behavior patterns across traffic, user sessions, and endpoints in real time.
In retail, this means flagging an unusual spike in checkout failures, identifying a bot swarm attempting inventory scraping, or correlating login attempts from geographically inconsistent IPs. AI tools reduce false positives by learning retailer-specific behaviors — like flash sales or product drops — and adjusting baselines accordingly.
The result is faster identification of zero-day exploits and adaptive attack campaigns. Retailers can integrate these tools directly into customer data platforms, POS systems, and inventory databases, enabling autonomous containment of threats without slowing transactions. As adversaries move faster, machine learning gives defenders the edge to predict and intercept in milliseconds.
Zero Trust Retail Architecture
With employees working remotely, vendors accessing inventory systems, and customers transacting globally, the traditional perimeter no longer exists. Zero Trust architecture assumes that no device or user should be trusted by default — even inside the network. For retailers, this means enforcing strict access controls, micro-segmentation, and identity verification at every digital layer.
Retail Zero Trust begins at the checkout: enforcing device fingerprinting, enforcing step-up authentication, and isolating payment systems from broader infrastructure. On the backend, it limits lateral movement — preventing attackers from jumping from an HR portal to customer databases.
Cybersecurity vendors are building Zero Trust natively into their platforms — integrating endpoint detection, cloud access brokers (CASBs), and identity providers into one seamless stack. This gives retailers granular control over who can access what, when, and under which conditions.
The future of retail security isn’t bigger walls — it’s smarter gates. Zero Trust ensures that if one door is breached, the attacker is still locked out of the rest.
| Trend | Functionality | Retail Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Based Threat Hunting | Detects anomalies using ML models | Stops stealthy scraping bots or dynamic skimmers |
| Zero Trust Architecture | Enforces least-privilege, never-trust model | Protects against lateral movement from vendor access |
| Automated Response Systems | Isolates affected systems instantly | Prevents breach escalation during flash sales |
| API Protection Platforms | Secures payment and inventory APIs | Blocks injection or scraping at integration layer |
| Edge Security with CDNs | Filters malicious requests at global edge points | Improves speed while blocking volumetric DDoS |
How ACSMI Certification Helps Cybersecurity Analysts Specializing in Retail
Retail cybersecurity is a niche with constantly evolving challenges — from POS injection malware to fraudulent API traffic during flash sales. Analysts working in this space must understand not only general security principles but also how retail environments function under pressure. That’s where the Advanced Cybersecurity & Management Certification (ACSMC) from ACSMI provides strategic value.
The ACSMI certification includes deep coverage of network segmentation, intrusion detection systems (IDS), incident response playbooks, and regulatory frameworks like PCI DSS and GDPR. But more critically, it tailors training for environments where uptime and speed are non-negotiable — exactly what e-commerce security demands.
Graduates of the ACSMC program are trained to interpret real-time threat intelligence, deploy scalable WAFs, and manage DDoS mitigation while aligning with business continuity metrics. This makes them especially effective in preventing revenue loss during sales events, reacting to supply-chain attacks, and ensuring data residency compliance in cross-border commerce.
In a market where retailers can lose millions per breach, having an analyst trained through ACSMI’s framework ensures faster detection, coordinated response, and policy-driven prevention strategies — making them indispensable to any retail security team.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Retail and e-commerce face a wide range of cyber threats, but the most frequent include card skimming malware, credential stuffing attacks, ransomware, and DDoS assaults. Attackers often inject malicious scripts into checkout pages to steal payment data, target login endpoints using leaked credentials, and disrupt sales during peak hours. Sophisticated bots are used to exploit inventory systems, scrape pricing data, and create fake accounts. These attacks are not only technical — they’re financial sabotage. The average breach in retail costs over $3.28 million, not including lost brand trust or regulatory fines under PCI DSS or GDPR. That's why threat detection and response in this sector must be real-time and retail-specific.
-
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a mandatory framework that protects cardholder data during collection, processing, and storage. It enforces encryption, segmentation of cardholder environments, access restrictions, and continuous monitoring. For retailers, PCI compliance isn't optional — failing to meet requirements can lead to fines up to $500,000 per breach, and possible revocation of payment processing rights. Compliance also reduces the attack surface by eliminating unnecessary access to sensitive data. Regular vulnerability scans, multi-factor authentication, and detailed audit trails are required to pass PCI DSS assessments. Retailers who prioritize compliance lower their risk profile while improving customer trust and transaction security.
-
A high-performing cybersecurity solution for e-commerce must go beyond antivirus software. Key features include a Web Application Firewall (WAF), DDoS mitigation, SSL monitoring, real-time intrusion detection, and bot management. These tools collectively protect against code injections, data scraping, credential stuffing, and malware attacks. Look for solutions that integrate directly with platforms like Shopify, Magento, or WooCommerce, without slowing site performance. Real-time alerting, attack behavior analytics, and automated incident containment are critical. Bonus features include content delivery networks (CDNs) for load balancing and global edge protection. Without this layered stack, retailers remain exposed at every login, checkout, and promotional campaign.
-
The right vendor depends on your retail operation's size, infrastructure, and security maturity. Akamai is ideal for global brands needing high-volume DDoS mitigation and bot defense. Cloudflare suits mid-sized retailers with its easy-to-deploy WAF and integrated CDN. Sucuri is best for CMS-based sites like WordPress or Joomla, offering malware scanning and lightweight protection. Palo Alto Networks is built for enterprise retailers with complex architectures needing deep packet inspection, micro-segmentation, and ML-based threat analysis. Evaluate each vendor on response times, uptime guarantees, compliance certifications, and ability to integrate with your stack. Always request case studies and performance benchmarks specific to retail.
-
AI has shifted retail cybersecurity from reactive to predictive. AI-based threat detection systems analyze traffic, behavior, and endpoint logs to identify subtle anomalies that traditional tools miss. For example, AI can flag bots testing promo codes, or detect an attacker’s lateral movement after breaching a single admin panel. It also improves accuracy — reducing false positives that waste team time. AI models are trained on vast threat intelligence feeds, learning new attack signatures, phishing templates, and card skimming techniques in real time. In fast-paced retail environments, AI enables split-second decisions to isolate threats without disrupting revenue-generating operations.
-
Zero Trust is a cybersecurity model that assumes no user or device is trustworthy by default — even if it's inside the network. In retail, this approach is critical because environments are fragmented: remote employees, third-party logistics tools, and customer portals all touch sensitive systems. Zero Trust enforces identity verification, least-privilege access, and network segmentation. It ensures a breach in one area (like a supplier portal) doesn't compromise customer data or checkout services. Top vendors now offer Zero Trust frameworks built for retail, incorporating cloud access brokers (CASBs), endpoint protection, and identity governance to contain breaches before they spread.
-
Retail cannot afford downtime — especially during flash sales, holidays, or peak traffic windows. The best cybersecurity vendors offer under 15-minute response times for critical incidents and 24/7 access to expert analysts. Vendors should provide automated traffic rerouting, patch deployment, and attack source isolation in real time. SOC support must go beyond alerting — analysts should collaborate on forensics, compliance, and recovery. Ideal vendors also offer incident dashboards, rollback capabilities, and proactive alerts about global attack trends. If a vendor can’t act within minutes, your business stands to lose customers, payment processor trust, and potentially millions in sales.
-
The Advanced Cybersecurity & Management Certification (ACSMC) by ACSMI equips professionals with both technical depth and retail-specific threat training. It covers PCI DSS, GDPR, cloud-based e-commerce infrastructure, and real-time incident response playbooks. Trainees learn how to handle skimming attacks, API abuse, and dynamic DDoS threats — all while preserving uptime. The program emphasizes security architecture design, detection tuning, and compliance-ready documentation, making graduates ideal for roles in SOCs and DevSecOps teams supporting retail. With dedicated modules on behavioral analytics, SSL monitoring, and bot countermeasures, ACSMI-certified professionals reduce attack dwell time and align security with business goals.
The Take Away
Retail and e-commerce are no longer just about speed and convenience — they’re about trust, continuity, and airtight security. In a landscape where every transaction can be targeted and every customer session exploited, choosing the right cybersecurity partner isn’t a luxury — it’s core infrastructure. Leaders like Akamai, Cloudflare, Palo Alto, and Sucuri offer layered protections tailored for the unique vulnerabilities of retail platforms.
But tools alone aren’t enough. It takes trained professionals — especially those with the ACSMI certification — to interpret threats, enforce compliance, and respond in real time. The future of retail security will be defined by AI-driven defenses, Zero Trust architecture, and business-aligned security workflows that protect both data and revenue.
Whether you're a startup launching your first storefront or an enterprise managing global logistics, the time to harden your digital foundation is now. Invest in the right platforms. Hire the right talent. And most importantly — build cybersecurity into every layer of your retail strategy.